Reservoir Modeling with Petrel
- 1. RESERVOIR MODELING WITH PETREL 2009.1.1 AND SIMULATION RUN WITH FRONTSIM Presented by Adeeba Rahman Setu 1007006 Supervised by Mr. Tareq-Uz-Zaman Assistant Professor Department of Petroleum & Mining Engineering
- 2. SELECTED FIELD Saldanadi Gas Field, Bangladesh
- 3. INTRODUCTION Importance of Reservoir Modeling o For new fields, 3D models may help development of the wells by identifying  the number of wells required,  the optimal completion of wells,  the present and future needs for artificial lift and  the expected production of oil, water and gas. o For already developed fields  to locate new well to increase oil and gas production
- 4. ï‚¢ Modeling a reservoir with Petrel ï‚¢ Interpretation of seismic data for pick horizons for delineating seismic horizon ï‚¢ Identifying faults in the area of study ï‚¢ Delineating structure for the purpose of reservoir modeling ï‚¢ To correlate wire-line log and seismic data ï‚¢ To create simulation of a reservoir model ï‚¢ Simulation run with FrontSim ï‚¢ History matching OBJECTIVES OF STUDY
- 5. WHY SOFTWARE IS USED IN THE THESIS? ï‚¢ Analytical methods generally cannot capture all the details of the given reservoir or process. ï‚¢ In modern reservoir engineering, they are generally used as screening or preliminary evaluation. ï‚¢ Reservoir simulation models are used by oil and gas companies in the development of new fields. ï‚¢ Models are used in developed fields where production forecasts are needed to help make investment decisions. ï‚¢ Improvements in simulation software have lowered the time to develop a model.
- 6. PREVIOUS MODELS DONE BY PETREL ï‚¢ Hugoton field (Hugoton and Panoma in Kansan and Guymon-Hugoton in Oklahoma) ï‚¢ Norne offshore Field ï‚¢ Sand bodies in reservoir in the Mumbai Offshore Basin ï‚¢ Beani Bazar Gas Field (Bangladesh) ï‚¢ Saldanadi Gas field etc. (Bangladesh)
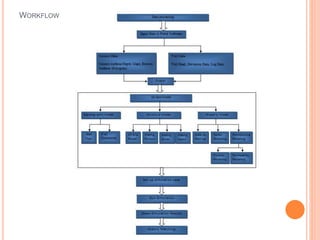
- 7. WORKFLOW
- 8. COLLECTED DATA ï‚¢ Seismic Data ï‚¢ Well Head Data ï‚¢ Deviation Data ï‚¢ Wireline Log Data ï‚¢ Petrophysical Data ï‚¢ Production Data
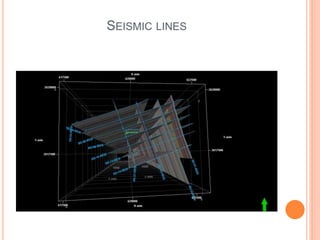
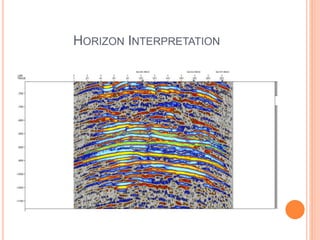
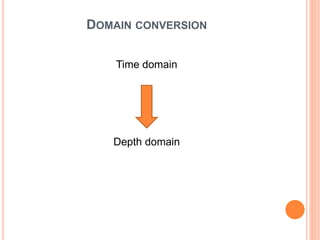
- 10. GEOPHYSICS ï‚¢ Seismic Interpretation ï‚— Seismic lines Interpretation ï‚— Horizon Interpretation ï‚— Fault interpretation ï‚¢ Domain conversion
- 11. SEISMIC LINES
- 13. FAULT INTERPRETATION ï‚¢ In the structure of this study there is no fault identified but as a requirement of Petrel software a fault has been interpreted.
- 14. DOMAIN CONVERSION Time domain Depth domain
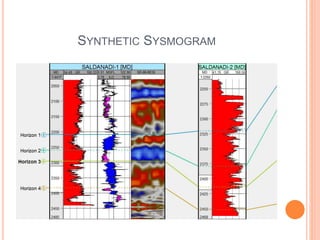
- 15. STRATIGRAPHIC MODELING ï‚¢ Well Correlation ï‚¢ Making Well Tops ï‚¢ Synthetic Seismogram
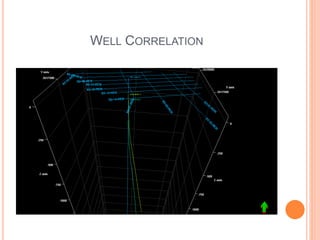
- 16. WELL CORRELATION
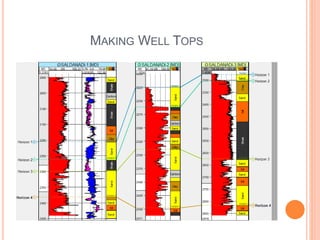
- 17. MAKING WELL TOPS
- 19. STRUCTURAL MODELING ï‚¢ Fault modeling ï‚¢ Pillar gridding ï‚¢ Making horizons ï‚— Making zones and layers ï‚— Making contacts
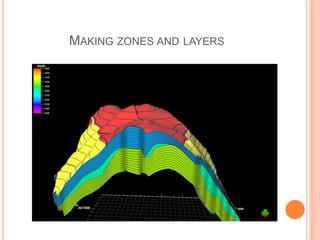
- 20. MAKING ZONES AND LAYERS
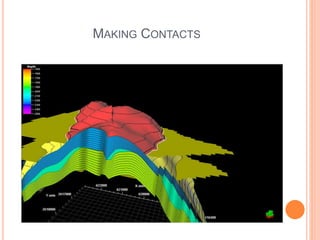
- 21. MAKING CONTACTS
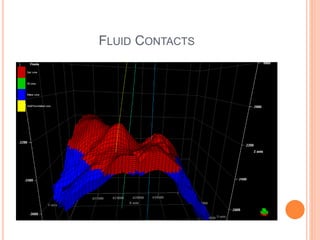
- 22. FLUID CONTACTS
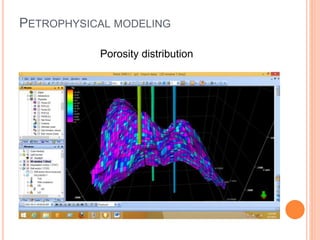
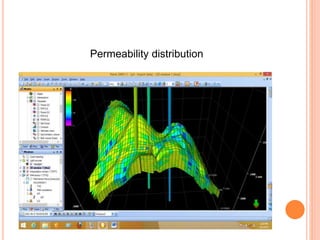
- 23. PROPERTY MODELING ï‚¢ Scale up well logs ï‚¢ Data analysis ï‚— Discrete data analysis ï‚— Continuous data analysis ï‚¢ Facies modeling ï‚¢ Petrophysical modeling
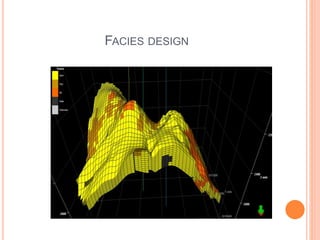
- 24. FACIES DESIGN
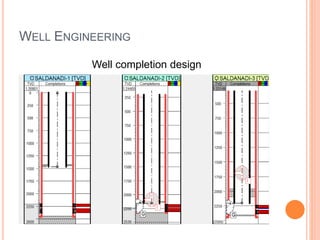
- 27. WELL ENGINEERING Well completion design
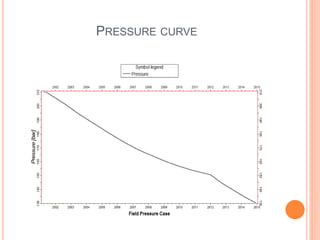
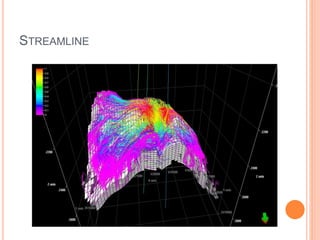
- 28. SIMULATION ï‚¢ Simulation results ï‚— Initial condition of different properties ï‚— Saturation function ï‚— Pressure decline curve ï‚— Streamline
- 29. SIMULATION RESULTS Initial condition of different properties
- 30. PRESSURE CURVE
- 31. STREAMLINE
- 32. HISTORY MATCHING Field Gas Production Rate Matching
- 33. Saldanadi-2 Gas Production Rate Matching
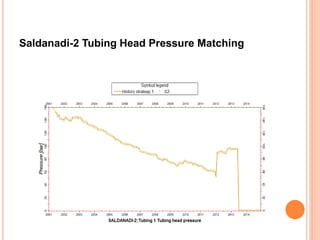
- 34. Saldanadi-2 Tubing Head Pressure Matching
- 35. CONCLUSION In previous a static model was developed on this structure. A dynamic model along with simulation run has been developed in my thesis work. Further to develop this reservoir: ï‚¢ More attention should be given on new well drilling study. ï‚¢ It is recommended to carry out 3D seismic survey before attempting any further drilling campaign over Saldanadi field.
- 36. THANK YOU ALL…