Red Eye Presentation Building Lifecycle Strategies (Pdf)
- 1. Building Customer Lifecycle Marketing Strategies Using Behavioural and Engagement Data 1 May 2011
- 2. Premise ŌĆ£ Using the new media of the 1:1 future you will be able to communicate directly with customers, individually, rather than shouting at them in groupsŌĆ” The technologies needed to track and communicate with customers, one at a time, are already here.ŌĆØ * ŌĆśThe One To One Future, Building Relationships One Customer at a TimeŌĆÖ, Don Peppers and Martha Rogers, 1993 Income for eCommerce organisations employing the latest Behavioural and Engagement strategies should be growing 150-250% per year.
- 3. Over 100% Year on Year Increase in Email Revenues ROI of 2,399%, 103% growth in email revenues compared to the same period 2009. Evans Cycles achieved these results through, amongst others, segmentation and life cycle marketing strategies. The email campaign plan segmented messaging and creative content based on individual preferences, engagement, online browsing and behavioural behaviour. Email marketing content was relevant to each individual user. The results included open rates as high as 84.9% (generic ŌĆśnewsletterŌĆÖ emails 16% - 25%) and click rates of 40.5% (generic emails 3.8% - 5%).
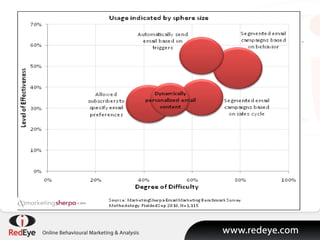
- 4. Diverging Strategies in Email
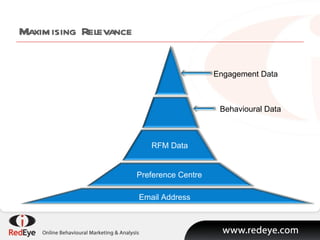
- 5. Maximising Relevance Email Address Preference Centre RFM Data Behavioural Data Engagement Data
- 6. What is Engagement Data? Engagement data identifies engagement with all media and the website. When Engagement is tracked and analysed the resulting segmentation will identify those customers likely to buy For instance, a customer engaged with email is 6.2 times more likely to purchase than one who is notŌĆ”
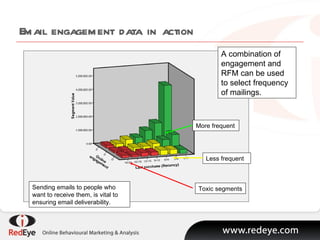
- 7. Email engagement data in action A combination of engagement and RFM can be used to select frequency of mailings. Sending emails to people who want to receive them, is vital to ensuring email deliverability. More frequent Less frequent Toxic segments
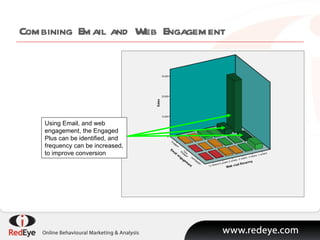
- 8. Combining Email and Web Engagement Using Email, and web engagement, the Engaged Plus can be identified, and frequency can be increased, to improve conversion
- 9. What is Behavioural Data? Repeat visitors are 8 times more likely to buy than first time visitors and the best way to get someone back to the website is via email Consumers respond better to more relevant communication Behavioural email targets consumers based on their online behaviour for best results Makes email marketing relevant to every recipient Typical results of 70% open rates, 30% click through rates and conversion rates over 10%
- 10. Why itŌĆÖs important Forrester research says 71% of shopping carts are abandoned Whilst recent studies have shown 46% of abandoned transactions would convert when remarketed to A single basket abandonment email will generate about 2% extra revenues A few dozen behavioural emails should be able to generate an extra 10% to 20% revenues
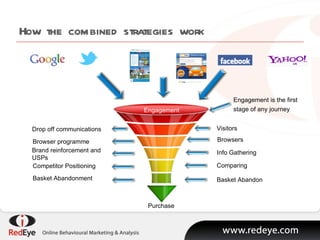
- 11. How the combined strategies work Visitors Browsers Info Gathering Comparing Basket Abandon Engagement is the first stage of any journey Purchase Drop off communications Browser programme Brand reinforcement and USPs Competitor Positioning Basket Abandonment Engagement
- 14. Different types of behavioural programmes Abandon Basket Incomplete quote Quote not purchased Registered not purchased Previous customer visited site but did not buy Content triggers to existing customer (e.g. Viewed section X) Errors on site completing process Add on product up-sell (e.g. Product insurance) Loyal customer programme Welcome program Nursery program Dis-engagement (see following slides) Incomplete quote Quote not buy Save quote not buy Abandon buying process Cross sell to existing customers visiting other products on-site Welcome program Add on product up-sell (e.g. Breakdown cover) Renewal program, timing based on when the customer returns to site Dis-engagement (see following slides) Abandon Basket Regular browser never purchased Previous customer visited site but did not buy Registered not purchased Loyal customer programme Content triggers to existing customer (e.g. Viewed baby product pages) Welcome program Nursery program Add on product up-sell (e.g. insurance) Dis-engagement (see following slides) Abandon buying process Quote not purchased Save quote not buy Regular browser never purchased Previous customer visited site but did not buy Loyal customer programme Purchase lifecycle triggers (pre-departure, welcome home etc...) Registered not purchased Content triggers to existing customer (e.g. Viewed hotel X or resort Y) Welcome program Nursery program Ancillary up-sell (e.g. Insurance, car hire etc...) Dis-engagement (see following slides) Partial registration Registered not deposited Deposit errors Deposited not played or bet Regular browser not playing or betting Loyal customer programme Cross sell based on content triggers (e.g. Viewed poker for first time) Welcome program Nursery program Dis-engagement (see following slides)
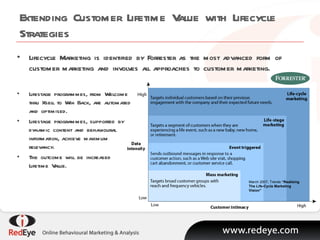
- 15. Extending Customer Lifetime Value with Lifecycle Strategies March 2007, Trends ŌĆ£Realizing The Life-Cycle Marketing VisionŌĆØ Lifecycle Marketing is identified by Forrester as the most advanced form of customer marketing and involves all approaches to customer marketing. Lifestage programmes, from Welcome thru Xsell to Win Back, are automated and optimised. Lifestage programmes, supported by dynamic content and behavioural information, achieve maximum relevancy. The outcome will be increased Lifetime Value.
- 16. The 6 Stages of Customer Lifecyle Tactical Engagement Purchase Re-Enforcement Retention Reactivation
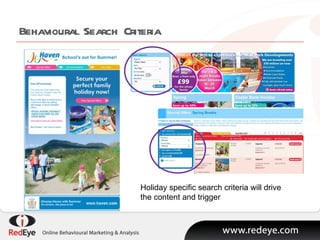
- 17. Behavioural Search Criteria Holiday specific search criteria will drive the content and trigger
- 18. Saved Event Mailings ŌĆō Travel Industry Client: Haven Holidays Campaign : ŌĆō Saved Search Data Logic: - 7 days after the event No purchase Results: Revenue increased by +168% Increased conv. +196%
- 19. Extended Product Specific Basket Abandon Program Client: Haven Holidays Campaign: Holiday Type driven Basket Process 24 hr emails Results: Revenue increased by +556% YoY
- 20. To make these programmes workŌĆ” An online database operating at a customer level Engagement data Browser/web analytics data Customer RFM data Product and customer lifecycle models Business rules
- 21. In Summary
- 22. Thank you.
Editor's Notes
- #2: The premise for my presentation today is borne out of a book that was published in 1993, Peppers and Rogers ŌĆśThe One to One Marketing FutureŌĆÖ. In that book, the authors stateŌĆ” As an impressionable marketing exec in 1993, I was always taken with the following quoteŌĆ”
- #3: Peppers and Rogers went on to identify 3 key factors in achieving this goalŌĆ” that the technology makes the communication ŌĆśAddressableŌĆÖ, ŌĆśTwo wayŌĆÖ and ŌĆśinexpensiveŌĆÖ. That vision on a mass scale was never really possible before the advent of email marketing but existed as an unobtainable vision for many direct marketer. But now a number of factors are converging that make this vision somewhat closer to realisation: Firstly, the depth of data, and its accuracy, that is now readily available and able to be deployed, is greater than ever. Electronic data systems, driving automated email programmes, are able to apply this data in a way that previous manual approaches could not have coped with. Thirdly, email marketing prices, that we always incredibly low in comparison with direct mail, have continued to fall. And finally there is the growing realisation amongst marketers that relevance drive profit. Mail someone what they want to read and you stand a greater chance of achieving a saleŌĆ”
- #4: My presentation today will give you a basic precise of how to double revenue year on year using the latest email marketing techniques.
- #5: As more businesses push into this area, email strategies are beginning to diverge into two distinct types. Two strategies are emerging and at the centre of these two strategies, linking them together, is the concept of engagement. Pre-engagement is the traditional newsletter, offer emails, segmented and pushed to the subscriber base. But these emails are increasingly becoming about achieving engagement. The goal for the recipient is to click through to the website. As it ever was, you may argue, but today that is the fundamental goal of this type of outbound emailŌĆ” to gain engagement. Previously mailers would review email reports looking for the amount of income driven by newsletters and weekly offer emails, but now engagement metrics, such as unique visitors to the website, are becoming more important. And whilst click rates, visitor rates and ROI are going up, open rates are going down. Why should this be? Well, once engagement is achieved, newsletters are effectively redundant as prospects and customers are increasingly interacting with more relevant, highly targeted and highly timely behavioural emails that in the diagram on the screen behind me are represented by the two bubbles nearer the top of the graph. So, we are seeing two types of strategy, the first about achieving engagement, the second about retaining engagement and achieving a sale. And once the goal of engagement is achieved, then the task is to successfully guide the customer through to the transaction and manage them through the customer lifecycle.
- #6: But I am getting slightly ahead of myself. Before discussing automated behaviour email programmes and lifecycles, I want to review the increasing wealth of data available and why that is enabling greater relevance. Historically, there was once a time when an optin email addresses and some barely literate copy was all you need to drive sales. But the novelty soon wore off, and preference centres were introduced for individuals to provide their own information about their mailing requirements. As email became a standard channel, so new techniques were required and segmentation strategies, pioneered by direct marketers, were pulled across into email marketing. But today, behavioural and engagement data has come to the fore as more relevant but, importantly, more predictive of likely behaviour.
- #7: We need to define both Engagement and Behavioural Data. Firstly Engagement data. This sounds like a simple question but engagement data is multi-layered by its nature as there can be many definitions of engagement. At its basic level Engagement Data informs your tactical mailing strategy ŌĆō engaged subscribers to your email list should receive email more regularly than disengaged. If someone is not visiting your site or opening your emails, what this means to me is that they are saying ŌĆ£leave me aloneŌĆØ. But website engagement is a different kettle of fish. Email marketing in reaction to website engagement, subtly using Behavioural Data increase relevance, are incredibly effective because they are relevant and timely.
- #8: This anonymised client graph depicts purchase data mapped against individuals engaged with email marketingŌĆ” to put is simply, if someone is opening and clicking email, they are far more likely to purchase.
- #9: And if you combine email and web engagement data, the impact is far more pronouncedŌĆ” All of this seems like common sense, ie to make a purchase you have to engage. But switch this around and look at it again. The most valuable use of engagement data is actually when you take and use engagement as an indication that someone is in the buying window. Hence, the straight forward supposition is that engagement is a an indication that a prospect needs to be converted. This then alters the whole communication strategy, It is at this stage that we must stop sending newsletters and offer driven email and start to use the next level of email marketing driven by engagement and Behavioural Data, to convert the customer.
- #10: Behavioural Data is was it says on the canŌĆ” data on customer/browser behaviour It is not RFM data, which segments customer by previous purchase history and thereby tries to predict future behavioural and propensity to purchase. Behavioural data is the next stage in the picture. WE used to say that the best guide to future behaviour was past behaviour. But now we can track and react to current behaviour through web analytics tracking at an individual level, this is no longer the case. Indeed, today the best guide to future behaviour is current, behavioural information.
- #11: With this data we can influence behaviour and the obvious application that it is put to is basket abandonment. Whereas the DMA Benchmark Report states that the benchmark open rate in Q3 2010 was 23%, behavioural email open rates are invariably 50%+. Why? Behavioural Data Makes Emails Highly Relevant.
- #12: So how does it all work? For the vast majority of ecommerce operations all media, including email, has the central aim of driving prospects and customers to your website, in achieving engagement. All visitors leave behind them valuable information. Take for instance [email_address] , who browses your site, looking at product X. On knowing this, your email system should automatically exclude Mr Bloggs from your ŌĆśone-size-fits-allŌĆÖ email to your base on Friday that offers 10% off of product Z. Instead, Mr Browser should drop into a personalised ŌĆśBrowser programme that takes into account 2 other important pieces of information. Firstly, at what stage the lifecycle strategy is Mr Bloggs? Is he a loyal customer, a single purchase customer, or perhaps a prospect who regularly browses? This data, retained in your online customer database, will support the next contact that you make with that customer. Also, at this stage you will need to draw in your behavioural data. What products has this customer browsed, on this visit or previously? Do they buy the same brand each time, or is this customer a serial abandoner? Many variables come into play at this stage, and individual businesses need to decide the hierarchy of variables applied to the message.
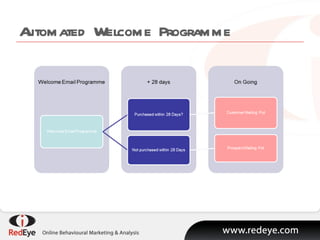
- #13: Building these automated behavioural programmes can be simple or complex. Start with a simple Welcome programme. In the diagram on the screen engagement data identifies which of two potential long term strategies a new customer will fall into.
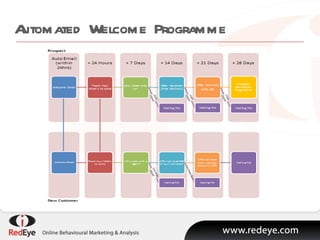
- #14: However, in my experience improved performance stats quickly lead marketers into developing more complex strategies. We work with customers who have between 20 and 50 variations on the welcome programme, addressing variable such as the source of the data and demographic details. Business rules are used to identify when an individual engages beyond the welcome programme. So, an individual who visits the website during the welcome programme can drop out into a browser programme. In this way, engaged individuals move between programmes , based on the lifecycle model, and are therefore receiving the most relevent emails at any stage of their journey.
- #16: But how can I use this approach to create a more relevant and profitable email strategy? For the sake of this presentation I want to consider 2 different lifecycles, the customer lifecycle and the product purchase lifecycle. The latter may vary in timescale between a day and a year for organisation such as low ticket ecommerce sites and insurers respectively. And the customer lifecycle can include many purchases or only one. I need to ask you to apply the thoughts in the next few slides to your own version of the customer and product lifecycle as it is not possible to propose a single, all encompassing lifecycle.
- #17: I raised earlier that there are now 2 divergent strategies that require our focus. In the first case, that of mailing to an opt-in subscriber base with the aim of achieving engagement, this I am refering to as Tactical. And the first stage of any tactical mailing is the Welcome Programme. Welcome programmes should introduce a new subscriber to the brand, set expectations as to what will be mailed to them and it avoids dumping an individual straight into a offer led newsletter mailing schedule. In this way, Welcome programmes reduce unsubscribes by raising brand values and ultimately improve customer lifetime value.
- #18: LetŌĆÖs look now at how Haven Holidays deals with key behavioural stages on itŌĆÖs site using email marketing. Firstly, Haven utilise behavioural search criteria to ensure that emails during the customer browser research period are as relevant as possible. Internal search criteria or holiday browsed data can can be pulled automatically into the dynamic templates. The results are excellent, of course. Version one of this programme was a static trigger. We knew that a visit had taken place. But when we modified the template to automatically pull in the behavioural data on search and browsed variables, the last click revenue performance increased by 61%.
- #19: Further on during the customer journey, the prospect has the opportunity to save a holiday that they have researched. Over the last 2 years, saved search, as you can see from the graph showing 2010 v 2011 data, is the fastest growing last click revenue stream for Haven. People ŌĆśs habits are changing. As a consumer, when you are researching a significant purchase like a holiday, you donŌĆÖt buy from the first email and individuals are unlikely to buy from irrelevant emails once they are engaged in the purchase process. However, engagement triggered behavioural emails are both timely and relevant and help push the customer through the purchasing process. Again with Saved Event Mailings, going from static triggers to behavioural triggers and implementing ongoing testin g plans has increased conversion on this behaviour programme by 96%.
- #20: Finally for today, Haven have implemented an extended basket abandonment programme. Rather than Having a static Basket Abandonment trigger, new templates and creative have been developed depending on what stage you drop off out of the booking process, the type of holiday and the specific holiday details. Again, the extension of this programme to take in more behavioural data has increase last click revenue by 556%
- #21: So, to maximise your strategy, you need to be able to bring together your email tool with a customer level database that is able to combine engagement and behavioural data back against existing customer data. With historic customer information defining the type of communication an individual receives, for instance a prospect mailing or a loyal customer mailing, then engagement data defines when to send and behavioural data defines the what, or the content.
- #22: In my allotted 25 minutes today I have tried to outline how Engagement and Behavioural strategies for email marketing can be built to manage customers throughout the majority of their customer lifecycle. Whatever stage of the lifecycle, automated programmes can be made relevant and profitable . But the key is that using these new techniques emails can be both automated therefore cheap and highly relevant, therefore profitable.
- #23: In my allotted 25 minutes today I have tried to outline how Engagement and Behavioural strategies for email marketing can be built to manage customers throughout the majority of their customer lifecycle. Whatever stage of the lifecycle, automated programmes can be made relevant and profitable . But the key is that using these new techniques emails can be both automated therefore cheap and highly relevant, therefore profitable.