Recommendations assumptions
- 1. + Recommendation Assumptions Prototyping Day @ Mozilla London 3 September 2015 Engineering Summit @ BBC 7 March 2018 Presented at
- 2. + Recommendations types Personal vs. Non personal
- 3. + Recommendations types ’ü« Personalized ’ü« User-interaction driven (passive/active) ’ü« Non personalized ’ü« Editorially curated ’ü« Stats Based
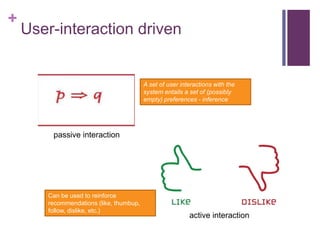
- 4. + User-interaction driven passive interaction active interaction A set of user interactions with the system entails a set of (possibly empty) preferences - inference Can be used to reinforce recommendations (like, thumbup, follow, dislike, etc.)
- 5. + Recommendations types ’ü« Personalized ’ü« User-interaction driven (passive/active) ’ü« Non personalized ’ü« Editorially curated ’ü« Stats Based
- 8. + Most popular If more than N% + K of people liked, listened to, blablablabed about something (+/- standard deviation), this something is likely to be recommended.
- 9. + Content similarity It can be content-to-content or cross content. To calculate the similarity we can use the actual content or the metadata or both.
- 10. + Co-occurrence relationship (market basket analysis) Understand what products or services are commonly purchased together. If you consume a certain group (cluster) of contents, you are more (or less) likely to consume another group of items ŌĆō Beers and nappies
- 11. + Assumptions ’ü« Similarity and Correlation ’ü« User activity assumptions ’ü« Device sensor analytics (accelerometer, gyroscope, compass, barometer, ambient light sensor, proximity sensor, thermometer, camera, microphone, GPS, etc.)
- 12. + Perturbations (external influences) ’ü« Model building phase ’ü« Recommendation phase
- 13. + Mood
- 14. + Wear & Tear
- 15. + Does the time matter?
- 16. + Does the time matter? ’ü« Are preferences or statistics about a topic valid forever? ’ü« If not, whatŌĆÖs the ŌĆ£bestŌĆØ time window to take in account? ’ü« How can we model a preference modification during the time? (Aging, change of taste) ’ü« How a good/bad feedback can affect a recommendation in the future and for how long?
- 18. + IŌĆÖve got questions for you ’ü« Inheritance, taxonomy, membership, how do we use these relationships between contents in a domain in order to infer a user interest? ’ü« Is the interest of a user black and white only? How can I express different type of interests (if any)? ’ü« Can we improve the quality of the user experience by presenting the right ŌĆ£amountŌĆØ of information of a recommended content according to ’ü« type and level of interest? ’ü« time available to consume the content? ’ü« mood?
- 19. + Thank you Simone.Spaccarotella@bbc.co.uk Senior Software Engineer | BBC Sounds