RESTful API (ru/en)
- 2. REPRESENTATIONAL STATE TRANSFER RoyThomas FieldingŌĆ© http://www.ics.uci.edu/~’¼üelding/pubs/dissertation/ ’¼üelding_dissertation.pdf
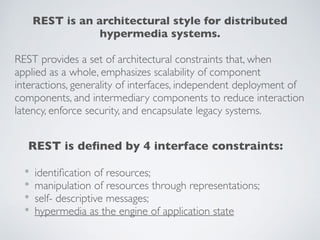
- 3. REST is an architectural style for distributed hypermedia systems. REST provides a set of architectural constraints that, when applied as a whole, emphasizes scalability of component interactions, generality of interfaces, independent deployment of components, and intermediary components to reduce interaction latency, enforce security, and encapsulate legacy systems. REST is de’¼üned by 4 interface constraints: * identi’¼ücation of resources; * manipulation of resources through representations; * self- descriptive messages; * hypermedia as the engine of application state
- 5. ąŻąĀą×ąÆąØąś 0,1,2 * ą×ą┐ąĖčüą░ąĮąĖąĄ čĆąĄčüčāčĆčüąŠą▓ * ąÜą╗ąĖąĄąĮčé ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčé ąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗąĄ HTTP ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗čŗ * ąĪąĄčĆą▓ąĄčĆ ąŠčéą▓ąĄčćą░ąĄčé HTTP Statue Codes * Content Negotiation
- 6. ąŻąĀą×ąÆąĢąØą¼ 3 * ą×ą▒ąĮą░čĆčāąČąĄąĮąĖąĄ čüąĄčĆą▓ąĖčüąŠą▓ č湥čĆąĄąĘ ąŠčéąĮąŠčłąĄąĮąĖčÅ * ąōąĖą┐ąĄčĆč鹥ą║čüč鹊ą▓čŗąĄ č乊čĆą╝ą░čéčŗ (html, HAL, JSON-LD ŌĆ”) * ąĀąĄčüčāčĆčüčŗ ąĮąĄ ą▓ą░ąČąĮčŗ, ą▓ą░ąČąĮčŗ ąĖčģ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖčÅ * URI ąĮąĄ ą▓ą░ąČąĄąĮ, ą▓ą░ąČąĄąĮ URI čłą░ą▒ą╗ąŠąĮ * ą×ą┐čŗčé ą║ą╗ąĖąĄąĮčéą░ ą║ą╗čÄč湥ą▓ąŠą╣ * ąĪąĄą╝ą░ąĮčéąĖą║ą░ ą┐čĆąĖą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ąĖ ą┐čĆąŠč鹊ą║ąŠą╗ą░
- 7. HATEOAS Hypertext As The Engine Of Application State ąŁč鹊 ąŠąĘąĮą░čćą░ąĄčé, čćč鹊 ą│ąĖą┐ąĄčĆą╝ąĄą┤ąĖą░ ą┤ąŠą╗ąČąĮąŠ ą▒čŗčéčī ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘąŠą▓ą░ąĮąŠ, ą┤ą╗čÅ ąŠą▒ąĮą░čĆčāąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čāčéąĖ ą┐ąŠ API. ąŁč鹊 čüą▓čÅąĘą░ąĮąŠ čü ą┐ąĄčĆąĄčģąŠą┤ą░ą╝ąĖ ą┐ąŠ čüąŠčüč鹊čÅąĮąĖčÄ. ą¤čĆąĖą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖąĄ - čŹč鹊 ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłą░čÅ ą╝ą░čłąĖąĮą░ čüąŠčüč鹊čÅąĮąĖą╣ http://timelessrepo.com/haters-gonna-hateoas
- 8. ąĀąĢąĪąŻąĀąĪ ąś ą¤ąĀąĢąöąĪąóąÉąÆąøąĢąØąśąĢ ŌĆó ąĀąĄčüčāčĆčü ą╝ąŠąČąĄčé č湥ą╝ čāą│ąŠą┤ąĮąŠ ąĖ ą╝ąŠąČąĄčé ąĖą╝ąĄčéčī ą▒ąŠą╗ąĄąĄ ąŠą┤ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖčÅ. ą¤čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖąĄ ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░ąĄčé čüąŠčüč鹊čÅąĮąĖąĄ čĆąĄčüčāčĆčüą░.
- 9. ąĪąĢą£ąÉąØąóąśąÜąÉ ą¤ąĀą×ąóą×ąÜą×ąøąÉ ŌĆó ąÜą░ą║ąĖą╝ ą┐ąŠą▓ąĄą┤ąĄąĮąĖąĄą╝ čģą░čĆą░ą║č鹥čĆąĖąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ čĆą░čüčüą╝ą░čéčĆąĖą▓ą░ąĄą╝čŗą╣ čĆąĄčüčāčĆčü ą▓ čĆą░ą╝ą║ą░čģ HTTP (Query Params, HTTPVerb)? ąĪąĢą£ąÉąØąóąśąÜąÉ ą¤ąĀąśąøą×ą¢ąĢąØąśą» ŌĆó ą¦č鹊 ą║ąŠąĮą║čĆąĄčéąĮąŠ ą┐čĆąŠąĖąĘąŠą╣ą┤ąĄčé čü čüąŠčüč鹊čÅąĮąĖąĄą╝ ą┐čĆąĖą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ąĖą╗ąĖ čĆąĄčüčāčĆčüą░? ą¦č鹊 ąĮą░ ą┐ąŠą┤ą░čéčī ąĮą░ ą▓čģąŠą┤ / čćč鹊 ą┐ąŠą╗čāčćąĖą╝ ąĮą░ ą▓čŗčģąŠą┤ąĄ?
- 10. ą¤ąĀą×ążąśąøąś ąĪą┐ąŠčüąŠą▒ ąŠą┐ąĖčüą░ąĮąĖąĄ čüąĄą╝ą░ąĮčéąĖą║ąĖ ą┐čĆąĖą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗą╣ ąĮąĄ ą╝ąĄąĮčÅąĄčé čüąĄą╝ą░ąĮčéąĖą║čā ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖčÅ čĆąĄčüčāčĆčüą░, ąĮąŠ ą┐ąŠąĘą▓ąŠą╗čÅąĄčé ą║ą╗ąĖąĄąĮčéą░ą╝ čāąĘąĮą░ą▓ą░čéčī ą▒ąŠą╗čīčłąĄ ąŠ ą┤ąŠą┐ąŠą╗ąĮąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čüąĄą╝ą░ąĮčéąĖą║ąĖ. ą¤ąĀąśą£ąĢąĀą½: HAL/Siren JSON-LD JSON-SchemaAPI Docs
- 12. ą¦ąóą× ąóąŻąó ąØąĢ ąóąÉąÜ? https://dev.twitter.com/rest/reference/post/statuses/destroy/id
- 15. SWAGGER API
- 16. API BLUEPRINT
- 18. SYMFONY/PHP ŌĆó NelmioApiDocBundle (+ ą║ąŠąĮą▓ąĄčĆčéą░čåąĖčÅ ą▓ Swagger) ŌĆó Jane (JSON-Schema) and Jane Open Api
- 19. ąĀąĢąÉąøąśąŚąÉą”ąśą» ŌĆó Symfony REST Edition = čģąŠčĆąŠčłąĖą╣ HTTP++ API ŌĆó API Platform (JSON-LD+Hydra) ŌĆó Fractlal, Negotiation ŌĆ”
- 20. API PLATFORM
- 21. JSON-LD
- 22. JSON-LD
- 23. JSON-LD + HYDRA
- 24. JSON API
- 25. ąóąĢąĪąóąśąĀą×ąÆąÉąØąśąĢ PHPUnit Behat Node.js / Chakram Node.js / Frisby Apiary/Dredd Postman HTTPie jq: like sed for JSON data