Reproductive health lifecycle approach
- 1. REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH & LIFE CYCLE APPROACH -VIDDYANSH SRIVASTAVA viddyanshsrivastava223@gmail.com
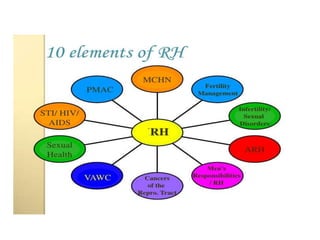
- 3. What is Reproductive health ? ŌĆó Reproductive health is ŌĆ£a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity, in all matters related to the reproductive system and to its functions and processes...ŌĆØ ŌĆó ŌĆ£The ability to reproduce and to regulate fertility, to go safely through reproductive events and to have sexual relations without the fear of disease or unwanted pregnancyŌĆØ
- 4. CONTŌĆ” ŌĆó The capacity to determine the number and spacing of births through the use of safe, effective, and acceptable contraceptive methods ŌĆó The capacity to terminate an unwanted pregnancy safely, legally and affordably; ŌĆó The capacity to conceive or to cause conception when a pregnancy is desired; ŌĆó The capacity to carry a wanted pregnancy to term and to deliver a healthy baby under safe conditions, including the postpartum period
- 5. CONTŌĆ” ŌĆó ŌĆóFreedom from reproductive tract infections (RTIs), including cancers of the reproductive tract, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and HIV/AIDS; ŌĆó ŌĆóThe capacity to breastfeed and to ensure the health and wellbeing of the new-born; ŌĆó ŌĆóFreedom from physical damage to the reproductive tract caused by childbirth, abortion or harmful traditional practices such as genital cutting
- 6. CONTŌĆ” ŌĆó ŌĆóFreedom from unwanted sexual relations and harmful or unwanted sexual practices, including violence and coercion within sexual relationships; ŌĆó ŌĆóThe capacity to enjoy and sustain sexual relations in a spirit of affection and partnership; ŌĆó ŌĆóA basic understanding of sexual and reproductive processes of both sexes and how they change throughout the life cycle, including physical and emotional aspects; ŌĆó ŌĆóFull access to appropriate and high quality reproductive health services.
- 8. AREAS OF CONCERNS AND MEASURE I. Bearing Children Safely II. Avoiding unwanted pregnancy III. Maintaining healthy reproductive system IV. Freedom from Sexual coercion and violence
- 10. LIFE CYCLE ŌĆó Human beings are born as infants and slowly go through stages before reaching adulthood. These stages are called a life cycle. ŌĆ£A life cycle is defined as the developmental stages that occur during an organism's lifetime. A life cycle ends when an organism diesŌĆØ
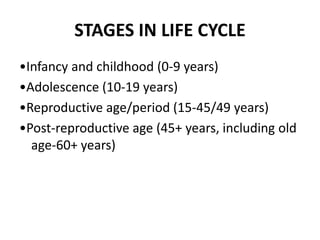
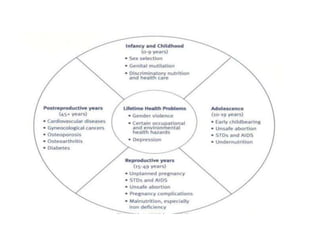
- 11. STAGES IN LIFE CYCLE ŌĆóInfancy and childhood (0-9 years) ŌĆóAdolescence (10-19 years) ŌĆóReproductive age/period (15-45/49 years) ŌĆóPost-reproductive age (45+ years, including old age-60+ years)
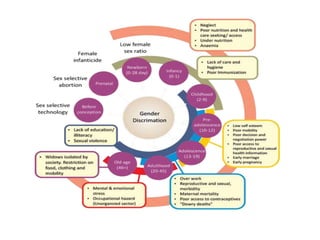
- 13. Infancy & childhood (0-9 yrs) ŌĆóSex selection (abortionŌĆ”) ŌĆóEducation ŌĆóGenital mutilation (FGM) ŌĆóDiscriminatory nutrition, groomingŌĆ” ŌĆóDiscriminatory health care ŌĆóEtcŌĆ”ŌĆ”
- 14. Adolescents (10-19 yrs) ŌĆóPhysiological changes in the body ŌĆóChild labour/work ŌĆóEarly marriage ŌĆóEarly child bearing ŌĆóAbortion ŌĆóInfection (disease, STIs/AIDs) ŌĆóUnder nutrition (anaemicŌĆ”.) ŌĆóAggression, sexual preferenceŌĆ”. ŌĆóViolence/abuse ŌĆóGender discrimination
- 15. Reproductive period/age (15-44 yrs) ŌĆó ŌĆóMarriage ŌĆōforced ŌĆ”ŌĆ” ŌĆó ŌĆóUnplanned pregnancy ŌĆó ŌĆóDiseases, STIs/AIDs ŌĆó ŌĆóAbortion, infertilityŌĆ”ŌĆ” ŌĆó ŌĆóPregnancy complications ŌĆó ŌĆóMalnutrition, growth ŌĆó ŌĆóChild bearing and rearing ŌĆó ŌĆóContraception ŌĆó ŌĆóAbuse and violence (domestic, outside homeŌĆ”) ŌĆó ŌĆóEtc, etcŌĆ”ŌĆ”
- 16. Post-Reproductive years (45+ yrs) ŌĆóCardio-vascular diseases ŌĆóGynecological cancers ŌĆóOsteoporosis/Osteoarthritis ŌĆóDiabetes ŌĆóCancers ŌĆóSexual dysfunction ŌĆóSub-fertility/infertility ŌĆóSTD/HIV ŌĆóMenopause etc ŌĆóAbuse, violence etc,
- 18. THANKYOU..!!!