RIA test
- 2. Introduction. ïī Radioimmunoassay was introduced by berson and Yalow in 1959 as as in vitro assay for insulin in human plasma. ïī It is a serological method based on immunological antigen-antibody reactions. ïī The target antigen is labelled radioactively and bound to specific antibodies. ïī A sample for example a blood serum is then added in order to initiate a competitive reaction of labeled antigens from the preparation and the unlabeled antigens from the serum sample, with specific antibodies. ïī The test can be used to determine very small quantities of antigens and antibodies in the serum.
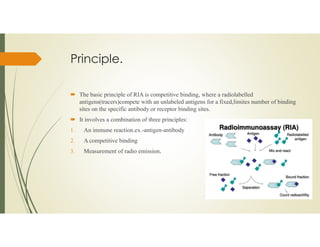
- 3. Principle. ïī The basic principle of RIA is competitive binding, where a radiolabelled antigens(tracers)compete with an unlabeled antigens for a fixed,limites number of binding sites on the specific antibody or receptor binding sites. ïī It involves a combination of three principles: 1. An immune reaction.ex.-antigen-antibody 2. A competitive binding 3. Measurement of radio emission.
- 4. General procedure. 1. Add buffer to the tubes. 2. Add known amounts of unlabeled antigens to the mixture. These compete for the binding sites of antibodies. 3. Add radioactive antigen to the mixture. 4. Add fixed amount of antibody to tubes. 5. Radioactive antigen is displaced from antibody molecule by the unlabeled antigen. 6. The antibody bound antigen is separated from the free antigen in the fluid and the radioactivity of each is measured.
- 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. PROCEDURE FOR RIA.
- 6. Advantages of RIA. ïī Useful for measuring trace amounts of antibodies, drugs and their metabolites,hormones,nucleic acid, proteins etc.in biological samples. ïī Requires very small amount of sample.ex.-only 5-50 micromoles/ml. ïī Simple,rapid,precise,accurate,specific and convenient method. ïī Reliable and reproducible.
- 7. Disadvantages. ïī Requires specific counting equipment. ïī Radiation hazards: uses of radiolabelled reagents. ïī Requires skilled personnel and is expensive process. ïī Laboratories require special license to handle radioactive materials.