Reciprocating pump
- 3. Group No: 9 Name Id Md. Rakibul Hasan 15107113 Dipayon Saha 15107114 Md. Saifuddin Rakib 15107115 Zakaria Masud Nadim Hossain Rabbani 15107122
- 4. Table of contents ïī Introduction ïī Components of reciprocating pump ïī Types of reciprocating pump ïī Effect of viscosity ïī Plunger pump- working principle, advantage, disadvantage and application. ïī Diaphragm pump- working principle, advantage, disadvantage and application. ïī Comparison of reciprocating and centrifugal pump. ïī Advantages & disadvantages of reciprocating pump
- 5. introduction ïī A reciprocating pump is a class of positive-displacement pumps which includes the piston pump, plunger pump and diaphragm pump. ïī The given pump is single acting single cylinder pump with air vessel. It can be used for less discharge at higher heads. ïī Priming is not required because it is a positive displacement pump. Reciprocating pumps are used in pumping water in hilly areas.
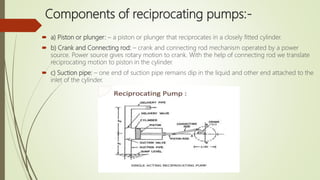
- 6. Components of reciprocating pumps:- ïī a) Piston or plunger: â a piston or plunger that reciprocates in a closely fitted cylinder. ïī b) Crank and Connecting rod: â crank and connecting rod mechanism operated by a power source. Power source gives rotary motion to crank. With the help of connecting rod we translate reciprocating motion to piston in the cylinder. ïī c) Suction pipe: â one end of suction pipe remains dip in the liquid and other end attached to the inlet of the cylinder.
- 7. ïī d) Delivery pipe: â one end of delivery pipe attached with delivery part and other end at discharge point. ïī e) Suction and Delivery value: â suction and delivery values are provided at the suction end and delivery end respectively. These values are non-return values. ïī F) AIR VESSEL : â It is a cast iron closed chamber having an opening at its pass through which the water flows into vessel.
- 8. Effect of Viscosity ïī Provides a nearly constant flow rate over a wider range of pressure. ïī Fluid viscosity has little effect on the flow rate as the pressure increases
- 9. Types of Reciprocating pump: ïī According to the contact of liquid with piston: ïī single acting pump and ïī double acting pump. ïī According to number of cylinders provides: ïī Single cylinder pump ïī Double cylinder pump ïī Triple cylinder pump
- 10. ïī Single acting pump: A single acting pump is one which has one suction valve, delivery valve and one suction and delivery pipe. It suck up the fluid only in one direction and in single stroke called suction stroke
- 11. ïī 2. Double acting pump: A double acting pump is one which has two suction valves, delivery valves and two suction and delivery pipes.
- 12. ïī According to the number of cylinders ïī 1. Single cylinder pump ïī Single cylinder pump is one in which their is only cylinder connected to a single shaft. could be a single acting or double acting pump. 2. Double cylinder pump ïī Double cylinder pump is one which have two cylinder attached to a single shaft. Separate suction and delivery valve is provided to each cylinder. Crank of the pump is set at an angle of 180 degree. 3. Triple cylinder pump ïī When the pump has three cylinders attached to a single shaft then the pump is called triple cylinder pump. Crank is set at an angle of 120 degree.
- 13. 1.Plunger pump ïī They are reciprocating pumps that use a plunger or piston to move media through a cylindrical chamber. ïī Other names are well service pumps, high pressure pumps, or high viscosity pumps. ïī Cylindrical mechanism to create a reciprocating motion along an axis, which then builds pressure in a cylinder or working barrel to force gas or fluid through the pump. ïī The pressure in the chamber actuates the valves at both the suction and discharge points. The volume of the fluid discharged is equal to the area of the plunger or piston, multiplied by its stroke length.
- 14. ADVANTAGES ïī Plunger pumps are used in applications that could range from 70 to 2,070 bar (1,000 to 30,000 psi) ïī Pressure and flow rate changes have little effect on performance. ïī Pressure can be controlled without affecting flow rate. ïī Wide pressure range - can achieve very high pressures Have high efficiency Capable of developing very high pressures. ïī Low and easy maintenance
- 15. DISADVANTAGES ïī Pulsating flow ïī Typically only handles lower flow rates ïī Typically heavy and bulky ïī High operating and maintenance costs. ïī not be compatible for use with highly acidic fluids
- 16. APPLICATIONS ïī Raw and Digested sewage sludge ïī Industrial and chemical waste and slurries ïī Lime putty and slurries ïī Pulp and paper stock ïī Settled oil solids
- 17. 2.Diaphragm Pump: A diaphragm pump (also known as a Membrane pump, Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump (AODD) or Pneumatic Diaphragm Pump) is a positive displacement pump that uses a combination of the reciprocating action of a rubber, thermoplastic or Teflon diaphragm and suitable valves on either side of the diaphragm (check valve, butterfly valves, flap valves, or any other form of shut-off valves) to pump a fluid.
- 18. 2.Diaphragm Pump WORKING PRINCIPLE ïī Suction stroke: To fill the pump cavity, positive suction head (inlet pressure) is required. When inlet valve A is lifted by the pressure of the suction head, the slurry completely fills the pump cavity. The diaphragm returns to its normal convex position and the air exhausts. Discharge valve B, seated by line pressure, prevents slurry from returning to the pump cavity.
- 19. ïī Discharge stroke: Compressed air is admitted to the chamber above the diaphragm. The diaphragm descends, gradually increasing the pressure in the pump cavity. This in turn closes inlet valve A and causes discharge valve B to when the line pressure is exceeded. Further movement of the diaphragm the slurry from the pump cavity.
- 20. ï have good suction lift characteristics. They can handle sludge and slurries with a relatively high amount of grit and solid content. ï Used for low pressure application like removing water from trenches ï have good dry running characteristics. ï are used to make air pumps for the filters on small fish tanks. ï can be up to 97% efficient. ï have good self priming capabilities. ï can handle highly viscous liquids. ï Can handle tough corrosives, abrasives, temperatures to 200°F and slurries containing up to 75% solids. ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES ï Most air diaphragm pumps require around 20 standard cubic-feet per minute and 100 psi of air intake to operate efficiently
- 21. APPLICATIONS of Diaphragm pump ïī For drum and small tank transfer, pickling solutions, chemical feed. ïī Filter press, tank cleaning systems, pigments and resins. ïī Paints, latex, ceramic slip, slurries, polymers, tank car fill and empty, foods. ïī Handling optical lens grinding rouges, waste glass slurries and cutting slurries. ïī Ship cleaning, dewatering holds, bilges, coffer dams, fire-fighting, sewage from holding tanks, offshore drilling, sand blast slurries. ïī Mill scale, pickling tank chemicals, foundry sand slurries, palm oils, cutting oils. Dewatering mines and construction sites, caissons, tunnels. ïī Transfer of frits, enamels, solvents, latex, pigments, additives, inhibitors, resins, dryers. ïī Decanting and emptying of acid and alkaline bath solutions, pumping of heavy contaminated sewage and slurries.
- 23. Advantages & Disadvantages of Reciprocating pump ïī Advantages of Reciprocating pump: ïī 1)Gives high pressure at outlet. 2)Gives high suction lift. 3)Priming is not required in this pump. 4)They are used for air also. ïī Disadvantages of Reciprocating pump: ïī 1)High wear and tear, so requires a lot maintenance. ïī 2)The flow is not uniform, so we have to fit a bottle at both ends. ïī 3)The flow is very less and cannot be used for high flow operations. ïī 4)More heavy and bulky in shape. ïī 5)Initial cost is much more in this pump.
- 24. Any questions ?
- 25. Thank you