Reporter gene and gene fusions T.Y.Bsc
Download as PPTX, PDF16 likes3,858 views
In this PPT You can learn briefly about Reporter Gene and Gene fusion And Gene manipulation method. Reference From Microbiology. Author - Brock. 12th Edition,
1 of 19
Downloaded 54 times


















Recommended
Co integrated vector



Co integrated vectorNirbhayAaditya
Ìę
In study of Ti plasmid based vector we study about co integrated vector and binary vector. Here i have tried to share basic about Co-integrated vectorDNA protein interaction.pptx



DNA protein interaction.pptxshwetaliprajapati
Ìę
DNA Protein interaction occur when a protein binds a molecule of DNA, often to regulate the biological function of DNA, usually the expression of a gene. DNA Protein interactions play very vital roles in any living cell. It controls various cellular processes which are very essential for living beings, viz. replication, transcription, recombination, DNA repair etc. There are several types of proteins found in a cell.Direct recognition occurs when the amino acid side chains of a protein interact with specific DNA bases.
Most protein-DNA interactions are mediated by direct physical interaction (hydrogen bonding or hydrophobic interactions) between the protein and the DNA base pairs.
DNA-binding proteins can be identified by many experimental techniques such as chromatin immunoprecipitation on microarrays, X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).Retrotransposons



RetrotransposonsAnamika Mazumdar
Ìę
Retrotransposons are genetic elements that copy and paste themselves throughout the genome using an RNA intermediate and reverse transcription. There are two main types: LTR retrotransposons, which mimic retroviruses through reverse transcription of an RNA copy into DNA; and non-LTR retrotransposons like LINEs and SINEs. LINEs (Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements) are autonomous retrotransposons over 6kb with endonuclease and reverse transcriptase proteins. SINEs (Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements) are shorter than 300bp and non-autonomous, relying on LINEs to reverse transcribe themselves.Open Reading Frames



Open Reading FramesOsama Zahid
Ìę
An open reading frame (ORF) is a part of a reading frame that contains no stop codons. ORFs are used as evidence to identify potential protein-coding genes in DNA sequences. The presence of a long ORF with codon usage matching the organism is used by some gene prediction algorithms to identify candidate protein-coding regions, but an ORF alone is not conclusive proof that a gene exists. Tools like ORF Finder, ORF Investigator, and ORF Predictor can be used to locate ORFs in DNA sequences.L21. techniques for selection, screening and characterization of transformants



L21. techniques for selection, screening and characterization of transformantsRishabh Jain
Ìę
This document discusses techniques for selecting and characterizing transformed cells containing recombinant DNA. Selectable marker genes allow transformed cells to survive in the presence of a selective agent, while reporter genes produce detectable gene products for identification. Common selectable markers include genes conferring resistance to neomycin or glyphosate. Common reporter genes encode enzymes like beta-galactosidase. Transformed clones can be identified through nucleic acid hybridization, PCR, or by detecting expressed protein products via techniques like western blotting.Reporter genes



Reporter genesAprajitaSharma15
Ìę
1) Reporter genes produce a detectable phenotype that allows transformed cells to be easily identified and selected. They are useful tools for studying gene expression.
2) Common reporter genes include GFP and luciferase, which produce fluorescent and luminescent proteins, respectively, that can be quantified.
3) Selectable marker genes, like antibiotic resistance genes, allow transformed cells to survive selective conditions that kill untransformed cells. This enables isolation of transformed cells.Exprssion vector



Exprssion vectorSushant Balasaheb Jadhav
Ìę
This presentation covers a general introduction to expression vector, its components, types, and its application. Then it covers some of the expression system with examples.Nucleases



Nucleasesbibianaantony
Ìę
Nucleases are enzymes that cut nucleic acids. There are two main types - endonucleases which cut within strands, and exonucleases which degrade strands from the ends. Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific recognition sequences. Key examples are EcoRI, HindIII, and BamHI. Ribonucleases degrade RNA and are divided into endo- and exoribonucleases. RNase A is a common example. Nucleases play important roles in DNA repair and RNA processing through their cleavage activities.Southern hybridization



Southern hybridizationAnushi Jain
Ìę
Southern blotting is a technique used to detect specific DNA sequences in a DNA sample. It involves extracting DNA from cells, cutting the DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes, separating the fragments via gel electrophoresis, transferring the DNA fragments to a membrane, and using a labeled probe to detect fragments that are complementary to the probe through hybridization. Southern blotting is useful for identifying mutations, DNA fingerprinting, and detecting DNA in applications like prenatal screening and forensics. While effective for detecting specific DNA sequences, it is a complex, time-consuming, and labor-intensive technique.Tumor formtion , ti ri plasmid , dna trnsfr.



Tumor formtion , ti ri plasmid , dna trnsfr.Sukirti Vedula
Ìę
This document summarizes information about tumor formation in plants caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes bacteria. It discusses how the Ti and Ri plasmids are transferred into plant cells, causing crown gall and hairy root diseases respectively. The Ti plasmid contains T-DNA which is integrated into the plant genome, inducing tumor formation and opine synthesis. DNA transfer techniques like electroporation, microprojectile bombardment, and microinjection are also summarized for introducing foreign genes into plant cells.Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression Vectors



Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression VectorsCharthaGaglani
Ìę
1. Cosmid vectors are hybrid vectors derived from plasmids that contain the cos site from bacteriophage lambda, allowing them to clone DNA fragments up to 40 kb in size.
2. Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are engineered yeast chromosomes that can clone very large DNA fragments, averaging 200-500 kb but up to 1 MB, taking advantage of yeast cell machinery.
3. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are DNA constructs based on fertility plasmids that can clone up to 300 kb fragments and address issues with YAC stability and recombination.Cloning vectors based on m13 and lambda bacteriophage



Cloning vectors based on m13 and lambda bacteriophageRashmi Rawat
Ìę
M13 bacteriophage vectors like M13mp1 were constructed by introducing the lacZ' gene into the intergenic region of M13. Later versions like M13mp2 and M13mp7 introduced additional restriction sites to allow for cloning.
Lambda bacteriophage vectors overcame limitations of lambda's genome size and multiple restriction sites. The non-essential region was deleted to increase capacity for foreign DNA. Natural selection was used to isolate lambda phages lacking unwanted restriction sites. Common lambda vectors include insertion vectors like gt10 that allow cloning into unique sites, and replacement vectors like EMBL4 that replace stuffer DNA between restriction sites.Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Transfer



Agrobacterium-mediated Gene TransferA Biodiction : A Unit of Dr. Divya Sharma
Ìę
An overview of the Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer process. Moreover, studied different kinds of Agrobacterium species are involved in this mechanism.
Agrobacterium is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria found mostly in the soil. It is a plant pathogen that is responsible for causing crown gall disease in them. This bacteria is also known as the natural genetic engineer because of it's the ability to integrate its plasmid Gene into the plant genome.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens transfer of their genetic material T-DNA of Ti-plasmid into the plant cell: A: Agrobacterium tumefaciens; B: Agrobacterium genome; C: Ti Plasmid : a: T-DNA , b: Vir genes , c: Replication origin , d: Opines catabolism genes; D: Plant cell
A Ti-Plasmid (tumor-inducing plasmid) is a ds, circular DNA that often, but not always. It's a piece of genetic equipment that transfers genetic material from bacterial cells means Agrobacterium tumefaciens into plant cells used to induce tumors in the plant. The Ti-plasmid is damage when Agrobacterium is grown above 28 °C. Such cured bacteria don't induce crown gall disease in the plant due to they are avirulent. The Ti-Plasmid are classified into two types on the basis of opine genes are present in T-DNA.
The Plasmid has 196 genes that code for 195 proteins. There is no one structural RNA. The plasmid is 206.479 nucleotides long. the GC content is 56% and 81% of the genetic material is coding genes.
The modification of this plasmid is a very important source in the production of transgenic plants.
The T-DNA must be cut out of the circular plasmid. A VirD1/D2 complex nicks the DNA at the left and right border sequences. The VirD2 protein is covalently attached to the 5' end. VirD2 contains a motif that leads to the nucleoprotein complex being targeted to the type IV secretion system (T4SS).
In the cytoplasm of the recipient cell, the T-DNA complex becomes coated with VirE2 proteins, which are exported through the T4SS independently from the T-DNA complex. Nuclear localization signals, or NLS, located on the VirE2 and VirD2 are recognized by the importin alpha protein, which then associates with importin beta and the nuclear pore complex to transfer the T-DNA into the nucleus. So that the T-DNA can integrate into the host genome.
We inoculate Agrobacterium containing our genes of interest, onto wounded plant tissue explants. The Agrobacterium then transfers the gene of interest into the DNA of the plant tissue.lambda cloning vector



lambda cloning vectorNOMI KhanS
Ìę
- Lambda bacteriophage cloning vectors were developed to overcome limitations in the size of DNA that could be inserted into unmodified lambda vectors.
- Segments of the non-essential lambda genome could be deleted to allow insertion of up to 18kb of new DNA while still allowing packaging.
- Natural selection was used to generate lambda strains lacking restriction sites, allowing restriction-based cloning.
- The first lambda vectors were insertion and replacement vectors, while later cosmids allowed cloning of fragments up to 52kb.Artificial chromosome



Artificial chromosomeSafali Gupta
Ìę
Artificial chromosomes can be constructed in vitro from defined DNA components to carry large DNA fragments stably like natural chromosomes. There are different types of artificial chromosomes including BACs, YACs, PACs, and HACs. BACs can carry up to 300 kbp of DNA and are useful for genome sequencing. YACs allow cloning of up to 500 kbp of foreign DNA in yeast cells but clones can be unstable. PACs derive from bacteriophage P1 and carry 100-300 kbp of DNA. HACs are human-sized artificial chromosomes that can act as new chromosomes in human cells, carrying therapeutic genes.2 d gel electrophoresis



2 d gel electrophoresisPiyush Ghoshe
Ìę
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on 2D electrophoresis. 2D electrophoresis is a technique used to separate mixed proteins based on their isoelectric point and mass. It involves two sequential electrophoretic steps: iso-electric focusing to separate proteins by charge, followed by SDS-PAGE to separate by molecular weight. The document describes the principles, methods, applications and references for 2D electrophoresis.Shuttle vector - a plasmid vector used in rDNA technology. 



Shuttle vector - a plasmid vector used in rDNA technology. neeru02
Ìę
Shuttle vectors are constructed so that they can propagate in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. They contain two origins of replication - one for each host cell type. YEp13 is an example of a shuttle vector that can replicate in yeast (eukaryotic) and E. coli (prokaryotic) cells. It contains sequences from the 2 micron yeast plasmid, including the LEU2 gene as a selectable marker, as well as sequences from the pBR322 plasmid which allow replication in E. coli. Shuttle vectors allow initial cloning experiments and selection to be done in E. coli before introducing the recombinant DNA into yeast cells.Artificial Vectors



Artificial VectorsArindam Ghosh
Ìę
Artificial vectors such as bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs), and human artificial chromosomes (HACs) can carry large DNA fragments for research purposes. BACs can hold up to 300kb of DNA and are used to sequence genomes. YACs can carry 500kb of DNA but are prone to rearrangement. HACs are separate microchromosomes that act as new chromosomes and can carry therapeutic genes for research including disease models.ENZYMES IN RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY



ENZYMES IN RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGYThippeswamy M
Ìę
DNA modifying enzymes play important roles in recombinant DNA technology. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA from deoxyribonucleotides and is essential for DNA replication. It consists of subunits that carry out polymerase and exonuclease activities. Reverse transcriptase generates cDNA from an RNA template. Alkaline phosphatase, phosphatase, kinase and methyltransferases modify DNA through addition or removal of phosphate groups or methyl groups and are used in cloning experiments and DNA sequencing. Terminal transferase adds nucleotides to DNA ends. Restriction enzymes are inhibited by DNA methylation.RFLP & RAPD



RFLP & RAPDArunima Sur
Ìę
This document provides information about molecular marker techniques RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) and RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA). RFLP is a non-PCR based technique that involves digesting genomic DNA with restriction enzymes, separating fragments via gel electrophoresis, and detecting variations. RAPD is a PCR-based technique that uses random primers to amplify random DNA segments, which are then separated and visualized. Both techniques can be used for genetic mapping, germplasm characterization, and other applications. Key differences between the two techniques include RFLP detecting fewer loci but being more reliable, requiring larger DNA quantities, and using species-specific probes.Electrophoretic mobility shift assay 



Electrophoretic mobility shift assay iqraakbar8
Ìę
This is technique used widely for protein separation from a mixture and is very easy and less costly method. șĘșĘߣs cover all essential points about EMSA and it is quite interesting to know that how it detect and separate different proteins and their mobility shift assay.
Ti plasmid



Ti plasmidVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
Ìę
The document summarizes key information about Ti plasmids, which are plasmids found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens that cause crown gall disease in plants. The Ti plasmid transfers a segment of DNA called T-DNA into the host plant genome, integrating genes that cause tumor formation. The plasmid has regions for T-DNA, virulence genes needed for transfer, and sometimes opine catabolism genes. Ti plasmids are used to create transgenic plants by replacing the tumor genes with a gene of interest in the T-DNA.TRANSPOSON TAGGING



TRANSPOSON TAGGINGMandeep Singh
Ìę
This document summarizes transposon tagging as a method to identify genes. Transposon tagging involves inserting a transposon near a gene of interest, which then allows the gene to be identified based on its proximity to the transposon. The document discusses different types of transposons used for tagging in plants and animals. It describes approaches for both targeted and non-targeted tagging and methods for identifying the tagged gene, including RFLP analysis and inverse PCR. As an example, it summarizes how the Cf-9 gene conferring resistance to leaf mold in tomato was identified using Ds transposon tagging.Screening and selection of recombinants 



Screening and selection of recombinants Kristu Jayanti College
Ìę
The document discusses various methods for screening and selecting recombinant cells. Direct selection methods include antibiotic resistance screening and blue-white color screening. Indirect selection methods include screening by nucleic acid hybridization, colony hybridization, immunological assays, and detecting protein/enzyme activity. These screening methods allow identification of recombinant cells that contain the gene of interest from a mixture of transformed cells.Site directed mutagenesis



Site directed mutagenesisArunima Sur
Ìę
Site-directed mutagenesis is a technique used to generate specific mutations in DNA at predetermined locations. It involves using a synthetic oligonucleotide primer containing the desired mutation to introduce changes into the DNA sequence during in vitro DNA replication or PCR. This allows researchers to study the effects of mutations and engineer proteins with improved or customized properties. Common methods for site-directed mutagenesis include using single or double primers, cassette mutagenesis by replacing DNA fragments, and PCR-based mutagenesis. The technique has various applications in investigating protein function and developing proteins for commercial uses.Dna shuffling



Dna shufflingamir hossein mohammadzadeh hosseini
Ìę
This document discusses the technique of DNA shuffling. It begins with a brief history of DNA shuffling, invented by Willem P.C. Stemmer in 1994. It then discusses the goal of DNA shuffling, which is to generate libraries of chimeric variants from related DNA sequences that can undergo directed evolution. Critical parameters for DNA shuffling include using a thermostable DNA polymerase and performing a fragmentation step using MnCl2 instead of MgCl2. Applications of DNA shuffling discussed include evolving improved enzymes, cytokines, antibodies, viral proteins, and vaccine candidates.Lambda vector



Lambda vectorkishoreGupta17
Ìę
A vector enabling cloning of large DNA size as compare to plasmid DNA and used to construct the genomic and C DNA libraryT dna & transposone tagging 1 (2)



T dna & transposone tagging 1 (2)Arunima Sur
Ìę
Gene tagging uses recognizable DNA fragments like T-DNA or transposons to disrupt gene function and identify genes responsible for mutant phenotypes. T-DNA tagging in plants involves random integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA that can disrupt genes and create mutants. Transposon tagging relies on the ability of transposons to move within genomes and disrupt gene function. Both techniques have been used successfully to isolate numerous plant genes involved in traits like color and development.Apollo Introduction for i5K Groups 2015-10-07



Apollo Introduction for i5K Groups 2015-10-07Monica Munoz-Torres
Ìę
This is an introduction to conducting manual annotation efforts using Apollo. This webinar was offered to members of the i5K Research community on 2015-10-07.Prokaryote genome



Prokaryote genomemonanarayan
Ìę
Bacterial genomes provide insights into bacterial function, origins, and diversity. They range in size from 0.6 to over 10 megabase pairs. Analysis of bacterial genomes reveals gene content and organization, as well as base pair composition trends. Bacterial chromosomes are typically circular and condensed via supercoiling, though some bacteria have linear or multiple chromosomes. Genome analysis techniques like GC skew help locate origins of replication.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Southern hybridization



Southern hybridizationAnushi Jain
Ìę
Southern blotting is a technique used to detect specific DNA sequences in a DNA sample. It involves extracting DNA from cells, cutting the DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes, separating the fragments via gel electrophoresis, transferring the DNA fragments to a membrane, and using a labeled probe to detect fragments that are complementary to the probe through hybridization. Southern blotting is useful for identifying mutations, DNA fingerprinting, and detecting DNA in applications like prenatal screening and forensics. While effective for detecting specific DNA sequences, it is a complex, time-consuming, and labor-intensive technique.Tumor formtion , ti ri plasmid , dna trnsfr.



Tumor formtion , ti ri plasmid , dna trnsfr.Sukirti Vedula
Ìę
This document summarizes information about tumor formation in plants caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes bacteria. It discusses how the Ti and Ri plasmids are transferred into plant cells, causing crown gall and hairy root diseases respectively. The Ti plasmid contains T-DNA which is integrated into the plant genome, inducing tumor formation and opine synthesis. DNA transfer techniques like electroporation, microprojectile bombardment, and microinjection are also summarized for introducing foreign genes into plant cells.Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression Vectors



Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression VectorsCharthaGaglani
Ìę
1. Cosmid vectors are hybrid vectors derived from plasmids that contain the cos site from bacteriophage lambda, allowing them to clone DNA fragments up to 40 kb in size.
2. Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are engineered yeast chromosomes that can clone very large DNA fragments, averaging 200-500 kb but up to 1 MB, taking advantage of yeast cell machinery.
3. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are DNA constructs based on fertility plasmids that can clone up to 300 kb fragments and address issues with YAC stability and recombination.Cloning vectors based on m13 and lambda bacteriophage



Cloning vectors based on m13 and lambda bacteriophageRashmi Rawat
Ìę
M13 bacteriophage vectors like M13mp1 were constructed by introducing the lacZ' gene into the intergenic region of M13. Later versions like M13mp2 and M13mp7 introduced additional restriction sites to allow for cloning.
Lambda bacteriophage vectors overcame limitations of lambda's genome size and multiple restriction sites. The non-essential region was deleted to increase capacity for foreign DNA. Natural selection was used to isolate lambda phages lacking unwanted restriction sites. Common lambda vectors include insertion vectors like gt10 that allow cloning into unique sites, and replacement vectors like EMBL4 that replace stuffer DNA between restriction sites.Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Transfer



Agrobacterium-mediated Gene TransferA Biodiction : A Unit of Dr. Divya Sharma
Ìę
An overview of the Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer process. Moreover, studied different kinds of Agrobacterium species are involved in this mechanism.
Agrobacterium is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria found mostly in the soil. It is a plant pathogen that is responsible for causing crown gall disease in them. This bacteria is also known as the natural genetic engineer because of it's the ability to integrate its plasmid Gene into the plant genome.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens transfer of their genetic material T-DNA of Ti-plasmid into the plant cell: A: Agrobacterium tumefaciens; B: Agrobacterium genome; C: Ti Plasmid : a: T-DNA , b: Vir genes , c: Replication origin , d: Opines catabolism genes; D: Plant cell
A Ti-Plasmid (tumor-inducing plasmid) is a ds, circular DNA that often, but not always. It's a piece of genetic equipment that transfers genetic material from bacterial cells means Agrobacterium tumefaciens into plant cells used to induce tumors in the plant. The Ti-plasmid is damage when Agrobacterium is grown above 28 °C. Such cured bacteria don't induce crown gall disease in the plant due to they are avirulent. The Ti-Plasmid are classified into two types on the basis of opine genes are present in T-DNA.
The Plasmid has 196 genes that code for 195 proteins. There is no one structural RNA. The plasmid is 206.479 nucleotides long. the GC content is 56% and 81% of the genetic material is coding genes.
The modification of this plasmid is a very important source in the production of transgenic plants.
The T-DNA must be cut out of the circular plasmid. A VirD1/D2 complex nicks the DNA at the left and right border sequences. The VirD2 protein is covalently attached to the 5' end. VirD2 contains a motif that leads to the nucleoprotein complex being targeted to the type IV secretion system (T4SS).
In the cytoplasm of the recipient cell, the T-DNA complex becomes coated with VirE2 proteins, which are exported through the T4SS independently from the T-DNA complex. Nuclear localization signals, or NLS, located on the VirE2 and VirD2 are recognized by the importin alpha protein, which then associates with importin beta and the nuclear pore complex to transfer the T-DNA into the nucleus. So that the T-DNA can integrate into the host genome.
We inoculate Agrobacterium containing our genes of interest, onto wounded plant tissue explants. The Agrobacterium then transfers the gene of interest into the DNA of the plant tissue.lambda cloning vector



lambda cloning vectorNOMI KhanS
Ìę
- Lambda bacteriophage cloning vectors were developed to overcome limitations in the size of DNA that could be inserted into unmodified lambda vectors.
- Segments of the non-essential lambda genome could be deleted to allow insertion of up to 18kb of new DNA while still allowing packaging.
- Natural selection was used to generate lambda strains lacking restriction sites, allowing restriction-based cloning.
- The first lambda vectors were insertion and replacement vectors, while later cosmids allowed cloning of fragments up to 52kb.Artificial chromosome



Artificial chromosomeSafali Gupta
Ìę
Artificial chromosomes can be constructed in vitro from defined DNA components to carry large DNA fragments stably like natural chromosomes. There are different types of artificial chromosomes including BACs, YACs, PACs, and HACs. BACs can carry up to 300 kbp of DNA and are useful for genome sequencing. YACs allow cloning of up to 500 kbp of foreign DNA in yeast cells but clones can be unstable. PACs derive from bacteriophage P1 and carry 100-300 kbp of DNA. HACs are human-sized artificial chromosomes that can act as new chromosomes in human cells, carrying therapeutic genes.2 d gel electrophoresis



2 d gel electrophoresisPiyush Ghoshe
Ìę
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on 2D electrophoresis. 2D electrophoresis is a technique used to separate mixed proteins based on their isoelectric point and mass. It involves two sequential electrophoretic steps: iso-electric focusing to separate proteins by charge, followed by SDS-PAGE to separate by molecular weight. The document describes the principles, methods, applications and references for 2D electrophoresis.Shuttle vector - a plasmid vector used in rDNA technology. 



Shuttle vector - a plasmid vector used in rDNA technology. neeru02
Ìę
Shuttle vectors are constructed so that they can propagate in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. They contain two origins of replication - one for each host cell type. YEp13 is an example of a shuttle vector that can replicate in yeast (eukaryotic) and E. coli (prokaryotic) cells. It contains sequences from the 2 micron yeast plasmid, including the LEU2 gene as a selectable marker, as well as sequences from the pBR322 plasmid which allow replication in E. coli. Shuttle vectors allow initial cloning experiments and selection to be done in E. coli before introducing the recombinant DNA into yeast cells.Artificial Vectors



Artificial VectorsArindam Ghosh
Ìę
Artificial vectors such as bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs), and human artificial chromosomes (HACs) can carry large DNA fragments for research purposes. BACs can hold up to 300kb of DNA and are used to sequence genomes. YACs can carry 500kb of DNA but are prone to rearrangement. HACs are separate microchromosomes that act as new chromosomes and can carry therapeutic genes for research including disease models.ENZYMES IN RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY



ENZYMES IN RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGYThippeswamy M
Ìę
DNA modifying enzymes play important roles in recombinant DNA technology. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA from deoxyribonucleotides and is essential for DNA replication. It consists of subunits that carry out polymerase and exonuclease activities. Reverse transcriptase generates cDNA from an RNA template. Alkaline phosphatase, phosphatase, kinase and methyltransferases modify DNA through addition or removal of phosphate groups or methyl groups and are used in cloning experiments and DNA sequencing. Terminal transferase adds nucleotides to DNA ends. Restriction enzymes are inhibited by DNA methylation.RFLP & RAPD



RFLP & RAPDArunima Sur
Ìę
This document provides information about molecular marker techniques RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) and RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA). RFLP is a non-PCR based technique that involves digesting genomic DNA with restriction enzymes, separating fragments via gel electrophoresis, and detecting variations. RAPD is a PCR-based technique that uses random primers to amplify random DNA segments, which are then separated and visualized. Both techniques can be used for genetic mapping, germplasm characterization, and other applications. Key differences between the two techniques include RFLP detecting fewer loci but being more reliable, requiring larger DNA quantities, and using species-specific probes.Electrophoretic mobility shift assay 



Electrophoretic mobility shift assay iqraakbar8
Ìę
This is technique used widely for protein separation from a mixture and is very easy and less costly method. șĘșĘߣs cover all essential points about EMSA and it is quite interesting to know that how it detect and separate different proteins and their mobility shift assay.
Ti plasmid



Ti plasmidVidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
Ìę
The document summarizes key information about Ti plasmids, which are plasmids found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens that cause crown gall disease in plants. The Ti plasmid transfers a segment of DNA called T-DNA into the host plant genome, integrating genes that cause tumor formation. The plasmid has regions for T-DNA, virulence genes needed for transfer, and sometimes opine catabolism genes. Ti plasmids are used to create transgenic plants by replacing the tumor genes with a gene of interest in the T-DNA.TRANSPOSON TAGGING



TRANSPOSON TAGGINGMandeep Singh
Ìę
This document summarizes transposon tagging as a method to identify genes. Transposon tagging involves inserting a transposon near a gene of interest, which then allows the gene to be identified based on its proximity to the transposon. The document discusses different types of transposons used for tagging in plants and animals. It describes approaches for both targeted and non-targeted tagging and methods for identifying the tagged gene, including RFLP analysis and inverse PCR. As an example, it summarizes how the Cf-9 gene conferring resistance to leaf mold in tomato was identified using Ds transposon tagging.Screening and selection of recombinants 



Screening and selection of recombinants Kristu Jayanti College
Ìę
The document discusses various methods for screening and selecting recombinant cells. Direct selection methods include antibiotic resistance screening and blue-white color screening. Indirect selection methods include screening by nucleic acid hybridization, colony hybridization, immunological assays, and detecting protein/enzyme activity. These screening methods allow identification of recombinant cells that contain the gene of interest from a mixture of transformed cells.Site directed mutagenesis



Site directed mutagenesisArunima Sur
Ìę
Site-directed mutagenesis is a technique used to generate specific mutations in DNA at predetermined locations. It involves using a synthetic oligonucleotide primer containing the desired mutation to introduce changes into the DNA sequence during in vitro DNA replication or PCR. This allows researchers to study the effects of mutations and engineer proteins with improved or customized properties. Common methods for site-directed mutagenesis include using single or double primers, cassette mutagenesis by replacing DNA fragments, and PCR-based mutagenesis. The technique has various applications in investigating protein function and developing proteins for commercial uses.Dna shuffling



Dna shufflingamir hossein mohammadzadeh hosseini
Ìę
This document discusses the technique of DNA shuffling. It begins with a brief history of DNA shuffling, invented by Willem P.C. Stemmer in 1994. It then discusses the goal of DNA shuffling, which is to generate libraries of chimeric variants from related DNA sequences that can undergo directed evolution. Critical parameters for DNA shuffling include using a thermostable DNA polymerase and performing a fragmentation step using MnCl2 instead of MgCl2. Applications of DNA shuffling discussed include evolving improved enzymes, cytokines, antibodies, viral proteins, and vaccine candidates.Lambda vector



Lambda vectorkishoreGupta17
Ìę
A vector enabling cloning of large DNA size as compare to plasmid DNA and used to construct the genomic and C DNA libraryT dna & transposone tagging 1 (2)



T dna & transposone tagging 1 (2)Arunima Sur
Ìę
Gene tagging uses recognizable DNA fragments like T-DNA or transposons to disrupt gene function and identify genes responsible for mutant phenotypes. T-DNA tagging in plants involves random integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA that can disrupt genes and create mutants. Transposon tagging relies on the ability of transposons to move within genomes and disrupt gene function. Both techniques have been used successfully to isolate numerous plant genes involved in traits like color and development.Similar to Reporter gene and gene fusions T.Y.Bsc (20)
Apollo Introduction for i5K Groups 2015-10-07



Apollo Introduction for i5K Groups 2015-10-07Monica Munoz-Torres
Ìę
This is an introduction to conducting manual annotation efforts using Apollo. This webinar was offered to members of the i5K Research community on 2015-10-07.Prokaryote genome



Prokaryote genomemonanarayan
Ìę
Bacterial genomes provide insights into bacterial function, origins, and diversity. They range in size from 0.6 to over 10 megabase pairs. Analysis of bacterial genomes reveals gene content and organization, as well as base pair composition trends. Bacterial chromosomes are typically circular and condensed via supercoiling, though some bacteria have linear or multiple chromosomes. Genome analysis techniques like GC skew help locate origins of replication.13-Transgenic crops and their molecular analysis.pptx



13-Transgenic crops and their molecular analysis.pptxGulab Devi Teaching Hospital, Lahore.
Ìę
This document discusses the molecular analysis of transgenic crops. Transgenic crops are genetically modified by inserting foreign genes through various methods like agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The molecular analysis techniques discussed include PCR to detect the presence of the foreign gene, Southern blotting to analyze gene integration patterns, Northern blotting and RT-PCR to examine gene expression at the RNA level, and Western blotting to detect expression of proteins encoded by the transgene. These techniques provide valuable data on the presence, integration, stability and expression of the transgene to evaluate transgenic crops for desired traits.Molecular basis of evolution and softwares used in phylogenetic tree contruction



Molecular basis of evolution and softwares used in phylogenetic tree contructionUdayBhanushali111
Ìę
This document discusses molecular evolution and software used for phylogenetic tree construction. It begins by defining molecular evolution as the process of mutation and selection at the molecular level. It then discusses different types of mutations that can occur in DNA and proteins, such as synonymous, nonsynonymous, nonsense, missense, and frameshift mutations. The document also discusses using molecular data to study evolution and reconstruct phylogenetic relationships. It describes several software programs used for phylogenetic tree construction, including EzEditor, BAli-Phy, Clustal Ï, BayesTraits, and fastDNAml, and provides brief summaries of their methods and purposes.Genetic Transformation of Maize: Conventional Methods and Precision Geno...



Genetic Transformation of Maize: Conventional Methods and Precision Geno...Ananya Sinha
Ìę
Genetic Transformation of Maize: Conventional Methods and Precision Genome Modification
This is a summary of the above chapter mentioned in "Biotechnology of Major Cereals".
The precision genome modification is defined majorly focused on comparing the conventional genome modification methods with the modern ones.Genomics(functional genomics)



Genomics(functional genomics)IndrajaDoradla
Ìę
description of functional genomics and structural genomics and the techniques involved in it and also decribing the models of forward genetics and techniques involved in it and reverse genetics and techniques involved in itIntroduction to Apollo: i5K E affinis



Introduction to Apollo: i5K E affinisMonica Munoz-Torres
Ìę
Apollo is a web-based application that supports and enables collaborative genome curation in real time, allowing teams of curators to improve on existing automated gene models through an intuitive interface. Apollo allows researchers to break down large amounts of data into manageable portions to mobilize groups of researchers with shared interests.
The i5K, an initiative to sequence the genomes of 5,000 insect and related arthropod species, is a broad and inclusive effort that seeks to involve scientists from around the world in their genome curation process, and Apollo is serving as the platform to empower this community.
This presentation is an introduction to Apollo for the members of the i5K Pilot Project on Eurytemora affinisEXPRESSION VECTORS and bacteriophage vectors.pptx



EXPRESSION VECTORS and bacteriophage vectors.pptxdoctoranushree14
Ìę
Expression vectors , their characteristics
phages used as vectorsGenetic transformation method in mammals cell by NIDHI MISHRA and tahura mari...



Genetic transformation method in mammals cell by NIDHI MISHRA and tahura mari...Tahura Mariyam Ansari
Ìę
this presentation includes method of gene transfer, factor that affect efficiency of gene transfer, fate of DNA in the recipient cells, autonomous replication vector and some other subtopics. Transcriptomics,techniqes, applications.pdf



Transcriptomics,techniqes, applications.pdfshinycthomas
Ìę
The analysis of global gene expression and transcription factor regulation, global approaches to alternative splicing and its regulation, long noncoding RNAs, gene expression models of signalling pathways, from gene expression to disease phenotypes, introduction to isoform sequencing, systematic and integrative analysis of gene expression to identify feature genes underlying human diseases.Regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes



Regulation of gene expression in eukaryotesKristu Jayanti College
Ìę
1) Eukaryotic gene expression is regulated at multiple levels including transcription, chromatin structure, post-transcriptional processing, and translation.
2) Regulation allows for adaptation and tissue-specific gene expression during development. Key differences from prokaryotes include the lack of operons and more complex regulation in eukaryotes.
3) Gene expression can be regulated short-term through transcriptional control, as seen in yeast galactose-utilizing genes, or long-term for development through mechanisms like chromatin remodeling.Dna mapping



Dna mappingSwathi Shetty
Ìę
This document provides information on various genetic mapping techniques. It discusses locus, genome, linked genes, genetic distance, and recombination frequency. It then describes genetic mapping and the different types of maps - genetic/linkage maps and physical maps. Genetic maps are based on recombination frequencies while physical maps use techniques like in situ hybridization. Restriction mapping and DNA footprinting are also summarized as methods to determine the order and location of genes and restriction sites on chromosomes. Transposable elements in eukaryotes are classified into Class I and II based on their mechanism of transposition via RNA intermediates or direct DNA-to-DNA movement.Forward and reverse genetics



Forward and reverse geneticsSachin Ekatpure
Ìę
This document discusses forward and reverse genetic approaches for understanding gene function. Forward genetics begins with a phenotype and identifies the underlying gene, while reverse genetics starts with a gene and determines its phenotype. Specific reverse genetic techniques described include large-scale random mutagenesis, homologous recombination, transposable element excision, RNA interference, genome editing using ZFNs/TALENs/CRISPR, and site-directed mutagenesis combined with transgenics. The document provides details on how each technique is used to alter genes and study their function.Gene_Expression.pptx



Gene_Expression.pptxBlackHunt1
Ìę
Regulation of gene expression allows organisms to benefit from efficiency, conserving energy and cell size. In prokaryotes, operons regulate groups of genes, turned on or off by repressors, activators, or inducers. Eukaryotes separate transcription and translation, introducing many regulatory mechanisms. These include epigenetic modifications, transcription factors, RNA processing, stability, and translation factors. Cancer arises from dysregulation of genes controlling cell growth, especially tumor suppressors and oncogenes.Gene expression



Gene expressionpavithra vinayak
Ìę
This document discusses genes and gene expression. It begins by defining genes as subunits of DNA that carry the genetic blueprint and code for specific proteins. It then explains that gene expression is the process by which genes are used to direct protein assembly. There are several mechanisms that regulate gene expression, including controlling transcription, RNA processing, translation, and more. Gene expression can be regulated positively or negatively. Key examples of gene regulation discussed are the lac and tryptophan operons in prokaryotes. The document also covers gene expression in eukaryotes and some of the control points involved.Transposons2.pptx



Transposons2.pptxRachana Choudhary
Ìę
transposon, class of genetic elements that can âjumpâ to different locations within a genome. Although these elements are frequently called âjumping genes,â they are always maintained in an integrated site in the genome. In addition, most transposons eventually become inactive and no longer move.1PROKARYOTIC GENE.pptx



PROKARYOTIC GENE.pptxMuhammadAli732496
Ìę
The document discusses genes in prokaryotes. It defines key terms like gene, prokaryotic gene, and operon. It explains that prokaryotic genes consist of a promoter region, RNA coding sequence, and terminator region. Gene expression involves transcription and translation processes that occur in the cytoplasm. Gene regulation is achieved through repressible and inducible operons like the trp and lac operons, which are controlled by repressor and activator proteins that bind to DNA in response to environmental stimuli.Gene knockout



Gene knockoutsamuel kwatia
Ìę
Gene knockout is a technique used to study gene function by inactivating genes in living organisms. It involves using gene targeting to disrupt a gene, preventing it from functioning normally. Researchers developed methods for knocking out genes in mice using embryonic stem cells, which won them the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. The basic process involves engineering a construct to disrupt a target gene, introducing it into embryonic stem cells, generating a knockout mouse, and studying the effects of the disrupted gene. Gene knockout is a valuable tool for biomedical research and understanding disease mechanisms.Genetic transformation method in mammals cell by NIDHI MISHRA and tahura mari...



Genetic transformation method in mammals cell by NIDHI MISHRA and tahura mari...Tahura Mariyam Ansari
Ìę
Recently uploaded (20)
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ìę
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatComprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
Ìę
đą Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
đŹ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
đ What Youâll Learn in This Presentation
â
History & Evolution of Antibiotics
â
Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
â
Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
â
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
â
Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
â
Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
â
Clinical Applications & Challenges.
đ Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
đ Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
đ Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!Bá» TEST KIá»M TRA GIởA KĂ 2 - TIáșŸNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUáșšN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bá» TEST KIá»M TRA GIởA KĂ 2 - TIáșŸNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUáșšN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ìę
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgDr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
Ìę
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
Ìę
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
Ìę
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ìę
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ìę
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comRRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
Ìę
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
Ìę
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo șĘșĘߣs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo șĘșĘߣsCeline George
Ìę
In this slide, weâll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
Ìę
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
Ìę
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningChapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
Ìę
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Bá» TEST KIá»M TRA GIởA KĂ 2 - TIáșŸNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUáșšN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bá» TEST KIá»M TRA GIởA KĂ 2 - TIáșŸNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUáșšN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ìę
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ìę
Reporter gene and gene fusions T.Y.Bsc
- 1. âą The Mandavi Education Society T.Y.Bsc(Microbiology) Krishna prajapati Teaching Assistance(Microbiology)
- 2. Reporter gene and gene fusions
- 3. Introduction âą DNA manipulation has revolutionary the study of gene regulation. âą A coading sequence from one source(the reporter)may be fused to a regulatory region from another source. âą Such gene fusions are often used in studying gene regulation especially where assaying the level of the natural gene product is difficult or time consuming. âą They may also be used to increase expression of desired gene product.
- 4. Reporter genes âą The key property of reporter gene is that it encodes a protein that is easy to detect and assay. âą Reporter gene are used for variety of purposes. âą They may used to report on the presence or absence of particular genetic elements(such as plasmid)or DNA inserted within the vector. âą They can also fused to other genes or to promoter of other genes so that gene expression can be studied.
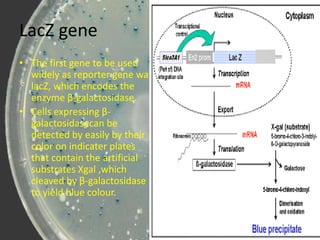
- 5. LacZ gene âą The first gene to be used widely as reporter gene was lacZ, which encodes the enzyme ÎČ-galactosidase. âą Cells expressing ÎČ- galactosidasecan be detected by easily by their color on indicater plates that contain the artificial substrates Xgal ,which cleaved by ÎČ-galactosidase to yield blue colour.
- 6. Blue white screening .
- 7. Conti..
- 8. Green flourescent protein(GFP) âą Another widely used reporter gene encodes luciferase. âą This enzymes makes cells expressing it luminescent. colonies containing the reporter system can be detected by on agar plate by their luminscense against a large background of other colonies.
- 9. Conti.. âą However,the expression of luciferase depends on more than one gene beacause several accesary factors are needed. âą By contrast, the green fluroscent protein needs no accessary factors and is widely used as reporter âą Gene for was GFP was originally cloned from the jelly Aequorea victoria,the GFP protein may be expressed in most bacterial cell. âą It is stable and causes little or no disruption of host cell metabolism.
- 10. Conti⊠⹠If expression of cloned gene linked to that of GFP, expression of GFP signals that the cloned gene has also been expressed. ⹠Recent advance in fluorescent labeling now allow the simultaneous use of multiple fluorescent markers.
- 11. Some like that..
- 12. Gene fusion.. âą It is possible to engineering construct that consist of segment from two different genes. âą such construct are known as gene fusions.
- 13. Conti.. âą If the promoter that controls a coding sequence is removed, the coding sequence can be fused to different regularly region to place the gene under the control of different promoter alternatively. âą The promoter region can be fused to gene whose product is east to assay.
- 14. There are two types of gene fusion Fig.. . Operon fusion âą In operon fusion, a coading sequence that retain its own translation start site and signals is fused to the transcriptional signals of another gene.
- 15. Gene fusion Protein fusion âą In protein fusion, two coading sequence are fused with the result that they share the same transcriptional and traslational start sites and signals. FigâŠ
- 16. ContiâŠ. âą Gene fusion are often used in studying gene regulation, especially if measuring the level of natural gene product is difficult and time consuming. âą The reulatery region of the gene of interest is fused to coding sequence for reporter gene, such as ÎČ- galactosidase or GFP. âą The reporter is then made under the condition that would trigger expression of the target gene. âą The expression of reporter is assay under variety of condition to determine how the gene of interest is regulated, where as protein fusion reveal translational cantrol.
- 18. Conti.. âą Gene fusion may also be used to test for the effect of regulatory genes. âą Mutation that effect regulatory genes are inroducted into cells carrying gene fusion, and expression is measured and compared to cell lacking the regulatory mutation. âą This allows the rapid screening of multiple regulatory genes that are suspected of controlling the target gene.







