Renewable resources
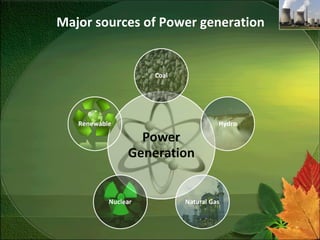
- 2. Major sources of Power generation
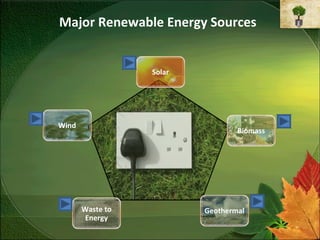
- 4. Major Renewable Energy Sources Solar Wind Biomass Waste to Geothermal Energy
- 5. Solar Energy That will be explained in the succeeding slide
- 6. Technology Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Photovoltaic (PV) It consists of â It consists of â âĒ Solar Collectors âĒ Turbine âĒSolar Arrays âĒ Generator & Transformer âĒ Inverter âĒ Cooling Tower âĒ Transformer
- 7. Future Technology â Solar-Hydrogen Revolution Usable Waste high-quality Heat energy Storage The and environment Solar light Transport Combustion Decomposition of water H Water Power 2H2 + O2 2H2O 2H2O 2H2 + O2 2 Vapor Plant
- 8. Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Sun does not shine All chemical and radioactive polluting byproducts of the consistently. thermonuclear reactions remain behind on the sun, Solar energy is a diffuse while only pure radiant energy source. To harness it, we reaches the Earth. must concentrate it into an amount and form that we can use, such as heat Energy reaching the earth is and electricity incredible. By one calculation, 30 days of Addressed by approaching sunshine striking the Earth the problem through: have the energy equivalent of 1) collection, the total of all the planetâs 2) conversion, fossil fuels, both used and 3) storage. unused!
- 9. Global & India scenario Global growth of Solar Power State-wise Power Generation 1.2% 8% 1.5% 2.2% MW 20.2% 66.9% Installed Capacity (as of 2011) : 979.4 MW Year
- 10. Indiaâs Leading Players in Solar Technology . . . . .
- 11. Other Applications Architecture & Agriculture & Solar Vehicles Water Urban Planning Horticulture Treatment Solar Sewage Solar Water Treatment Heating Solar Lighting Cooking
- 12. Biomass Energy It is organic material made from plants and animals (microorganisms). It contains stored energy from the sun. That will be explained in the succeeding slide
- 13. Process FOR COMBUSTION: BIOMASS FUEL + OXYGEN ï HEAT + WATER + CARBON DIOXIDE
- 14. Technology Feed Gas Drying Zone Distillation The main products Zone obtained from Biomass â Reduction âĒ Methane Gas Zone âĒ Ethanol Hearth Zone âĒ Biodiesel Air Ash Zone
- 15. Growth in Recent Times Present Installed Capacity in India List of Commissioned Biomass Projects (as of 31.03.11) 8.2% 8.75% 22.24% MW 13.64% 18.33% 13.71% 15.13% Year Indiaâs Potential (2012) : 25,000MW
- 17. Positives & Not-so Positives Pros Cons
- 18. Leading Players of Biomass Energy in India
- 19. Geothermal Energy That will be explained in the succeeding slide
- 20. Technology Average gradient: â 2.5 - 3.0oC / 100m Variation: â 1.0 - 25oC / 100m So if assuming average, temps at depth will be: 0m 15°C 2000 m 70°C 4000 m 120°C
- 21. Types of Geothermal Power Plants Dry steam Flash steam Binary steam
- 22. Interesting Facts about Geothermal Energy The Cerro Prieto Geothermal Power Station is the largest geothermal power station in the world. Geothermal production of energy is 3rd highest among renewable energies! In Iceland, Geothermal Energy provides âĒ86% of their space heating âĒ16% of their electricity generation Produces 5% of Californiaâs electricity, heats thousands of homes, greenhouses, office buildings.
- 23. Positives and Not-so Positives Pros Cons Useful minerals, such as zinc and silica, can be extracted from underground water. Brine can salinate soil Geothermal plants do not require a Extracting large amounts of water can lot of land, 400m2 can produce a cause land subsidence, and this can lead gigawatt of energy over 30 years. to an increase in seismic activity Geothermal electric plants production in Can release H2S, the ârotten eggsâ gas. 13.380 g of Carbon dioxide per kWh Geothermal plants can be online There is the fear of noise pollution 90%-100% of the time. during the drilling of wells
- 24. Direct Uses of Geothermal Energy Space Heating Melting Snow Drying Aquaculture Hot water Air Conditioning Industrial Processes Greenhouses Resorts and Pools
- 25. India Scenario Indian geothermal provinces have the capacity to produce 10,600 MW Exploration of Himalayan provinces could yield enormous geothermal energy India's fist Geothermal power plant with an initial capacity of 25 Megawatts will be coming up in Andhra Pradesh's Khammam district by 2012.
- 26. Major Players Global Companies Indian Companies
- 27. Waste to Energy That will be explained in the succeeding slide
- 28. Technology Different Processes Most WtE processes produce electricity directly through combustion, or produce a combustible fuel commodity, such as methane, methanol, ethanol or synthetic fuels
- 29. Future projects East Delhi Municipal Corporation to build two plants at Ghazipur of 16 MW and a capacity of 46 lakh metric tonnes Solar Bio Energy System commissioned its first Thermophillic Biomethanation plant in Solapur, Maharashtra of 4 MW and a capacity of 80 tonnes organic compost Tihar Jail ties up with BARC to produce biogas and manure from biodegradable kitchen waste
- 30. WtE in a nutshell Advantages Interesting Facts Commercial Aspects The majority of waste that Segregated municipal solid waste On average, one ton of is generally not available at the would normally go into waste produces 525 plant site landfill sites can be re-used kilowatt-hours (kWh) of The fuel is obtainable cheaply electricity Lack of financial resources with Municipal Corporations/Urban Reliable source of fuel Each year the average Local Bodies family throws away 1.5 Lack of conducive policy guidelines Disadvantages tons of rubbish from State Governments in respect Thousands of ton of of allotment of land, supply of WtE facilities are expensive Metal can be recovered garbage and power purchase / from the ash by recycling evacuation facilities The public at large is still unconvinced that WtE is free The efficiency of a waste-to-energy from harmful chemicals plant is 20 - 30 %.
- 31. Present Installed Capacity in India Total Capacity (2011) : 1683 MW 62 MW 191MW 73 MW 78 MW 176 MW 112 MW 151 MW 123 MW 131 MW 148 MW Itâs a new concept in the country Commercial technologies are required to be imported
- 32. Leading Companies in India
- 33. Wind Energy That will be explained in the succeeding slide
- 34. Technology Rotor Blade Tower Nacelle Rotor Hub Low-speed shaft Rotor Hub Gearbox High-speed shaft Transformer Brake Brake Generator
- 35. Techno-Commercial Aspects Cost Positives Types Energy Pay per Back Time! MW -Clean 1. Wind farms- -Renewable âĒ Onshore Very short âĒ Offshore 4.5- Not-so time. Just 5.25 Cr. Positives 2. Blades â 3-8 months, âĒ HAWT According to - Always canât âĒ VAWT American Wind run at 100 % Energy - Can be Noisy Association - Back up power might be required.
- 36. Wind Power growth in India Andhra Pradesh Wind Power Capacity (MW) 16,084 Rajasthan Karnataka Tamil Nadu 6007 MW Maharashtra Gujarat Year # Figures as of 31 March, 2011 Estimated Potential (MNRE) : 50,000 MW for 2011 Courtesy : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_power_in_India
- 37. Leading Players in Wind Power Technology 12.7 % 21.2 % 9% 3.6 % 8.7 % 6.3 % 7.4 % 8% 7.6 % 7.8 % 7.7 % SUZLONâs market share in India is approximately 50%
- 38. Government Policies Courtesy : http://www.eai.in/ref/ae/win/policies.html
- 39. India's power sector Problems Present Installed Capacity (as of Septâ12) 3% Total : 207850 MW 12 % 19 % 66 % Some Important facts Avg per Capita consumption (2009) : 288KWh India needs to add about 135 GW before 2017, to satisfy the projected demand Courtesy : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electricity_sector_in_India#Demand
- 40. A Short Video on the future of Renewable Energy Future of Renewable Energy
- 41. THANK YOU A Presentation by- Alok Gupta Gaurav Gautam Himanshu Kashyap Nimit Kaushik Sethuraman Arvind Iyer