Report
- 1. 0 | P a g e report RFID RFID ABSTRACT: Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is the wireless non-contact use of radio-frequency electromagnetic fields to transfer data, for the purposes of automatically identifying and tracking tags attached to objects BY ST : Abanoub Morris TO ENG: Hesham Bakry
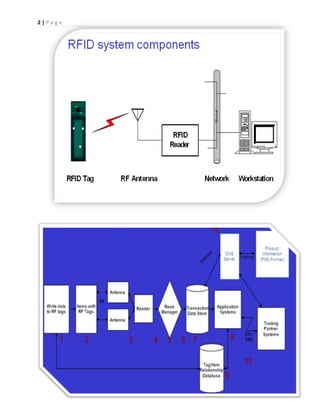
- 2. 1 | P a g e Effect on manufacturing  Need to ensure error-free, custom assembly  Need inventory of components for the various customization options  Critical Issues – Assembly process control – Inventory management – Supply chain integration – Customer insight  One solution: RFID  What is RFID?  RFID = Radio Frequency IDentification.  An ADC (Automated Data Collection) technology that:  uses radio-frequency waves to transfer data between a reader and a movable item to identify, categorize, track..  Is fast and does not require physical sight or contact between reader/scanner and the tagged item.  Performs the operation using low cost components.  Attempts to provide unique identification and backend integration that allows for wide range of applications.  Other ADC technologies: Bar codes, OCR
- 3. 2 | P a g e
- 4. 3 | P a g e RFID tag memory  Read-only tags • Can never be changed  Write once, read many (WORM) tags – Data written once, e.g., during packing or manufacturing • Similar to a compact disc or DVD  Read/Write – Tag data can be changed over time • Part or all of the data section can be locked
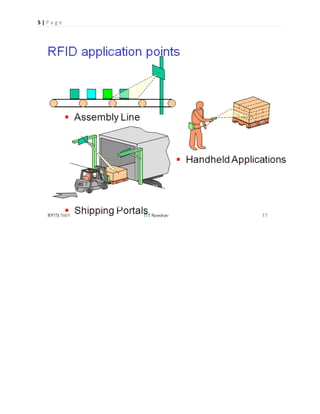
- 5. 4 | P a g e RFID readers  Reader functions: – Remotely power tags – Establish a bidirectional data link – Inventory tags, filter results – Communicate with networked server(s) – Can read 100-300 tags per second RFID applications  Manufacturing and Processing – Warehouse order fulfillment  Supply Chain Management – Logistics management  Retail – Auto checkout with reverse logistics  Security – Access control  Location Tracking – Traffic movement control and parking management
- 6. 5 | P a g e