Recycling and bypassing operation
Download as PPTX, PDF11 likes11,644 views
Recycling operations return a portion of the exit stream from a process unit back to its entrance to maximize the utilization of valuable reactants, improve performance, and conserve heat. Common applications of recycling include returning distillate or catalyst back to distillation columns or reactors. Recycling improves selectivity and rate of reactions while minimizing byproducts and losses. A purge stream is also often used to prevent the buildup of inert components in a recycling loop.
1 of 13
Downloaded 95 times











Recommended
2.2 McCabe-Thiele method



2.2 McCabe-Thiele methodSouth-Eastern Finland University of Applied Sciences
╠²
The McCabe-Thiele method is a graphical technique for determining the minimum number of stages required for distillation. It involves plotting the equilibrium relationship between liquid and vapor phases on a diagram and constructing operating lines to represent the mass balances in the rectifying and stripping sections. Intersections between the lines indicate the number of ideal stages. The method was developed in 1925 and remains useful for preliminary column design. Key considerations include the feed composition and enthalpy, reflux ratio, and use of partial condensers or reboilers.Difference between batch,mixed flow & plug-flow reactor



Difference between batch,mixed flow & plug-flow reactorUsman Shah
╠²
This slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineering. Fluid Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Mass Transfer Chemical Engineering. Energy Engineering, Mass Transfer 2, Heat Transfer, Material balance with chemical reaction



Material balance with chemical reactionJayJawalge
╠²
1) Material balances apply the law of conservation of mass to chemical processes, ensuring mass is neither created nor destroyed.
2) To perform a material balance, a process flow diagram is drawn with stream labels and unknowns assigned symbols. A basis is selected before writing balance equations.
3) For reactive systems, stoichiometric ratios from chemical equations are used in material balances to determine limiting reactants and calculate yields, selectivity, and conversion.Pvt behaviour



Pvt behaviourAwais Sharif
╠²
The document discusses the phase behavior of pure substances through P-T and P-V diagrams. A P-T diagram shows the relationships between pressure, temperature, and phases (solid, liquid, gas). Key points on the diagram include the sublimation, fusion, and vaporization curves that separate the phases and meet at the triple point. The critical point marks the highest P and T where the substance can exist as a liquid and gas. A P-V diagram adds volume information and shows isotherms representing constant temperature lines that intersect phase boundaries.Types of reactor



Types of reactorIhsan Ali
╠²
The document describes different types of reactors used in chemical processes. It discusses batch reactors, continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTR), plug flow reactors, fixed bed reactors, and fluidized bed reactors. For CSTRs, it provides the design equation that relates the reactor volume to the inlet and outlet flow rates of a reactant and the rate of reaction. It also gives an example of using this equation to calculate the volume of a CSTR needed to achieve 80% conversion of a reactant based on given kinetic data.Bollman extractor



Bollman extractorPadmaratinam
╠²
The document describes the Bollman extractor, which is a type of basket extractor used for leaching solids. It consists of a vertical chamber with a series of perforated baskets attached to a chain conveyor. Dry solids are added to the top baskets and leached by a solvent solution as the baskets descend counter-currently. The wet solids are removed at the bottom and the recovered solvent is evaporated and stripped to extract oil. The Bollman extractor provides continuous counter-current contact between solids and solvent for effective leaching.material balance and its applications



material balance and its applicationsKarnav Rana
╠²
This document provides an overview of material balances and their applications in process engineering. It begins by explaining that material balances are used to account for the mass of materials entering and leaving a process based on the law of conservation of mass. The general material balance equation is presented, which accounts for inputs, outputs, generation, consumption and accumulation of a material within a system. Examples are then provided to demonstrate how to set up and solve material balance problems for physical processes and distillation columns. Procedures for performing material balances on single and multiple unit processes are also outlined.Transesterification and its mechanism, its application in dairy industry



Transesterification and its mechanism, its application in dairy industryARCHANA MADPATHI
╠²
Transesterification, mechanism of trans esterification, importance of transesterification, conclusion and references1.1 Vapor Liquid Equilibrium



1.1 Vapor Liquid EquilibriumSouth-Eastern Finland University of Applied Sciences
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs for the eLearning course Separation and purification processes in biorefineries (https://open-learn.xamk.fi) in IMPRESS project.
Section: Distillation
Subject: 1.1 Vapor Liquid EquilibriumManufacturing process of methanol



Manufacturing process of methanolrita martin
╠²
Methanol most flexible chemical commodities and energy sources produced from convert the feedstock natural gas into a synthesis gas and also by catalytic synthesis of methanolgas absorption



gas absorptionAbhijit Panchmatiya
╠²
Gas absorption is a process used to separate gases by contacting a gas mixture with a liquid solvent. The key principles are the solubility of the absorbed gas and the rate of mass transfer as the gas dissolves into the liquid. Absorption is usually carried out counter-currently in vertical columns. The solvent is fed at the top while the gas enters at the bottom, allowing the absorbed substances to be washed out in the downward flowing liquid. Proper selection of solvent considers factors like gas solubility, volatility, cost, and viscosity. Rate of absorption is determined by volumetric mass transfer coefficients, which can be calculated from operating line and equilibrium curve diagrams.VLE VAPOR LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM - Introduction 



VLE VAPOR LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM - Introduction Usama Khan
╠²
This document discusses vapor/liquid equilibrium (VLE) and provides models for predicting VLE using simple models like Raoult's law and Henry's law. It defines key terms like mass fraction, mole fraction, molar concentration. Duhem's theorem is introduced which states that the equilibrium state is determined by fixing any two independent variables for a closed system. Simple calculations are shown for using Raoult's law to determine the bubble point and dew point temperatures and pressures of a binary system from its phase compositions or known temperature. P-x-y and T-x-y diagrams are used to illustrate the VLE behavior between the phases.Fluidization



FluidizationKarnav Rana
╠²
Fluidization refers to a process where solid particles are made to behave like a fluid by passing a liquid or gas through it. There are two main types of fluidization - particulate and aggregative. The key conditions for fluidization include maintaining a superficial velocity lower than the particle terminal velocity and keeping the particle size between 30-300 micrometers. Common applications of fluidization include fluid catalytic cracking, drying, and granulation. The main advantages are uniform temperature distribution due to mixing and easy handling of solids. The main disadvantages are non-uniform gas-solid contacting and erosion due to particle abrasion.Tank in series model



Tank in series modelSunny Chauhan
╠²
The document describes the tanks-in-series model for modeling flow. The model represents a system as a series of perfectly mixed tanks or compartments. Flow passes sequentially from one compartment to the next. The model is useful for systems with laminar or turbulent flow, such as pipes, packed beds, or conveyers. It is simpler than the dispersion model but can still model deviations from plug flow. The document provides equations to model different applications of the tanks-in-series model, such as closed recirculation systems or systems with recirculation and throughflow.Chemical Reactors



Chemical ReactorsAwais Chaudhary
╠²
The document discusses different types of chemical reactors used in industrial processes. It describes basic reactor components like tanks and pipes and operating modes like batch, continuous stirred-tank, and plug flow reactors. Key aspects covered include material and heat transfer, reaction rates, and the influence of temperature, pressure and catalysts. Common reactor designs are presented, such as jackets, coils and packed beds for heat exchange. The document also discusses homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.Size reduction (GIKI)



Size reduction (GIKI)SAFFI Ud Din Ahmad
╠²
(No "Download lock")........... Study it, Download it, Understand it, Apply it and Serve the community.
ž▒┘Äž©┘É┘æ ž▓ž»┘Æ┘å┘Ŗ┘É ž╣┘É┘ä┘Æ┘ģž¦┘ŗ (Arabic)..............Ameen.Chemical reaction engineering



Chemical reaction engineeringPrem Baboo
╠²
This document discusses different types of chemical reactors, including plug flow reactors and continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTR). It provides information on their design considerations, advantages, disadvantages, and equations. Plug flow reactors allow minimal back mixing and each particle has the same residence time. CSTRs ensure proper mixing through the use of an impeller and assume perfect mixing. The document also provides examples of design equations for ideal reactors and discusses factors to consider for reactor selection like yield, cost, and safety.Batch Reactor



Batch ReactorAwais Chaudhary
╠²
In this topic we have discussed working principle of a Batch Reactor. We've also discussed its kinetics like its Rate equation, Material and Energy balance. Its Design steps also have been discussed.Chapter 6



Chapter 6sc9112008
╠²
This document discusses reactor design for single chemical reactions. It compares the size and performance of batch, mixed flow, and plug flow reactors. For single reactions where product distribution is fixed, plug flow reactors generally require less volume than mixed flow reactors to achieve the same conversion. The size ratio of mixed to plug flow reactors depends on the reaction order and conversion level. Connecting reactors in series improves performance by making the flow more plug-like.Lecture 3 kinetics of homogeneous reactions



Lecture 3 kinetics of homogeneous reactionsUsman Shah
╠²
This slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineeringThis slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineering. Fluid Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Mass Transfer Chemical Engineering. Energy Engineering, Mass Transfer 2, Heat Transfer, Distillation Column-Pohnchon savrit method.pptx



Distillation Column-Pohnchon savrit method.pptxbintenasir4
╠²
basics of ponchon savrit method to calculate no. of trays in distillation column and this could be more feasible for those who are willing to study separation processes related to their chemical engineering fields. moreover, if you find difficulty in taking lectures on YouTube, you can just click on this link and just download the slides for its study. as every student in this world in willing to study the basics of chemical engineering, this could be more beneficial for those students. also if your teacher wants any presentation slides on this specific topic, you can just download these slides from the website and can present in a better way to proceed you knowledge and journey of your education.Non ideal flow



Non ideal flowKarnav Rana
╠²
This document discusses non-ideal flow and residence time distribution (RTD) analysis for non-ideal reactors. It begins by describing deviations from ideal reactor behavior, such as dead zones and bypassing, and how these affect residence times. It then covers RTD concepts like E(t), F(t), and normalized E(╬Ė) curves. Measurement of RTD using tracers is described. Ideal reactor RTDs and models for non-ideal reactors like segregation and tanks-in-series are presented. The document stresses that RTD alone may not characterize non-ideal reactors and that flow models are also needed to analyze performance.Samical: Unit Process and Unit Operations



Samical: Unit Process and Unit OperationsSAMICAL CHEM
╠²
This document discusses unit processes and unit operations in chemical engineering. It defines unit processes as chemical reactions that produce useful products, providing information on reaction conditions. Unit operations involve physical separations with no chemical changes. Examples of common unit processes and unit operations are provided. The document also analyzes the manufacturing processes for ammonia and nitric acid production, identifying the unit processes and unit operations in each step and explaining the chemical or physical changes occurring.Elementary and non elementary reaction(no-18) - copy



Elementary and non elementary reaction(no-18) - copyPrawin Ddy
╠²
The document discusses the differences between elementary and non-elementary reactions. Elementary reactions occur in a single step, while non-elementary reactions occur through a series of steps. For elementary reactions, the order is the same as the stoichiometric coefficient, but for non-elementary reactions the order does not necessarily match the stoichiometry. Non-elementary reactions are represented by rate equations that may have fractional orders, unlike elementary reactions which always have integer orders.Differential method of analysis of data



Differential method of analysis of dataUsman Shah
╠²
This slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineering. Fluid Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Mass Transfer Chemical Engineering. Energy Engineering, Mass Transfer 2, Heat Transfer, Recycle Reactor (Basics & Design Eqn)



Recycle Reactor (Basics & Design Eqn)Jaydeep Vakil
╠²
This PPT contains basics and design equations of Recycle Reactor. Also contains performance curve of it. Material and energy balance



Material and energy balanceMagnusMG
╠²
Material and energy balances are used to track quantities as they pass through processes. They are based on the principles of conservation of mass and energy.
A material balance equates total input mass to total output mass plus any accumulation. It can be done on a total mass basis or by tracking individual components. Concentrations are commonly used to quantify compositions.
An energy balance equates total energy input to total energy output plus any storage. Different forms of energy must be accounted for as some can be interconverted. Sankey diagrams provide a visual representation of energy flows.
Balances get more complex for real processes but the basic approach is generally applicable. They are important for process control, optimization, and examining efficiency.Rate equations for heterogeneous reactions combining linear and nonlinear exp...



Rate equations for heterogeneous reactions combining linear and nonlinear exp...Rashmin Patel
╠²
The document discusses rate equations for heterogeneous chemical reactions that involve both linear and nonlinear processes. It begins by introducing heterogeneous reactions and providing examples. It then discusses how rate equations are developed by treating heterogeneous reactions as series of steps involving both chemical reactions and physical transport processes. The document presents equations for developing an overall rate expression when the individual steps are linear or nonlinear. It shows that for linear processes, the overall rate can be expressed as an additive resistance relationship, but for nonlinear processes, eliminating intermediate concentrations is more complicated.Material Balance Selected Topics ppt.pptx



Material Balance Selected Topics ppt.pptxDrAtulHMakwana
╠²
Basic terms related to Material Balance - Selected Topics Microsoft PowerPoint - Ch90279.PDF



Microsoft PowerPoint - Ch90279.PDFhesam ahmadian
╠²
This document discusses the recycle structure design level for a chemical process. It addresses questions like how many reactor systems and recycle streams are required. Using examples, it explains how to determine the number of recycle streams based on boiling points of components leaving the reactor. The document also discusses whether excess reactants should be used, if a gas compressor is needed, and how to determine the reactor heat requirements and temperature changes.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
1.1 Vapor Liquid Equilibrium



1.1 Vapor Liquid EquilibriumSouth-Eastern Finland University of Applied Sciences
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs for the eLearning course Separation and purification processes in biorefineries (https://open-learn.xamk.fi) in IMPRESS project.
Section: Distillation
Subject: 1.1 Vapor Liquid EquilibriumManufacturing process of methanol



Manufacturing process of methanolrita martin
╠²
Methanol most flexible chemical commodities and energy sources produced from convert the feedstock natural gas into a synthesis gas and also by catalytic synthesis of methanolgas absorption



gas absorptionAbhijit Panchmatiya
╠²
Gas absorption is a process used to separate gases by contacting a gas mixture with a liquid solvent. The key principles are the solubility of the absorbed gas and the rate of mass transfer as the gas dissolves into the liquid. Absorption is usually carried out counter-currently in vertical columns. The solvent is fed at the top while the gas enters at the bottom, allowing the absorbed substances to be washed out in the downward flowing liquid. Proper selection of solvent considers factors like gas solubility, volatility, cost, and viscosity. Rate of absorption is determined by volumetric mass transfer coefficients, which can be calculated from operating line and equilibrium curve diagrams.VLE VAPOR LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM - Introduction 



VLE VAPOR LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM - Introduction Usama Khan
╠²
This document discusses vapor/liquid equilibrium (VLE) and provides models for predicting VLE using simple models like Raoult's law and Henry's law. It defines key terms like mass fraction, mole fraction, molar concentration. Duhem's theorem is introduced which states that the equilibrium state is determined by fixing any two independent variables for a closed system. Simple calculations are shown for using Raoult's law to determine the bubble point and dew point temperatures and pressures of a binary system from its phase compositions or known temperature. P-x-y and T-x-y diagrams are used to illustrate the VLE behavior between the phases.Fluidization



FluidizationKarnav Rana
╠²
Fluidization refers to a process where solid particles are made to behave like a fluid by passing a liquid or gas through it. There are two main types of fluidization - particulate and aggregative. The key conditions for fluidization include maintaining a superficial velocity lower than the particle terminal velocity and keeping the particle size between 30-300 micrometers. Common applications of fluidization include fluid catalytic cracking, drying, and granulation. The main advantages are uniform temperature distribution due to mixing and easy handling of solids. The main disadvantages are non-uniform gas-solid contacting and erosion due to particle abrasion.Tank in series model



Tank in series modelSunny Chauhan
╠²
The document describes the tanks-in-series model for modeling flow. The model represents a system as a series of perfectly mixed tanks or compartments. Flow passes sequentially from one compartment to the next. The model is useful for systems with laminar or turbulent flow, such as pipes, packed beds, or conveyers. It is simpler than the dispersion model but can still model deviations from plug flow. The document provides equations to model different applications of the tanks-in-series model, such as closed recirculation systems or systems with recirculation and throughflow.Chemical Reactors



Chemical ReactorsAwais Chaudhary
╠²
The document discusses different types of chemical reactors used in industrial processes. It describes basic reactor components like tanks and pipes and operating modes like batch, continuous stirred-tank, and plug flow reactors. Key aspects covered include material and heat transfer, reaction rates, and the influence of temperature, pressure and catalysts. Common reactor designs are presented, such as jackets, coils and packed beds for heat exchange. The document also discusses homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.Size reduction (GIKI)



Size reduction (GIKI)SAFFI Ud Din Ahmad
╠²
(No "Download lock")........... Study it, Download it, Understand it, Apply it and Serve the community.
ž▒┘Äž©┘É┘æ ž▓ž»┘Æ┘å┘Ŗ┘É ž╣┘É┘ä┘Æ┘ģž¦┘ŗ (Arabic)..............Ameen.Chemical reaction engineering



Chemical reaction engineeringPrem Baboo
╠²
This document discusses different types of chemical reactors, including plug flow reactors and continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTR). It provides information on their design considerations, advantages, disadvantages, and equations. Plug flow reactors allow minimal back mixing and each particle has the same residence time. CSTRs ensure proper mixing through the use of an impeller and assume perfect mixing. The document also provides examples of design equations for ideal reactors and discusses factors to consider for reactor selection like yield, cost, and safety.Batch Reactor



Batch ReactorAwais Chaudhary
╠²
In this topic we have discussed working principle of a Batch Reactor. We've also discussed its kinetics like its Rate equation, Material and Energy balance. Its Design steps also have been discussed.Chapter 6



Chapter 6sc9112008
╠²
This document discusses reactor design for single chemical reactions. It compares the size and performance of batch, mixed flow, and plug flow reactors. For single reactions where product distribution is fixed, plug flow reactors generally require less volume than mixed flow reactors to achieve the same conversion. The size ratio of mixed to plug flow reactors depends on the reaction order and conversion level. Connecting reactors in series improves performance by making the flow more plug-like.Lecture 3 kinetics of homogeneous reactions



Lecture 3 kinetics of homogeneous reactionsUsman Shah
╠²
This slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineeringThis slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineering. Fluid Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Mass Transfer Chemical Engineering. Energy Engineering, Mass Transfer 2, Heat Transfer, Distillation Column-Pohnchon savrit method.pptx



Distillation Column-Pohnchon savrit method.pptxbintenasir4
╠²
basics of ponchon savrit method to calculate no. of trays in distillation column and this could be more feasible for those who are willing to study separation processes related to their chemical engineering fields. moreover, if you find difficulty in taking lectures on YouTube, you can just click on this link and just download the slides for its study. as every student in this world in willing to study the basics of chemical engineering, this could be more beneficial for those students. also if your teacher wants any presentation slides on this specific topic, you can just download these slides from the website and can present in a better way to proceed you knowledge and journey of your education.Non ideal flow



Non ideal flowKarnav Rana
╠²
This document discusses non-ideal flow and residence time distribution (RTD) analysis for non-ideal reactors. It begins by describing deviations from ideal reactor behavior, such as dead zones and bypassing, and how these affect residence times. It then covers RTD concepts like E(t), F(t), and normalized E(╬Ė) curves. Measurement of RTD using tracers is described. Ideal reactor RTDs and models for non-ideal reactors like segregation and tanks-in-series are presented. The document stresses that RTD alone may not characterize non-ideal reactors and that flow models are also needed to analyze performance.Samical: Unit Process and Unit Operations



Samical: Unit Process and Unit OperationsSAMICAL CHEM
╠²
This document discusses unit processes and unit operations in chemical engineering. It defines unit processes as chemical reactions that produce useful products, providing information on reaction conditions. Unit operations involve physical separations with no chemical changes. Examples of common unit processes and unit operations are provided. The document also analyzes the manufacturing processes for ammonia and nitric acid production, identifying the unit processes and unit operations in each step and explaining the chemical or physical changes occurring.Elementary and non elementary reaction(no-18) - copy



Elementary and non elementary reaction(no-18) - copyPrawin Ddy
╠²
The document discusses the differences between elementary and non-elementary reactions. Elementary reactions occur in a single step, while non-elementary reactions occur through a series of steps. For elementary reactions, the order is the same as the stoichiometric coefficient, but for non-elementary reactions the order does not necessarily match the stoichiometry. Non-elementary reactions are represented by rate equations that may have fractional orders, unlike elementary reactions which always have integer orders.Differential method of analysis of data



Differential method of analysis of dataUsman Shah
╠²
This slide completely describes you about the stuff include in it and also everything about chemical engineering. Fluid Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Mass Transfer Chemical Engineering. Energy Engineering, Mass Transfer 2, Heat Transfer, Recycle Reactor (Basics & Design Eqn)



Recycle Reactor (Basics & Design Eqn)Jaydeep Vakil
╠²
This PPT contains basics and design equations of Recycle Reactor. Also contains performance curve of it. Material and energy balance



Material and energy balanceMagnusMG
╠²
Material and energy balances are used to track quantities as they pass through processes. They are based on the principles of conservation of mass and energy.
A material balance equates total input mass to total output mass plus any accumulation. It can be done on a total mass basis or by tracking individual components. Concentrations are commonly used to quantify compositions.
An energy balance equates total energy input to total energy output plus any storage. Different forms of energy must be accounted for as some can be interconverted. Sankey diagrams provide a visual representation of energy flows.
Balances get more complex for real processes but the basic approach is generally applicable. They are important for process control, optimization, and examining efficiency.Rate equations for heterogeneous reactions combining linear and nonlinear exp...



Rate equations for heterogeneous reactions combining linear and nonlinear exp...Rashmin Patel
╠²
The document discusses rate equations for heterogeneous chemical reactions that involve both linear and nonlinear processes. It begins by introducing heterogeneous reactions and providing examples. It then discusses how rate equations are developed by treating heterogeneous reactions as series of steps involving both chemical reactions and physical transport processes. The document presents equations for developing an overall rate expression when the individual steps are linear or nonlinear. It shows that for linear processes, the overall rate can be expressed as an additive resistance relationship, but for nonlinear processes, eliminating intermediate concentrations is more complicated.Similar to Recycling and bypassing operation (20)
Material Balance Selected Topics ppt.pptx



Material Balance Selected Topics ppt.pptxDrAtulHMakwana
╠²
Basic terms related to Material Balance - Selected Topics Microsoft PowerPoint - Ch90279.PDF



Microsoft PowerPoint - Ch90279.PDFhesam ahmadian
╠²
This document discusses the recycle structure design level for a chemical process. It addresses questions like how many reactor systems and recycle streams are required. Using examples, it explains how to determine the number of recycle streams based on boiling points of components leaving the reactor. The document also discusses whether excess reactants should be used, if a gas compressor is needed, and how to determine the reactor heat requirements and temperature changes.Hydrogen recovery from purge gas(energy saving)



Hydrogen recovery from purge gas(energy saving)Prem Baboo
╠²
Ammonia is continuously condensed out of the loop and fresh synthesis gas is added. Because the synthesis gas contains small quantities of methane and argon, these impurities build up in the loop and must be continuously purged to prevent them from exceeding a certain concentration. Although this purge stream can be used to supplement reformer fuel gas, it contains valuable hydrogen which is lost from the ammonia synthesis loop In order to achieve optimum conversion in synthesis convertor, it is necessary to purge a certain quantity of gas from synthesis loop so as to as to reduce inerts concentration in the loop. Purge gas stream from ammonia process contains ammonia, hydrogen, nitrogen and other inert gases. Among them, ammonia itself is the valuable product lost with the purge stream. Moreover it has a serious adverse effect on the environment.This purge gas containing about 60% Hydrogen was fully utilised as primary reformer fuel. Azeotropic Distillation



Azeotropic DistillationMalayGorai
╠²
This document provides an overview of azeotropic distillation. It begins with an introduction that defines azeotropic distillation as a process where an entrainer is added to a feed mixture to form an azeotrope that can be separated. The document then discusses the working principle, provides examples of residue curve maps, and outlines considerations for process design and simulation. Finally, it discusses several industrial applications of azeotropic distillation, including alcohol dehydration, acetic acid dehydration, and ester production, before concluding and listing references.Ammonia Plant and Catalyst By Prem Baboo.pdf



Ammonia Plant and Catalyst By Prem Baboo.pdfPremBaboo4
╠²
Research Gate is an academic social networking site for scientists and researchers. This document discusses catalysts used in ammonia plants. It describes how catalysts work by providing alternate reaction paths with lower activation energies than non-catalytic reactions. It also discusses factors that influence catalyst performance like size, shape, promoters, and poisons. Specific catalysts used in different sections of an ammonia plant are described.Production of Bio-diesel (Butyl Oleate) by Reactive Distillation Technique



Production of Bio-diesel (Butyl Oleate) by Reactive Distillation TechniqueIRJET Journal
╠²
This document discusses producing biodiesel (butyl oleate) through the reactive distillation of oleic acid and n-butanol. Reactive distillation combines chemical reaction and distillation in a single vessel, offering advantages over conventional processes. These include improved conversion and selectivity, reduced catalyst needs, and ability to overcome azeotropes. The document reviews the esterification reaction of oleic acid and n-butanol catalyzed by Amberlyst-15. It also discusses advantages of reactive distillation such as simplifying separation, increased conversion near 100%, improved selectivity, reduced catalyst and byproduct formation, and heat integration benefits.Designcriteriaforwastewatertreatment 120411055901-phpapp02



Designcriteriaforwastewatertreatment 120411055901-phpapp02reyn007
╠²
This document discusses the design and processes involved in sludge treatment for wastewater. It begins by defining sludge and its sources. The goals of sludge treatment are then outlined as volume reduction, pathogen elimination, organic stabilization, and recycling of substances. Various sludge treatment processes are then described in detail, including thickening, stabilization through aerobic/anaerobic digestion, dewatering, and drying. The document also discusses activated sludge processes and trickling filter processes for wastewater treatment.Project-Final-Report



Project-Final-ReportAndrew Wu
╠²
This document discusses options for distilling dilute ethanol to produce 99.5% ethanol. It analyzes pressure swing distillation versus azeotropic distillation, with benzene as a common entrainer. Preliminary simulations show pressure swing distillation yields the desired product composition with less ethanol loss. A three-column system is also considered but deemed too costly. The document outlines objectives of determining the optimal distillation method, finalizing a process flow diagram, performing safety and economic analyses, and achieving a 5% annual ROI.Lpg Biogas Biomass Reformer Hydrogen Fuel cell power gas 



Lpg Biogas Biomass Reformer Hydrogen Fuel cell power gas Daniel Donatelli
╠²
Lpg Biogas Biomass Reformer Hydrogen Fuel cell power gas
#Lpg #Biogas #Biomass #Reformer #Hydrogen #Fuel #cell methane #power #gas www.securesupplyusa.biz whats app+66 83 647 3443Validation of compressed air and nitrogen



Validation of compressed air and nitrogenManiKandan1405
╠²
Brief discussion about validation of compressed air and nitrogen with specific examples in detail.
Comparison of compressed air and nitrogenHvac design for pharmaceutical facilities



Hvac design for pharmaceutical facilitiesAjay Srinivas Chama
╠²
This document provides an overview of HVAC design considerations for pharmaceutical facilities. It discusses regulations for cleanroom environments from organizations like the FDA and outlines key HVAC functions like particulate control, pressure regulation, temperature/humidity control. Sources of particulates are explained along with cleanroom classifications. The pharmaceutical manufacturing process is briefly summarized, covering stages like reaction, separation, drying and formulation. Strict HVAC is needed to help minimize contamination during sensitive production stages.INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS CHEMISTRY.pptx



INTRODUCTION TO PROCESS CHEMISTRY.pptxPurushothamKN1
╠²
This document discusses scaling up a process for producing paste-glue from the laboratory scale to the pilot and near-commercial scales. Two methods for synthesizing the paste-glue using corn-based starch are developed at the laboratory scale. For Method 1, starch is decomposed with water and enzyme and polymer is produced separately, then combined. For Method 2, monomer, catalyst and decomposed starch are combined directly. The laboratory scale reactions are then scaled up 1000x for pilot studies. The pilot reactions produce paste-glue but with poorer properties, likely due to excessive exothermic reaction not controllable at larger scale. Further modifications are needed to successfully scale up the process.Importance of HVAC System



Importance of HVAC SystemMd. Foysal Fuad Chowdhury
╠²
The document discusses the importance of HVAC systems in the pharmaceutical industry. Strict regulations require tight control of temperature, humidity, air pressure and filtration to minimize contamination. HVAC must maintain clean air by filtering particles and pressurizing clean rooms. It also summarizes the multi-step pharmaceutical manufacturing process, which includes reactions, separations, crystallization, purification and drying. Maintaining precise environmental conditions is critical throughout production to ensure product safety, purity and effectiveness.Control of air pollutants



Control of air pollutantsJenson Samraj
╠²
Everyone can raise a question that how to prevent an Air pollution and so on. So here is our presentation on Control of Air pollution. So using the technique called adsorption sampling is an interesting one to all of the human beings
Presentation1



Presentation1Fady Punk
╠²
A batch reactor undergoes a controlled chemical reaction within a contained vessel. Reactants are added at the start and nothing is added or removed until the reaction is complete. Semi-batch reactors are similar but allow reactants or products to be continuously added or removed during the reaction. Batch reactors are useful for small scale or specialized productions like pharmaceuticals due to their flexibility, but they have higher operating costs than continuous reactors.Advance Green Chemistry.ppt



Advance Green Chemistry.pptwadhava gurumeet
╠²
This document provides information about green chemistry. It discusses natural processes versus chemical processes and how green chemistry aims to make chemical processes more environmentally friendly. Some key points made include:
- Green chemistry seeks to prevent pollution by designing chemical synthesis and products to be benign.
- Natural processes are more environmentally friendly than traditional chemical processes which use toxic solvents and generate hazardous wastes.
- Green chemistry principles include using safer solvents like water or ionic liquids, performing solvent-free reactions, and using renewable feedstocks and benign catalysts.
- New techniques like microwave irradiation and ultrasound can help drive chemical reactions in a more energy efficient and atom economic manner.Turning Waste Into Revenue Through BioTransformation



Turning Waste Into Revenue Through BioTransformationnjcnews777
╠²
The City of Waco Wastewater Treatment Plant operates a sludge pelleting process that converts wastewater sludge into a marketable pellet used as a soil conditioner and nutrient. This process generates about $275,000 in annual revenue. The plant also uses methane from anaerobic digestion to generate electricity, offsetting $17,380 in monthly electricity costs. Future plans include expanding electricity generation and adding composting and methane co-generation to further reduce costs and diversify biotransformation options.Estimating the Amount of Moisture Content in Crude Oil Samples



Estimating the Amount of Moisture Content in Crude Oil SamplesIRJESJOURNAL
╠²
Abstract :- Determination of the amount of water in crude oil and petroleum products has always been important. Rather than paying crude oil prices for water, contracts have been based on "net dry oil". This is calculated by reducing the total gross standard volume (GSV) by the amount of water and sediment present as determined by analysing a sample of the oil. Accurate analysis for the water content is usually more difficult than the determination of gross volume, temperature, and gravity of the oil.Continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR )



Continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR )SANJAY KUMAR JOGAR
╠²
This document discusses continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTR) for treating dairy wastewater. CSTRs are completely mixed anaerobic reactors that maximize contact between biomass and waste to optimize digestion. They have low operating costs since they produce biogas and are suitable for high-strength organic wastes like those from dairy processing. CSTRs are simple in design with short construction periods and can effectively treat wastewater from industries like dairies, breweries, and food processing. The document provides details on CSTR configuration, advantages, applications, specifications and inhibition challenges from lipids in dairy wastewater.Pilot plan scale up for semisolid and parenteral by Khushboo kunkulol



Pilot plan scale up for semisolid and parenteral by Khushboo kunkulolKhushbooKunkulol
╠²
This document provides an overview of pilot plant scale up for semisolid and parenteral pharmaceutical products. It discusses why pilot plants are used, including evaluating process changes at larger scale, producing trial batches, and gathering data for full-scale production. It describes typical equipment and facilities for parenteral production, including areas for storage, preparation, production, filling, and quality assurance. Key aspects of semisolid and parenteral formulations are also summarized, such as common solvents, solubilizers, buffers, and sterilization methods. Critical manufacturing parameters and general stability considerations for scale up are highlighted.Recycling and bypassing operation
- 2. Recycle operations ’éŚ The recycling operation with chemical reactions is common in industrial processes. ’éŚ This is mainly performed to utilize the valuable reactants to their maximum so that the loss of the reactants minimized. ’éŚ Recycling is returning back a portion of the steam leaving a process unit to the entrance of the process unit for further processing.
- 3. ’éŚ Recycling operations, commonly encountered in unit operations and unit processes are performed for: ’āśMaximum utilization of the valuable reactants. ’āśImprovement of the performance of the operation. ’āśUtilization of the heat being lost in the exit stream. ’āśBetter operating conditions of system. ’āśImprovement of the selectivity of a product. ’āśMaintaing process rate at a high value. ’āśEnrichment of a product.
- 4. ’éŚ In distillation operations, a part of the distillate is fed back to column to enrich the product, so that almost pure product can be obtained. ’éŚ In drying operations, a major portion of the hot air leaving the dryer is recirculated to conserve heat-to utilize the heat being lost in the exit air. ’éŚ In absorption towers, better wetting of tower packings is done by recycling part of the exit solvent stream. ’éŚ In chemical reactions, exit catalyst or spent catalyst is returned to the reactor for reuse after being regenerated. ’éŚ For achieving complete conversion, keeping the yield of byproduct to minimum and effecting reactions at a high rate.
- 5. ’éŚ A Recycle stream is a process stream that returns material leaving a process unit back to the entrance of the same unit ’éŚ Recycle operations are carried out under steady-rate conditions. ’éŚ In these operations these is no build-up or material takes place inside the process or in the recycle stream.
- 7. ’éŚ About the entire process including the recycle stream ŌĆōwhere in the fresh feed is equated with the net product. ’éŚ About the junction point 1 at which the fresh feed combines with the recycle stream. ’éŚ About the junction the gross product is divided into recycle and net product. ’éŚ Involving only process feed and gross product streams.
- 8. Purging operation ’éŚ In this operation, a fraction of the recycle stream is continuously bled-of order to limit the concentration of inerts to a desired level in the mixed stream. ’éŚ In the synthesis of ammonia, some of the gas stream must be purged to prevent build of argon and methane.
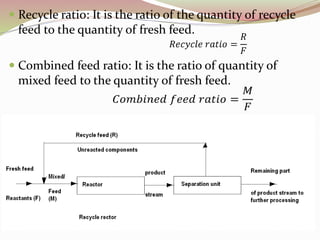
- 9. ’éŚ The recycling of air/recirculation of air in the drying of solids is shown diagrammatic. ’éŚ In a recycling operation: combined feed=Fresh feed +Recycle feed ’éŚ The combined feed is a mixture of the fresh feed and the recycle feed/recycle stock ’éŚ Gross product= Recycle feed + Net Product ’éŚ The gross product is a mixture of the net product and the recycle feed.
- 10. ’éŚ Recycle ratio: It is the ratio of the quantity of recycle feed to the quantity of fresh feed. ’éŚ Combined feed ratio: It is the ratio of quantity of mixed feed to the quantity of fresh feed.
- 11. ’éŚ Purge Ratio: It is the of ratio of the quantity of purge stream to the quantity of recycle feed. ’éŚ In manufacture of ammonia, built up of CH4 in recycle loop a certain tolerance limit is avoided by purging.
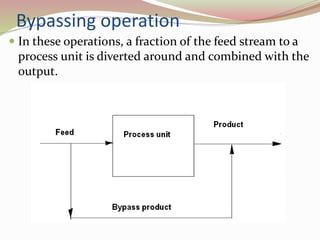
- 12. Bypassing operation ’éŚ In these operations, a fraction of the feed stream to a process unit is diverted around and combined with the output.
