Remote Sensing - The 5 Senses Enhanced
- 1. REMOTE SENSING THE 5 SENSES ENHANCED
- 2. WE WORK USING OUR FIVE SENSES TO TELL US ABOUT THE EARTH ŌĆó Sight ŌĆō observing a volcanic eruption ŌĆó Hearing ŌĆō sounds of a rockslide ŌĆó Touch ŌĆō pumice vs obsidian ŌĆó Taste ŌĆō salt ŌĆó Smell ŌĆō swamps ŌĆó HOW DO WE USE THESE IN A REMOTE WAY ŌĆō SENSING FROM FAR AWAY? This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
- 3. 1. TASTE AND SMELL ŌĆō MOUTH AND NOSE ŌĆó Taste and smell are combined because they use chemoreceptors ŌĆó Chemo ŌĆō chemical; Receptors ŌĆō receivers ŌĆó These 2 senses are combined to determine good versus bad ŌĆó Example ŌĆō Spoiled Milk or Memory Triggers This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
- 4. 1. TASTE AND SMELL ŌĆō MASS SPECTROMETER ŌĆó In geology we use what's called a Mass Spectrometer ŌĆó Acts like a nose when drilling ŌĆó Very sensitive to chemicals in the air ŌĆō AKA Very accurate Chemoreceptors ŌĆó These sensors allow us to detect helium, CO2, Nitrogen, and other elements
- 6. 1. TASTE AND SMELL ŌĆō MASS SPECTROMETER ŌĆó It can smell small changes in water, soil, etc. ŌĆó How long it takes for a body to use medicine ŌĆó Trace evidence for detectives ŌĆó Many applications to smell things our noses canŌĆÖt This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
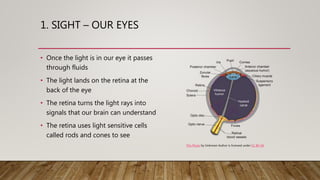
- 7. 1. SIGHT ŌĆō OUR EYES ŌĆó Once the light is in our eye it passes through fluids ŌĆó The light lands on the retina at the back of the eye ŌĆó The retina turns the light rays into signals that our brain can understand ŌĆó The retina uses light sensitive cells called rods and cones to see This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
- 8. 1. SIGHT - CAMERAS ŌĆó The lens is a glass plate that covers the opening to the camera body ŌĆó The lens directs from an object to the film when the shutter opens ŌĆó When you push the button on a camera, it opens a shutter, which is a lid that protects the film ŌĆó The shutter is like your eyelids, and when you open them, then the light comes in This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY
- 9. 1. SIGHT ŌĆō CAMERAS ON DRONES, ROVERS, SATELLITES ŌĆó Cameras mounted on a remote controlled drone ŌĆó Cameras also sent to space ŌĆó On satellites and rovers and probes sent to other planets ŌĆó We can see beyond what our eyes can see through remotely sensing sight This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
- 10. 1. SIGHT ŌĆō INCLUDES INFRARED, NIGHT VISION, ZOOMS ŌĆó Plants ŌĆó Fire ŌĆó Lost people ŌĆó Diseases / bugs
- 11. 1. HEARING ŌĆō OUR EARS ŌĆó The inner ear is shaped like a snail and is called the cochlea ŌĆó Inside the cochlea, there are thousands of tiny hair cells ŌĆó Hair cells change the vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain through the hearing nerve ŌĆó The brain tells you that you are hearing a sound and what kind of sound it is This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
- 12. 1. HEARING ŌĆō SEISMIC ŌĆó Electric vibrators or falling weights drop on the ground making a sound ŌĆó The sound waves are reflected off of different layers underground ŌĆó Measuring the time for the waves to get to a receiver (ear) ŌĆó Tells us what is underground
- 13. 1. HEARING - SEISMIC ŌĆó We use the listening trucks or geophones to measure along a line ŌĆó Going back and forth on many lines makes a picture that we can see ŌĆó This picture shows us what is underground
- 14. 1. HEARING - SEISMIC
- 15. 1. TOUCH ŌĆō OUR FINGERS AND HANDS ŌĆó Tell if something is hot or cold ŌĆó Dull or sharp ŌĆó Rough or smooth ŌĆó Receptors on your skin or nerves This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
- 16. 1. TOUCH ŌĆō WIRELINE LOGS ŌĆó Temperature ŌĆō hot or cold ŌĆó Type of fluid in rock (water or oil) ŌĆó Type of rock (lithology) and rock quality (porosity/permeability) ŌĆó Cracks or broken ŌĆó Touches the rock using different sensors at depth
- 17. Permeability? What Fluid? Type of Rock? Porosity?
- 18. THE END ŌĆō ANY QUESTIONS?