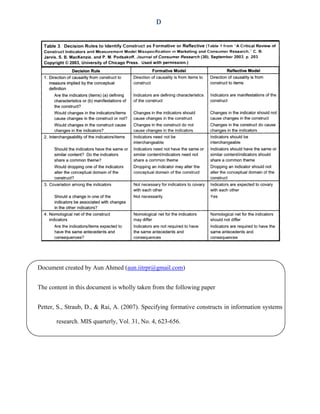
Reflective and formative constructs differences
- 1. Reflective, formative, and multidimensional constructs A. Definitions B. Diagrammatic representation C. Mathematical representation D. Decision rules to identify reflective/formative constructs A 1. Reflective construct When measures (also called indicators or items) are used to examine an underlying construct that is unobservable (i.e., a latent variable), the measures can be referred to as reflective indicators or effect indicators. The unobservable construct, which consists of the reflective indicators and the error term for each indicator, is called a reflective construct. 2. Formative construct Indicators that determine a construct are called causal or formative indicators. Constructs comprised of these causal indicators along with a disturbance term are called formative constructs or composite variables. 3. Multidimensional constructs Multidimensional constructs are constructs with more than one dimension, and each dimension can be measured using either reflective or formative indicator
- 2. B Structural models comprised of all reflective constructs are reflective models; however, if at least one construct within the model is formative, the model is considered to be a formative model
- 3. C
- 5. Document created by Aun Ahmed (aun.iitrpr@gmail.com) The content in this document is wholly taken from the following paper Petter, S., Straub, D., & Rai, A. (2007). Specifying formative constructs in information systems research. MIS quarterly, Vol. 31, No. 4, 623-656. D