RETAINERS IN FPDppt
- 1. RETAINERS IN FPD DR GIRISH GALAGALIDR MDS Dept of Prosthodontics Navodaya Dental College
- 2. CONTENTS ïŪ INTRODUCTION ïŪ CLASSIFICATION OF RETAINERS ïŪ REQUIREMENTS ïŪ FULL VENEER CROWN 1.full metal 2.metal ceramic 3.full ceramic Indication /contraindication Advantages /Disadvantages ïŪ PARTIAL VENEER CROWN RETAINERS; Types indication /contraindication advantages/disadvantages ïŪ RESIN BONDED RETAINERS ;CLASSIFICATION Indication/contraindication/Advantages ïŪ RADICULAR RETAINERS ïŪ SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
- 3. INTRODUCTION
- 4. CLASSIFICATIONS 1.EXTRACORONAL A.FULLVENEER CROWN a. Complete metal b.Full ceramic c.Metal ceramic B.PARTIAL VENEER CROWN a.ant.3/4 crown b.post.3/4 crown c.Seven eight crown C.RESIN BONDED RETAINERS
- 6. REQUIREMENTS 1. Withstand masticatory forces 2. Restore anatomy of tooth 3. Pulp consideration 4. Esthetics 5. Hygienic
- 7. FULLMETAL CROWN All axial surfaces of tooth included ADVANTAGES 1.Highly retentive 2.High resistance 3.Superior strength 4 Axial contour modification 5.Occlusal modification .
- 8. DISADVANTAGES ïŪ 1.More extensive preparation ïŪ 2.Not feasible for elec vitality test ïŪ 3.Esthetic
- 9. INDICATIONS ïŪ Extensive coronal destruction ïŪ Short clinical crown ïŪ Max retentive and resistance needed ïŪ Axial correction needed ïŪ Endodontically treated tooth
- 10. CONTRAINDICATION ïŪ If treatment objective can be met with more conservative preparation ïŪ High esthetic demand ïŪ When less than max retentive and resistance needed
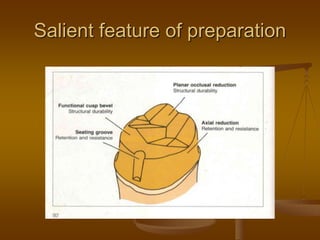
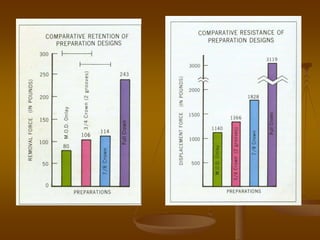
- 11. Salient feature of preparation
- 12. ALL CERAMIC CROWN RETAINER ïŪ Most esthetic restoration ïŪ No metal to block light transmission, brittle ïŪ Not effective as retainer for FPD ïŪ Requires connector of large dia, cross sectional dimension and its effect on periodontia
- 13. INDICATIONS 1.High esthetic demand 2.Teeth with proximal /facial caries 3.Sufficient coronal structure to support 4.Favourable Occlusal load distribution 5.Centric contact :on an area where porcelain is supported by tooth str. 6.Incisal edge reasonably intact
- 14. CONTRAINDICATION 1.High caries index 2.Conservative restoration can be used 3.Insufficient tooth structure to support 4.Thin teeth facio-lingually 5.Unfavourable occlusal load distribution 6.Bruxism 7.Edge âedge occlusion 8.Short clinical crown 9.Opposing tooth occluding in cervical fifth of lingual surface
- 15. ADVANTAGES 1.Improved esthetics 2.Good tissue response 3.Slightly more conservative than metal ceramic restoration
- 16. DISADVANTAGES 1.Less strength of restorative material 2.More destructive preparation 3.Proper preparation is extremely critical 4.Restricted only for anteriors
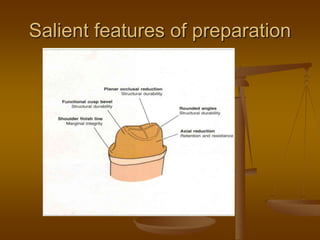
- 17. Salient features of preparation
- 18. METAL CERAMIC CROWN RETAINER Thin ceramic layer bonded to cast metal coping Strength(metal) + esthetic(porcelein) Deep reduction IMP; 1,overconturing 2.shade/translucency
- 19. INDICATIONS a.High esthetic demand b.Act as retainer for FPD c.All other full metal crown retainer
- 20. CONTRA-INDICATIONS a.Active caries b.Periodotally untreated teeth c.Young patients d.Where conservative treatment feasible
- 21. ADVANTAGES A.Strenth +esthetics B.Excellent retentive qualities C.Axial form correction D.Occlusal correction
- 22. DIS-ADVANTAGES 1.High tooth reduction 2.Perio consideration 3.Inferior esthetic-to all porcelain 4.Expensive 5.Subjectable to stress fracture
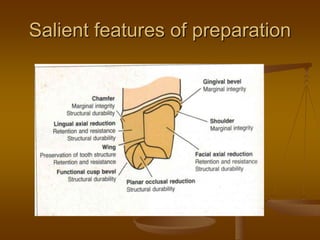
- 23. Salient features of preparation
- 24. PARTIAL VENEER CROWN RETAINER ïŪ Extra coronal restoration covers only part of clinical crown ïŪ More demanding preparation ,not routinely used ïŪ Based on premise;tooth structure should not be covered unless needed ïŪ No technician can match tooth for its texture, appearence ïŪ Gingival health
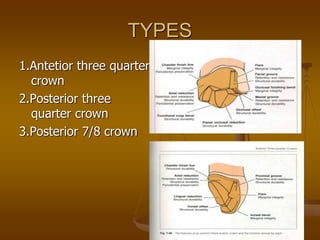
- 25. TYPES 1.Antetior three quarter crown 2.Posterior three quarter crown 3.Posterior 7/8 crown
- 26. INDICATIONS ïŪ Sturdy clinical crown ïŪ Intact buccal surface; no need of contour ïŪ No conflict b/w axial relationship and proposed path of withdrawal of FPD
- 27. Contra-indication ïŪ Short clinical crown ïŪ As retainer for long span FPD ïŪ Anterior endodontic tooth ïŪ Shape and alignment of teeth ïŪ High caries index ïŪ Thin teeth
- 28. Advantages ïŪ Conservative tooth preparation ïŪ Accessibility ïŪ Less gingival involvement ïŪ Good/complete seating of prosthesis ïŪ Feasible;elec vitality test
- 29. Dis-advantages ïŪ Less retentive/resistant than full crown ïŪ Limited path of withdrawal adjustment ïŪ Requires dextrisity from operator ïŪ Cannot be used on nonvital tooth
- 30. RESIN-BONDED RETAINERS To overcome the tooth reduction required for placement of retainer CLASSIFICATION 1.ROCHETTE BRIDGE 2.MARYLAND BRIDGE 3.CAST METAL FPD 4.VIRGENIA BRIDGE
- 31. Advantages ïŪ Low cost, little/less tooth preparation ïŪ No need:anaesthesia ïŪ Supragingival margins ïŪ Rebonding possible
- 32. Dis-advantages ïŪ Irreversible ïŪ Uncertain longetivity ïŪ No space for correction ïŪ No alignment correction ïŪ Difficult temporization
- 33. Indications ïŪ Caries free abutment ïŪ Mandibular incisor replacement ïŪ Maxillary incisor replacement ïŪ Period-splint ïŪ Single posterior tooth replacement
- 34. Contra-indication ïŪ Extensive caries ïŪ Deep vertical overbite ïŪ Nickel sensitivity
- 35. Inlays/onlays Indication Contra indication Advantages ïDis advantages ïSmall caries lsion-in sound tooth ïAdequate dentinal support ïLow caries rate ïRetainer for single tooth replacement where expected masticatory load ïIsless ïHigh caries index ïPoor plaque control ïSmall teeth ïAdolescents ïPoor dentinal support ïLongevity ïNo discolouration ïLeast complex preparation ïmay display the metal ïWedge retention
- 37. RADICULAR RETAINERS Consists of post/core that obtains its retention and resistance to displacement from prepared root portion of an endontically treated tooth Root preparation retain core while core establish resistance/retention for a complete veneer crown that restores pulpless tooth to normal form/function These can be custom made/prefabricated Dep:post length/shape/dia/surface confi
- 38. CRITERIA FOR SELECTION ïŪ Alignment of abutment tooth &retention ïŪ Appearance ïŪ Condition of abutment tooth ïŪ Cost ïŪ Preservation of tooth structure
- 42. REFERENCES ïŪ H.T.Shillingburg:fundamentals of fixed prosthodontics 3rd edn QB 2002 ïŪ Annusavice :phillips science of dental materials 11th edition elselvier 2003 ïŪ Rosenstiel:cotemporary fixed prosthodontics 3rd edn Mosby 2002 ïŪ D C N A: ceramics oct 1977 21;4 ïŪ M.A.Marzouk;Operative Dentistry .Modern theory and practice 1997 ïŪ Shillingberg; fundamentals of tooth preparation for cast metal and porcelain restoration QB 1987
- 43. Thank you