Recombinant DNA Technology: A Tool for Genetic Engineering and Gene Therapy
- 2. Outline ’ĆĪ DNA ’ĆĪ Gene ’ĆĪ History of Recombinant DNA technology ’ĆĪ Recombinant DNA ’ĆĪ Recombinant DNA Technology ’ĆĪ 5 Stages involved obtaining rDNA ’ĆĪ Examples Of Use Of rDNA Technology ’ĆĪ Advantages of Recombinant Technology ’ĆĪ Disadvantages of Recombinant Technology ’ĆĪ Applications Of rDNA Technology
- 3. DNA ’üČ DNA is the keeper of the all information needed to recreate an organism ’üČ Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA. ’üČ All DNA is made up of a base consisting of sugar phosphates and nitrogen bases. ’üČ ŌĆ£Double helix" ’üČ The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose. ’üČ DNA contain an anti-parallel strands. ’üČ DNA contains 4 nitrogen bases they are: Purines: Adenine, Guanine Pyrimidines : Thymine, Cytosine ’üČ They are found in pairs, A&T and G&C THE GENETIC SECRET DNA is the keeper of the all the information needed to recreate an organism
- 4. GENE ’é┤ A gene is a stretch of DNA that codes for a type of protein that has a function in the organism. ’é┤ It is a unit of heredity in a living organism. ’é┤ All living things depend on genes. ’é┤ Genes hold the information to build and maintain an organismŌĆÖs cell and pass genetics traits to off spring. DNA does not actually make the organism, it only makes proteins. The DNA is transcribed into mRNA and mRNA is translated into protein, and the protein then forms the organism.
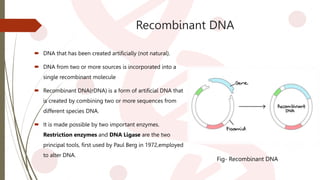
- 6. Recombinant DNA ’é┤ DNA that has been created artificially (not natural). ’é┤ DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single recombinant molecule ’é┤ Recombinant DNA(rDNA) is a form of artificial DNA that is created by combining two or more sequences from different species DNA. ’é┤ It is made possible by two important enzymes. Restriction enzymes and DNA Ligase are the two principal tools, first used by Paul Berg in 1972,employed to alter DNA. Fig- Recombinant DNA
- 7. Recombinant DNA Technology ’é┤ Recombinant DNA (r-DNA) technology has made a revolutionary impact in the area of human healthcare by enabling mass production of safe, pure and effective r-DNA expression products. ’é┤ Genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification and gene splicing are terms are applied to the direct manipulation of an organisms gene. ’é┤ The development of these new technologies have resulted into production of large amount of biochemically products Recombinant DNA Technology is defined ŌĆ£the joining together of DNA molecules from different organisms and inserting it into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture and industry. ŌĆó To create new ŌĆó To create safer/ more version therapeutic agents Recombinant DNA r-DNA involves using microorganisms
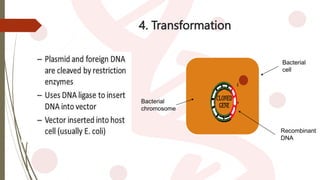
- 8. 5 Stages involved obtaining rDNA Isolation Cutting Ligation and Insertion Transformation Expression
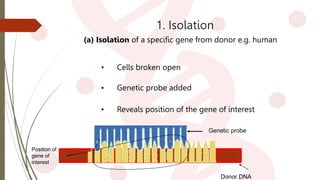
- 9. Donor DNA 1. Isolation (a) Isolation of a specific gene from donor e.g. human ŌĆó Genetic probe added ŌĆó Cells broken open ŌĆó Reveals position of the gene of interest Genetic probe Position of gene of interest
- 10. 1. Isolation (b) Isolation of plasmid from a bacterial cell Bacterial cell Plasmid
- 11. 2. Cutting ’é┤ Restriction enzymes act as molecular scissors and cut DNA at specific sites called restriction sites Restriction site Restriction site Restriction ezymes Restriction site Restriction site Donor DNA plasmid Restriction ezymes
- 12. 2. Cutting(contiŌĆ”.) Donor DNA Sticky Ends Plasmid
- 13. DNA Ligase Ligation ŌĆō re-joining cut fragments of DNA and forming artificial recombinant molecules
- 16. 5. Expression ’é┤ Bacterial cell reproduces by Binary Fission ’é┤ Bacterial cell produces the polypeptide ’é┤ Coded for by the donor DNA
- 17. Examples Of Use Of rDNA Technology Golden Rice ŌĆō a possible solution to Vitamin A deficiency. Insect Resistant Crops ŌĆō more crops produce without infected by insects Insulin production
- 18. Advantages of Recombinant Technology Provide substanti quantity No need for or factors Unlimited utilizatio Cheap Better crops
- 19. Disadvantages of Recombinant Technology Lower efficacy in larger animals & humans Limited to protein antigens Threat of autoimmune reactions Produce of monsters Produce of dangerous toxic chemicals Produce highly lethal microbes Use in microbiological warfare to kill humans, animals, plants
- 20. Applications Of rDNA Technology 1. Insulin for diabetics. 2. Production of factor VIII for males suffering from haemophilia A. 3. Production of factor IX for haemophilia B. 4. Production Human growth hormone (HGH). 5. Production of erythropoietin (EPO) for treating anemia. 6. Production of several types of interferon. 7. Granulocyte ŌĆōmacrophage colony-stimulating factor(GSM-CSF) for stimulating the bone marrow after a bone marrow transplant. 8. Many monoclonal antibodies production 9. Pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications 10. In gene therapy 11. For medical diagnosis 12. Production of xenotransplants
Editor's Notes
- #10: Gene Probe┬Ā(DNA Probe) A single-stranded┬ĀDNA┬Āor RNA fragment used in┬Āgenetic┬Āengineering to search for a particular┬Āgene┬Āor other┬ĀDNA┬Āsequence.
- #21: Hemophilia┬Āis a mostly inherited genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to make blood clots Xenotransplantation, or heterologous transplant is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another.