Revolution in telecommunication and its impact in business
- 1. REVOLUTION IN TELECOMMUNICATION AND ITS IMPACT IN BUSINESS
- 4. Applications of Telecommunications Business Telecommunications Business Telecommunications Telecommunications Architectures Telecommunications Architectures Electronic commu- nications system Electronic commu- nications system Electronic meeting systems Electronic meeting systems Business process systems Business process systems • Centralized • Distributed • Client/server • Interorganizational • Global • Electronic mail • Voice mail • Bulletin Board systems • Videotex • Fascimile • Public Information Service • Desktop Video conferencing • Decision room conferencing • Computer conferencing • Teleconferencing • Online transaction processing • Inquiry/Response • EDI / XML • Electronic Funds Transfer • Activity monitoring • Process control • Telecommuting
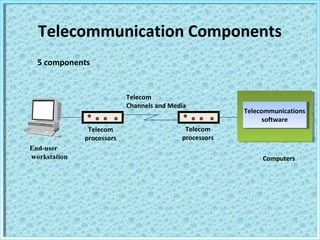
- 5. Telecommunication Components End-user workstation Telecommunications software Telecommunications software Computers Telecom processors Telecom processors Telecom Channels and Media 5 components
- 6. REVOLUTION IN TELECOMMUNICATION • INTRODUCTION OF TELEGRAPH • Started in 1850,the first electric telegraph line between Kolkata(Calcutta) and Diamond Harbor. • In 1854 Telegraph facilities were opened to the public. • INTRODUCTION OF TELEPHONE • In 1881 The Oriental Telephone Company Limited of England opened Telephone Exchanges at Kolkata(Calcutta),Mumbai,Chennai(Madras) and Ahmedabad. • 28 January 1882,Red Letter Day in the history of telephone in India as Major E.Baring,member of the Governor General of India’s Council declared open the Telephone Exchange in Kolkata,Chennai and Mumbai.
- 8. MODERN GROWTH IN LANDLINE AND WIRELESS TELEPHONES • Until Recently,only BSNL and MTNL were allowed to provide Basic Phone Service through Copper wires in India. • However,Private Operators like Vodafone,Bharti Airtel,Tata Indicom,Idea Cellular,Aircel and Loop Mobile have also entered the fray. • India has opted for both GSM and CDMA technologies. • The calls across INDIA are one of the cheapest in the world. INTERNET AND BROADBAND • Internet Penetration is one of the lowest in the world. • Current Definition of Broadband in India is 256 Kbit/s. • Total broadband connections in the country have reached 8.03 million comprising 6% of the population. • BSNL,Tata Teleservices,Airtel,Reliance Communication are the major ISPs in India.
- 9. NEXT GENERATION NETWORKS • MOBILE NUMBER PORTABILITY(MNP) • Allows users to retain their numbers,while shifting to a different service provider. • But has been postponed in metros and category ‘A’ service areas. • INTERNATIONAL • Nine Satellite earth stations-8 Intelsat and 1Inmersat. • Nine Gateway exchanges operating from different Indian cities. • SUBMARINE CABLES • LOCOM linking Chennai to Penang,Malaysia. • INDIA-UAE Cable linking Mumbai to Al Fujayrah,UAE. • Fibre-Optic Link Around the Globe(FLAG) with a landing site at Mumbai(2000).
- 11. The Internet and Telecommunication Services • Brief Internet Timeline – 1960s: Internet began in 1960s as government project (ARPANET) – 1993: Internet commercialized • TCP/IP (core Internet protocol suite) – 1994: World Wide Web (WWW) • Tim Berners-Lee • URLs, HTML, HTTP • Internet brought telecommunications to the masses • Power of the internet: – Ubiquitous network effects – Cheap – Simple – Standard
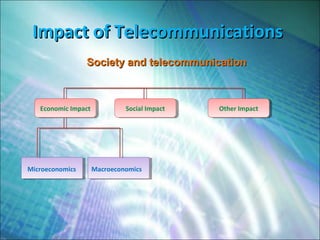
- 12. Impact of TelecommunicationsImpact of Telecommunications Society and telecommunicationSociety and telecommunication Economic ImpactEconomic Impact Social ImpactSocial Impact Other ImpactOther Impact Microeconomics Macroeconomics
- 13. CONCLUSION