1 of 9
Download to read offline








Recommended
PMP PPT.pptx



PMP PPT.pptxfatumaabdinour
Ìý
The document outlines a performance management process (PMP) with the following key steps:
1) Setting organizational goals and cascading them to departments and teams.
2) Planning phase where managers collaborate with employees to set objectives, identify training needs, and develop SMART goals.
3) Execution phase where progress is monitored regularly through feedback meetings.
4) Assessment and review phases where performance is evaluated against objectives and development plans are updated.Common analysis measures used in human resources management



Common analysis measures used in human resources managementSeta Wicaksana
Ìý
This document discusses common analysis measures used in human resources management. It describes measures for workforce planning, performance and productivity, costs, organizational performance, regulatory compliance, organization design and development, leadership ability, learning and development, and attraction and recruitment. For each area, it lists specific metrics that are used to measure and analyze aspects of human resources and organizational performance.course of Performance monitoring for employee



course of Performance monitoring for employeeMoulid Abdirahman Ali
Ìý
Prepared by Moulid Abdirahman Ali PMS - Unit 3.pptx



PMS - Unit 3.pptxYogesh Daudkhane
Ìý
Performance monitoring involves appraising employee performance on an ongoing basis to ensure goals are met and competencies are developed. It is done through maintaining performance records, identifying key performance indicators, and conducting periodic reviews. The objectives of performance monitoring include fulfilling tasks and goals on time, improving employee performance, and facilitating career development through continuous learning. The process involves using written reports, scheduled meetings, and on-site inspections to gather information on employee performance.Performance Monitoring for all managers and health workers in leadership pos...



Performance Monitoring for all managers and health workers in leadership pos...wiremba
Ìý
iremba wilfred
is a tutor of Mulago School of Nursing and Midwifery.Performance Monitoring for managers (1).pptx



Performance Monitoring for managers (1).pptxwiremba
Ìý
all from Iremba Wilfred
A tutor at mulago school of nursing and midwiferyResult orientation



Result orientationZaffar Khan Academic CIPD
Ìý
The document discusses result orientation and performance management. It defines result orientation as focusing on outcomes rather than processes, and using the most effective processes. Performance management is defined as collaboratively planning, monitoring, and reviewing employee goals and contributions. An effective performance management system has features like setting goals, providing feedback, training, and supporting organizational strategy. It also discusses the performance management cycle and contributions and disadvantages of performance management systems. Finally, it outlines 14 characteristics of an ideal performance management system, such as being congruent with strategy, specific, reliable, and ethical.Pm performance and_value_list_of_measures



Pm performance and_value_list_of_measuresOmair Mustafa
Ìý
This document provides a comprehensive list of measures that can be used to determine the value and performance of project management. It begins by outlining goals of implementing a project management measurement system, such as identifying the business impact of improvement initiatives. The document then lists over 30 potential measures across categories like financial, customer, project processes, and learning and growth. It provides summaries of the top 10 benchmarking measures, differences between performance and value measures, and examples of measures specific to distributed project management and IT organizations.Performance Management



Performance ManagementSheetal Wagh
Ìý
Introduction to Performance Management - Meaning, Process, Need, Difference between Performance Appraisal and Performance Management, Components of Performance Management SystemPerformance Appraisal.pptxfinal.pptx FINAL HRMOB.pptx2024.pptx



Performance Appraisal.pptxfinal.pptx FINAL HRMOB.pptx2024.pptxjhemykamanas
Ìý
The document discusses performance appraisals, which are regular reviews of an employee's job performance that are conducted in a systematic way. Performance appraisals are important for encouraging positive performance, satisfying employee curiosity, employee development, and justifying pay raises and promotions. When designing a performance appraisal system, considerations include the frequency of reviews, associated costs, linking pay to reviews, setting goals, developing evaluation forms, and selecting evaluators such as managers, peers, customers. Legal issues and potential errors in appraisal systems are also discussed.a1b0c0d2-c613-4f77-bc49-f0eeb304e8f2.pptx



a1b0c0d2-c613-4f77-bc49-f0eeb304e8f2.pptxNeelamBhatt11
Ìý
Performance management is a means of improving organizational, team, and individual performance by aligning goals and managing performance according to organizational strategy. It involves setting clear targets and goals, measuring performance against these goals, providing feedback, and addressing any performance issues. Key aspects of performance management include planning, monitoring, reviewing performance and development, as well as rating and rewarding performance. An effective performance management system aims to improve employee and organizational performance.Performance Management rev 1.pptx



Performance Management rev 1.pptxFreelance Consultant
Ìý
For presentation design on powerpoint kindly visit links below and message for more details:
http://pph.me/masroorkhan
https://www.fiverr.com/masroorahmedkha
https://www.guru.com/freelancers/masroor-ahmed-khan
Training and Development



Training and DevelopmentPadmasinh Patil
Ìý
This document outlines the key steps in the performance appraisal process and how it can be used to establish an effective employee evaluation system. It discusses identifying training needs, setting objectives, measuring performance, providing feedback, and evaluating results. When using performance appraisal for the construction industry specifically, the document recommends focusing on key performance indicators like project timelines, costs, and quality. It also emphasizes regular communication, training opportunities, and celebrating successes to boost employee motivation.Hr metrics



Hr metricsashwini sakpal
Ìý
In this ppt, you will understand what is HR Metrics and how it is used in all HR Functions. How the metrics are calculated with formulas is mentioned in the ppt with the simplest explanation. PPT on implementing Kirkpatrickk Model



PPT on implementing Kirkpatrickk ModelShobitash Jamwal
Ìý
This document discusses implementing an effectiveness measurement tool for training and development (T&D) programs using Microsoft Excel. It outlines Kirkpatrick's four-level model for evaluating T&D programs and describes a sample process using reaction, learning, and behavior forms to measure effectiveness at each stage. Key steps include collecting scores from participant reaction forms after training, learning forms one month post-training, and behavior forms from line managers. The tool calculates scores at each stage and marks programs as effective or ineffective based on pre-set thresholds. Screenshots demonstrate the tool's layout and color-coded results.enhancing and rewarding performance



enhancing and rewarding performancePreeti Bhaskar
Ìý
Establishing the performance management system
Establishing reward and pay plans,
Employee benefits
Ensuring a safe and healthy work environment,
ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptx



ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptxhossam kachwar
Ìý
This document discusses concepts related to total quality management (TQM) including definitions, approaches, and differences from ISO 9001. It provides definitions of TQM from various sources that emphasize continuous improvement, meeting customer needs, and involving all employees. It describes the historical development of quality approaches from quality inspection to quality assurance systems to TQM. It also discusses concepts related to improving organizational performance including types of performance and comparative excellence approaches. Key differences between TQM and ISO 9001 are outlined. The document stresses that while TQM was important, the new focus is on institutional excellence driven by innovation and quality.Performance management 



Performance management Bitha Anoj
Ìý
This document discusses performance management and the roles of various parties involved. It outlines the key steps in developing an effective performance evaluation system, including creating evaluation forms, setting performance measures, providing feedback guidelines, and establishing disciplinary procedures. It emphasizes that performance evaluations should be conducted fairly and consistently using standardized forms and measures. The roles of top managers, line managers, and employees are also summarized. Top managers are responsible for setting goals and culture, while line managers implement policies and need proper training. Employees should actively participate in the performance management process.Job Satisfaction - Measurement & Importance.



Job Satisfaction - Measurement & Importance.AmandaBvera
Ìý
This presentation speaks about job satisfaction. It covers the concept of measurement of job satisfaction and covers a few important measures of job satisfaction including the selection of an appropriate measure of job satisfaction. It also includes features and importance of job satisfaction. Easy to read and understand.Indukaka ipcowala instiutute of management



Indukaka ipcowala instiutute of managementIIIM
Ìý
The report discusses performance management and defines it as a strategic approach to improving employee and organizational performance. It outlines the key aspects of an effective performance management process including setting clear expectations, regularly monitoring performance, providing feedback, evaluating results, and rewarding good performance. The goals of performance management are to increase communication, clarify goals and responsibilities, identify and address performance issues, and provide the basis for personnel decisions. An effective performance management system that engages employees can help an organization achieve its long-term and short-term goals.57827159 mu-0016



57827159 mu-0016sanjeeta03
Ìý
The aims of performance management are to assist in achieving work standards, identifying employee skills, ensuring goals are met, providing feedback, and evaluating company performance. The process of defining expectations involves reviewing role profiles, discussing key result areas and targets, and agreeing on required competencies and behaviors. The characteristics of performance appraisal are that they must match job descriptions, be legally compliant, involve trained appraisers, and include follow-up after the appraisal is conducted.Performance Evaluation revised.ppt



Performance Evaluation revised.pptChandanaAbeyesekera
Ìý
This document provides an overview of performance evaluation (PE) concepts and processes. It defines PE, discusses its purposes, and outlines the key steps in conducting PE. Some common PE methods are described, including graphic rating scales, multiple choice, and MBO. The document emphasizes developing objective criteria and standards to evaluate employees fairly. It also notes potential evaluator biases and suggests designing separate PE forms and procedures tailored for different employee groups.Unit IV Performance Management 4 LHs..pptx



Unit IV Performance Management 4 LHs..pptxAgniDharParajuli5
Ìý
Performance management is a continuous process that aligns employee goals with organizational objectives. It includes setting performance standards, providing feedback and development, and conducting performance appraisals. The goal is to create an environment where employees can perform to their highest abilities in a way that supports organizational goals. Performance appraisals evaluate employee strengths, weaknesses, and potential on a periodic basis. They provide the basis for decisions around promotion, pay, training, and termination.Individual performance commitment_and_review_form_(ipcrf)_for_teachers



Individual performance commitment_and_review_form_(ipcrf)_for_teacherstitserchriz Gaid
Ìý
The document is a form used by the Department of Education of the Philippines (DepEd) for its results-based performance management system. It consists of four parts: Part I evaluates employees' accomplishments of key results areas and objectives; Part II evaluates competencies; Part III summarizes ratings for discussion; and Part IV identifies development plans. The form aims to link individual achievements to organizational goals, promote growth, and allow open discussion of expectations between employees and supervisors.PEOPLE METRICS.pptx



PEOPLE METRICS.pptxGenelleSoriano
Ìý
This document discusses key people metrics that organizations use to track human capital and measure HR initiatives. It outlines three important metrics: employee turnover rate, percentage of response to open positions, and employee satisfaction. Employee turnover rate is calculated based on the number of employees who left over a period of time compared to total employees. The percentage of response to open positions indicates how well jobs are being exposed. Employee satisfaction is measured through surveys to understand employee happiness, growth opportunities, rewards, and team support. Tracking these people metrics helps organizations understand and improve their human resources practices.week 1 SP23.pptx



week 1 SP23.pptxiqbal394476
Ìý
This document discusses teaching methodology and performance management. It includes:
1. An outline of a class on teaching practices that engages students through communication, assignments, diagrams, practice, and presentations.
2. An agenda for a week 1 HR class that covers strategy, AI and HR, performance overview, and assessments.
3. An overview of the performance management process including planning, execution, assessment, review, and renewal of goals. Key aspects like feedback, documentation, and development are discussed.PM-UNIT-1.pptx



PM-UNIT-1.pptxpratiksha817967
Ìý
This document provides an overview of performance management. It defines performance management as involving thinking through various facets of performance, identifying critical dimensions, planning, reviewing, developing, and enhancing performance. It discusses the evolution of performance management from early appraisal systems to its current focus on development. Key aspects covered include objectives like boosting performance, objectives of an ideal system like strategic congruence and validity, and challenges like linking rewards to performance.More Related Content
Similar to Research Operational definition and scales.pptx (20)
Pm performance and_value_list_of_measures



Pm performance and_value_list_of_measuresOmair Mustafa
Ìý
This document provides a comprehensive list of measures that can be used to determine the value and performance of project management. It begins by outlining goals of implementing a project management measurement system, such as identifying the business impact of improvement initiatives. The document then lists over 30 potential measures across categories like financial, customer, project processes, and learning and growth. It provides summaries of the top 10 benchmarking measures, differences between performance and value measures, and examples of measures specific to distributed project management and IT organizations.Performance Management



Performance ManagementSheetal Wagh
Ìý
Introduction to Performance Management - Meaning, Process, Need, Difference between Performance Appraisal and Performance Management, Components of Performance Management SystemPerformance Appraisal.pptxfinal.pptx FINAL HRMOB.pptx2024.pptx



Performance Appraisal.pptxfinal.pptx FINAL HRMOB.pptx2024.pptxjhemykamanas
Ìý
The document discusses performance appraisals, which are regular reviews of an employee's job performance that are conducted in a systematic way. Performance appraisals are important for encouraging positive performance, satisfying employee curiosity, employee development, and justifying pay raises and promotions. When designing a performance appraisal system, considerations include the frequency of reviews, associated costs, linking pay to reviews, setting goals, developing evaluation forms, and selecting evaluators such as managers, peers, customers. Legal issues and potential errors in appraisal systems are also discussed.a1b0c0d2-c613-4f77-bc49-f0eeb304e8f2.pptx



a1b0c0d2-c613-4f77-bc49-f0eeb304e8f2.pptxNeelamBhatt11
Ìý
Performance management is a means of improving organizational, team, and individual performance by aligning goals and managing performance according to organizational strategy. It involves setting clear targets and goals, measuring performance against these goals, providing feedback, and addressing any performance issues. Key aspects of performance management include planning, monitoring, reviewing performance and development, as well as rating and rewarding performance. An effective performance management system aims to improve employee and organizational performance.Performance Management rev 1.pptx



Performance Management rev 1.pptxFreelance Consultant
Ìý
For presentation design on powerpoint kindly visit links below and message for more details:
http://pph.me/masroorkhan
https://www.fiverr.com/masroorahmedkha
https://www.guru.com/freelancers/masroor-ahmed-khan
Training and Development



Training and DevelopmentPadmasinh Patil
Ìý
This document outlines the key steps in the performance appraisal process and how it can be used to establish an effective employee evaluation system. It discusses identifying training needs, setting objectives, measuring performance, providing feedback, and evaluating results. When using performance appraisal for the construction industry specifically, the document recommends focusing on key performance indicators like project timelines, costs, and quality. It also emphasizes regular communication, training opportunities, and celebrating successes to boost employee motivation.Hr metrics



Hr metricsashwini sakpal
Ìý
In this ppt, you will understand what is HR Metrics and how it is used in all HR Functions. How the metrics are calculated with formulas is mentioned in the ppt with the simplest explanation. PPT on implementing Kirkpatrickk Model



PPT on implementing Kirkpatrickk ModelShobitash Jamwal
Ìý
This document discusses implementing an effectiveness measurement tool for training and development (T&D) programs using Microsoft Excel. It outlines Kirkpatrick's four-level model for evaluating T&D programs and describes a sample process using reaction, learning, and behavior forms to measure effectiveness at each stage. Key steps include collecting scores from participant reaction forms after training, learning forms one month post-training, and behavior forms from line managers. The tool calculates scores at each stage and marks programs as effective or ineffective based on pre-set thresholds. Screenshots demonstrate the tool's layout and color-coded results.enhancing and rewarding performance



enhancing and rewarding performancePreeti Bhaskar
Ìý
Establishing the performance management system
Establishing reward and pay plans,
Employee benefits
Ensuring a safe and healthy work environment,
ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptx



ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptxhossam kachwar
Ìý
This document discusses concepts related to total quality management (TQM) including definitions, approaches, and differences from ISO 9001. It provides definitions of TQM from various sources that emphasize continuous improvement, meeting customer needs, and involving all employees. It describes the historical development of quality approaches from quality inspection to quality assurance systems to TQM. It also discusses concepts related to improving organizational performance including types of performance and comparative excellence approaches. Key differences between TQM and ISO 9001 are outlined. The document stresses that while TQM was important, the new focus is on institutional excellence driven by innovation and quality.Performance management 



Performance management Bitha Anoj
Ìý
This document discusses performance management and the roles of various parties involved. It outlines the key steps in developing an effective performance evaluation system, including creating evaluation forms, setting performance measures, providing feedback guidelines, and establishing disciplinary procedures. It emphasizes that performance evaluations should be conducted fairly and consistently using standardized forms and measures. The roles of top managers, line managers, and employees are also summarized. Top managers are responsible for setting goals and culture, while line managers implement policies and need proper training. Employees should actively participate in the performance management process.Job Satisfaction - Measurement & Importance.



Job Satisfaction - Measurement & Importance.AmandaBvera
Ìý
This presentation speaks about job satisfaction. It covers the concept of measurement of job satisfaction and covers a few important measures of job satisfaction including the selection of an appropriate measure of job satisfaction. It also includes features and importance of job satisfaction. Easy to read and understand.Indukaka ipcowala instiutute of management



Indukaka ipcowala instiutute of managementIIIM
Ìý
The report discusses performance management and defines it as a strategic approach to improving employee and organizational performance. It outlines the key aspects of an effective performance management process including setting clear expectations, regularly monitoring performance, providing feedback, evaluating results, and rewarding good performance. The goals of performance management are to increase communication, clarify goals and responsibilities, identify and address performance issues, and provide the basis for personnel decisions. An effective performance management system that engages employees can help an organization achieve its long-term and short-term goals.57827159 mu-0016



57827159 mu-0016sanjeeta03
Ìý
The aims of performance management are to assist in achieving work standards, identifying employee skills, ensuring goals are met, providing feedback, and evaluating company performance. The process of defining expectations involves reviewing role profiles, discussing key result areas and targets, and agreeing on required competencies and behaviors. The characteristics of performance appraisal are that they must match job descriptions, be legally compliant, involve trained appraisers, and include follow-up after the appraisal is conducted.Performance Evaluation revised.ppt



Performance Evaluation revised.pptChandanaAbeyesekera
Ìý
This document provides an overview of performance evaluation (PE) concepts and processes. It defines PE, discusses its purposes, and outlines the key steps in conducting PE. Some common PE methods are described, including graphic rating scales, multiple choice, and MBO. The document emphasizes developing objective criteria and standards to evaluate employees fairly. It also notes potential evaluator biases and suggests designing separate PE forms and procedures tailored for different employee groups.Unit IV Performance Management 4 LHs..pptx



Unit IV Performance Management 4 LHs..pptxAgniDharParajuli5
Ìý
Performance management is a continuous process that aligns employee goals with organizational objectives. It includes setting performance standards, providing feedback and development, and conducting performance appraisals. The goal is to create an environment where employees can perform to their highest abilities in a way that supports organizational goals. Performance appraisals evaluate employee strengths, weaknesses, and potential on a periodic basis. They provide the basis for decisions around promotion, pay, training, and termination.Individual performance commitment_and_review_form_(ipcrf)_for_teachers



Individual performance commitment_and_review_form_(ipcrf)_for_teacherstitserchriz Gaid
Ìý
The document is a form used by the Department of Education of the Philippines (DepEd) for its results-based performance management system. It consists of four parts: Part I evaluates employees' accomplishments of key results areas and objectives; Part II evaluates competencies; Part III summarizes ratings for discussion; and Part IV identifies development plans. The form aims to link individual achievements to organizational goals, promote growth, and allow open discussion of expectations between employees and supervisors.PEOPLE METRICS.pptx



PEOPLE METRICS.pptxGenelleSoriano
Ìý
This document discusses key people metrics that organizations use to track human capital and measure HR initiatives. It outlines three important metrics: employee turnover rate, percentage of response to open positions, and employee satisfaction. Employee turnover rate is calculated based on the number of employees who left over a period of time compared to total employees. The percentage of response to open positions indicates how well jobs are being exposed. Employee satisfaction is measured through surveys to understand employee happiness, growth opportunities, rewards, and team support. Tracking these people metrics helps organizations understand and improve their human resources practices.week 1 SP23.pptx



week 1 SP23.pptxiqbal394476
Ìý
This document discusses teaching methodology and performance management. It includes:
1. An outline of a class on teaching practices that engages students through communication, assignments, diagrams, practice, and presentations.
2. An agenda for a week 1 HR class that covers strategy, AI and HR, performance overview, and assessments.
3. An overview of the performance management process including planning, execution, assessment, review, and renewal of goals. Key aspects like feedback, documentation, and development are discussed.PM-UNIT-1.pptx



PM-UNIT-1.pptxpratiksha817967
Ìý
This document provides an overview of performance management. It defines performance management as involving thinking through various facets of performance, identifying critical dimensions, planning, reviewing, developing, and enhancing performance. It discusses the evolution of performance management from early appraisal systems to its current focus on development. Key aspects covered include objectives like boosting performance, objectives of an ideal system like strategic congruence and validity, and challenges like linking rewards to performance.ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptx



ورشة عمل إدارة الجودة الشاملة(برنامج تطوير القدرات المؤسسية).pptxhossam kachwar
Ìý
More from skshamshad1 (19)
Assessment very important for business management students



Assessment very important for business management studentsskshamshad1
Ìý
very important for management students Business-Research-Methods-1.ppt, Nature of research



Business-Research-Methods-1.ppt, Nature of researchskshamshad1
Ìý
Research is very important these days for all industriesOrganizational change and forces of change and resistance to change



Organizational change and forces of change and resistance to changeskshamshad1
Ìý
Resistance to change and its importance in organizationsBRM 29 july.pptx.. Introduction to Resra



BRM 29 july.pptx.. Introduction to Resraskshamshad1
Ìý
Importance of business research and its role in enhancing business effectivenessRecently uploaded (20)
Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ºÝºÝߣs



Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ºÝºÝߣsCeline George
Ìý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on accounting access rights in odoo 18. To ensure data security and maintain confidentiality, Odoo provides a robust access rights system that allows administrators to control who can access and modify accounting data. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ìý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxIntellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
Ìý
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
Ìý
In this slide we’ll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
Ìý
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
Ìý
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
Ìý
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHInterim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
Ìý
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
Ìý
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningRRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
Ìý
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ìý
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ìý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ìý
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ìý
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatChapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
Ìý
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
Ìý
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
✅ Soft Tissue Therapy – The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
✅ Sports Taping Techniques – Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
✅ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia – A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ìý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ìý
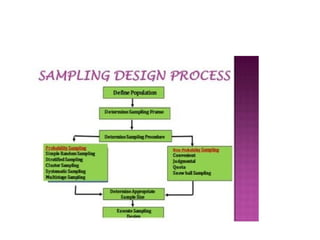
Research Operational definition and scales.pptx
- 1. Operational definition • Operational definitions in management specify the exact procedures or criteria used to measure or assess concepts or variables. • They are crucial for ensuring clarity and consistency in managing processes and evaluating performance
- 2. Examples Employee Productivity: • Operational Definition: Employee productivity is measured as the number of units produced or tasks completed per hour of work. For example, if an employee completes 50 reports in an 8-hour workday, their productivity is 6.25 reports per hour.
- 3. Example 1 Customer Satisfaction: • Operational Definition: Customer satisfaction is measured using a survey with a 1-5 rating scale, where 1 represents "very dissatisfied" and 5 represents "very satisfied." The average score from these surveys over a quarter determines the overall customer satisfaction rating.
- 4. Example 2 Project Completion Time: • Operational Definition: Project completion time is the total number of calendar days from the project start date to the final approval date. For example, if a project starts on January 1 and is approved on February 15, the completion time is 45 days.
- 5. Example 3 Employee Turnover Rate: • Operational Definition: Employee turnover rate is calculated by dividing the number of employees who leave the company (voluntarily or involuntarily) during a year by the average number of employees during that year, then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if 10 employees leave out of an average of 100 employees, the turnover rate is 10%.
- 6. Example 4 Employee Engagement: • Operational Definition: Employee engagement is measured through a survey with questions about employees’ emotional commitment to their work and the organization, such as their willingness to put in extra effort, their connection to company values, and their intention to stay with the company. The engagement score is the average of responses on a scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) on statements related to engagement.
- 7. OD • Operational definitions are crucial because they ensure that everyone understands and uses terms in the same way, which helps maintain clarity and consistency in management related processes and applications.
- 8. • Reliability ensures consistency and repeatability of results. • Validity ensures accuracy and relevance of the measurement.


















