Research assumptions, delimitations and limitations
- 1. Prof X Emerensia HOD in Child Health Nursing RVS College of Nursing, Sulur, Coimbatore
- 2. ? Assumptions are basically beliefs and ideas that we hold to be true ? Often with little or no evidence and are not statistically tested in research
- 3. Assumptions are statements that are taken for granted or are considered true, even though they have not been scientifically tested
- 4. ? Research Topic selection ? Theory under Investigation (Literature Review) ? Phenomenon under Investigation ? To conduct the study (Instrument, Methodology, Analysis) ? To present the Result (Level of Significance) ? Participants in the study
- 5. Example: ? Research is build upon assumptions ? Assumptions provide Basis to conduct the research study Information taken through Survey Interview
- 6. ? Assumptions listed in Research Paper may be Good sources of Research topics ? Tested assumptions through research studies expand professional body of knowledge
- 7. ASSUMPTIONS HYPOTHESIS Beliefs and ideas that we hold to be true Prediction With little or no evidence and not statistically tested in research Statistically tested and may be accepted or rejected Researchers attempt to discover the correlation Predicts relationship between variables and statistically tested to conclude the study Generally formulated through Qualitative, Descriptive and exploratory research studies and may be used in non cause-effect studies to guide research process Used in Quantitative studies where interplay of dependent and independent variables is investigated such as experimental and Correlational studies
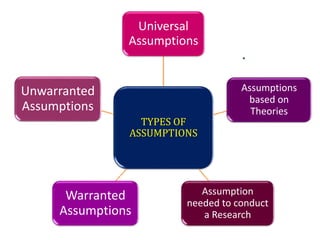
- 8. TYPES OF ASSUMPTIONS Universal Assumptions Assumptions based on Theories Assumption needed to conduct a Research Warranted Assumptions Unwarranted Assumptions
- 9. Universal Assumptions Beliefs that are assumed to be true by a large part of society, but testing such assumptions is not always possible Example: ? There is a supernatural power that governs this Universe
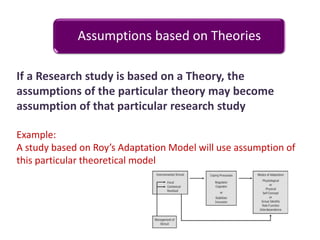
- 10. Assumptions based on Theories If a Research study is based on a Theory, the assumptions of the particular theory may become assumption of that particular research study Example: A study based on Roy¡¯s Adaptation Model will use assumption of this particular theoretical model
- 11. Assumption needed to conduct a Research Common sense assumptions may be developed to conduct a particular study Example: ? Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease is more common among Urban People as compared to Rural People ? Nursing care influences the recovery of patients
- 12. Warranted Assumptions Assumptions are stated along with evidence to support Example: ? Regular prayers bring success, because they boost morale
- 13. Unwarranted Assumptions Assumptions are stated without any supportive evidence Example: ? God exists everywhere in this universe
- 14. ASSUMPTION ¨C QUALITATIVE RESEARCH ? Concerned primarily with process, rather than outcomes/products ? Interested in meaning ¨C how people make sense of their lives, experiences, and life styles ?Primary Instrument for Data Collection and Analysis (Data are collected through the Human instrument, rather than through inventories, Questionnaires or machines)
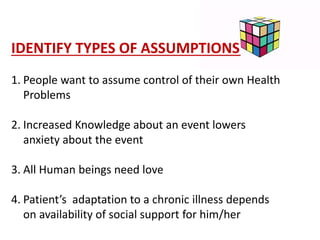
- 15. IDENTIFY TYPES OF ASSUMPTIONS 1. People want to assume control of their own Health Problems 2. Increased Knowledge about an event lowers anxiety about the event 3. All Human beings need love 4. Patient¡¯s adaptation to a chronic illness depends on availability of social support for him/her
- 16. ?Boundaries set by the Researcher before starting the study to clearly define the scope of the Study ?Mention in the initial chapter of Dissertation/Thesis
- 17. ?Weakness of the study ?Challenges faced by the researcher beyond his/her control ?Mention in the last chapter of Dissertation/Thesis
- 18. ? Control the range of the study ? Reduce the amount of time spent ? Clearly define and narrow down the scope of the study (Eg: Study might be delimited to secondary schools of a city or rural female students of a city) ? Make study feasible and practicable ?Identify the constraints or weaknesses of study and strengthening of evidences generated through the study
- 19. ?Through delimitation, readers can have an idea about credibility and Generalizability of research findings ?Define the boundaries of selected parameters such as Geographical location, Age, Gender, Population traits, Population size, Sample size, study instrument Variables Studied, Theoretical perspectives and other similar considerations
- 20. PHRASES THAT EXPRESS THE DELIMITATIONS AND LIMITATION ?The study does not cover the¡¡¡. ?This study is limited to ¡¡.. ?The researcher limited this research to¡¡.
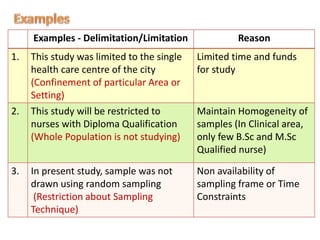
- 21. Examples - Delimitation/Limitation Reason 1. This study was limited to the single health care centre of the city (Confinement of particular Area or Setting) Limited time and funds for study 2. This study will be restricted to nurses with Diploma Qualification (Whole Population is not studying) Maintain Homogeneity of samples (In Clinical area, only few B.Sc and M.Sc Qualified nurse) 3. In present study, sample was not drawn using random sampling (Restriction about Sampling Technique) Non availability of sampling frame or Time Constraints
- 22. Examples - Delimitation/Limitation Reason 4. In Present study, locally published studies were considered for literature review and for discussion of study findings (Literature will not reviewed) Inability to access International Literature 5. In Present study, randomized control trial design was not used (Methodological Procedures not used) Quasi nature of independent variable 6. Researcher was limited to data collected through telephonic method (Particular Tools not used) Limited Time for study 7. Researcher limited the follow-up of patients for only 5 days (Things researcher not doing) Hospital protocol (Patients who underwent laparotomy are discharged on 5th postoperative day)
- 24. ?They restrict the ability of research findings to generalize because of the use of specific theoretical concepts in study ?Or Limiting the study variables through operational definitions
- 25. They usually result from some methodological factors such as ? Unrepresentative sample ? Weak design ? Single setting ? Limited control over extraneous variables ? Poor implementations of treatment protocol ? Research tool with limited reliability and validity ? Poor data collection procedure ? Ineffective use of statistical analysis
- 26. GUIDELINESFOR WRITING DELIMITATIONS ? Describe each delimitation in detailed but concise terms ? Explain reason for not considering certain parameters in study ? Mention why a particular delimitation is considered for a research study ? Clearly explain the reason for not considering certain parameter in study ? Identify and mention the intended impact of each delimitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of a study
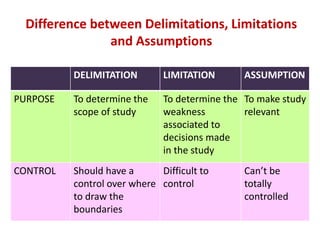
- 27. Difference between Delimitations, Limitations and Assumptions DELIMITATION LIMITATION ASSUMPTION PURPOSE To determine the scope of study To determine the weakness associated to decisions made in the study To make study relevant CONTROL Should have a control over where to draw the boundaries Difficult to control Can¡¯t be totally controlled