Respiratory system2
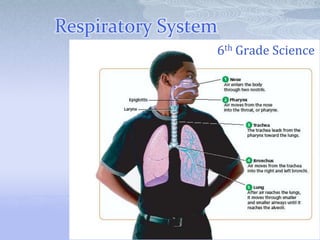
- 1. Respiratory System 6th Grade Science
- 2. I. Function A. Take in oxygen from air B. Remove carbon dioxide C. Provides Energy for all cells D. Smell E. Water balance F. Communication
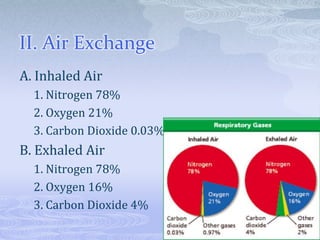
- 3. II. Air Exchange A. Inhaled Air 1. Nitrogen 78% 2. Oxygen 21% 3. Carbon Dioxide 0.03% B. Exhaled Air 1. Nitrogen 78% 2. Oxygen 16% 3. Carbon Dioxide 4%
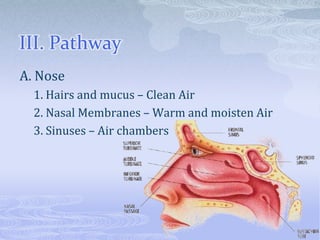
- 4. III. Pathway A. Nose 1. Hairs and mucus – Clean Air 2. Nasal Membranes – Warm and moisten Air 3. Sinuses – Air chambers
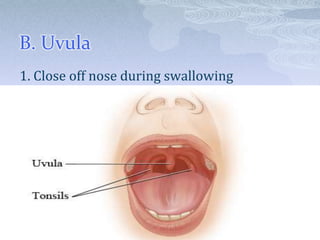
- 5. B. Uvula 1. Close off nose during swallowing
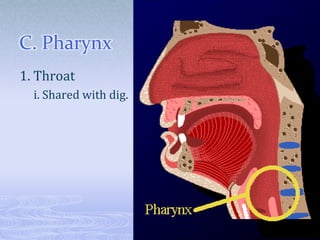
- 6. C. Pharynx 1. Throat i. Shared with dig.
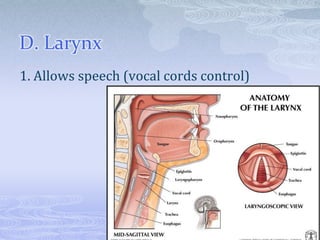
- 7. D. Larynx 1. Allows speech (vocal cords control)
- 8. E. Trachea 1. Wrapped in cartilage ring to keep open 2. Cilia to sweep stuff out of lungs i. Bring up to pharynx for swallowing ii. Contract violently if irritated – sneeze
- 9. F. Bronchi 1. Branches into each lung 2. Continued until reached end
- 10. G. Alveoli 1. Tiny sacs for gas exchange i. Oxygen into blood ii. Carbon dioxide into alveoli 2. Numbers – 300 million 3. Area – 7 meters2
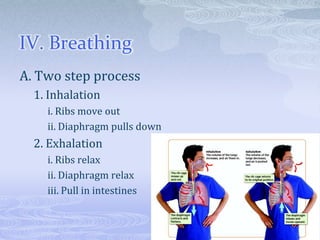
- 11. IV. Breathing A. Two step process 1. Inhalation i. Ribs move out ii. Diaphragm pulls down 2. Exhalation i. Ribs relax ii. Diaphragm relax iii. Pull in intestines
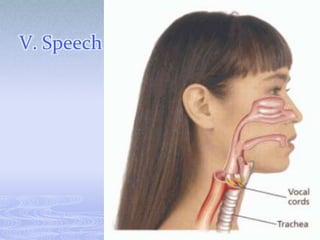
- 12. V. Speech
- 13. VI. Damage and Disease A. Smoking 1. ~1,100 deaths every day 2. 4,000 different chemicals i. Tar – Chemicals that coat airways ii. Carbon Monoxide – Replaces oxygen in blood iii. Nicotine – Addictive stimulant
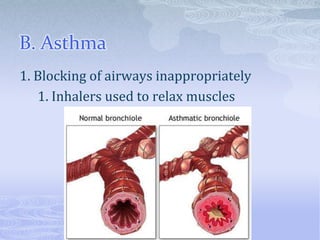
- 14. B. Asthma 1. Blocking of airways inappropriately 1. Inhalers used to relax muscles
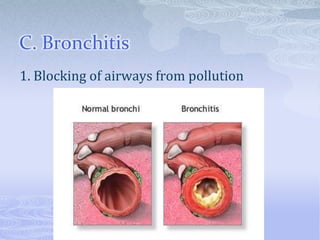
- 15. C. Bronchitis 1. Blocking of airways from pollution
- 16. E. Emphysema 1. Lung damage – No gas exchange
- 17. F. Lung Cancer 1. 400 people each day 2. 53 cancer chemicals in cigarettes
- 18. G. Atherosclerosis 1. Tar chemicals harden arteries i. Smokers have twice as many heart attacks