Rice by product
- 1. By-product from rice mill, rice husk, rice bran and its utilization Presented by Amita FMPE (PhD)
- 2. INTRODUCTION
- 4. ï By-product - A by product is a secondary product derive from a manufacturing process or chemical reaction during production of main product. ï Rice Straw - Straw is produced by harvesting of paddy. Straw comes from what is left on the plant after it is harvested. 1 ton of paddy crop produces 290 kg straw 290 kg straw produce 100 kWh of power Calorific value = 2400 kcal/kg ï Rice Husk - Husk are generated during the first stage of rice milling, when rough rice and paddy rice is husked and the grains are threshed. 1 ton of paddy produces 220 kg husk 1 ton husk is equivalent to 410-570 kWh electricity Calorific value = 3000 kcal/kg ï Rice bran - Rice bran is the layer between the inner grain and the outer hull of whiter rice is called as bran. Source: https://www.bioenergyconsult.com/tag/paddy-wastes/
- 5. The main by-products of rice are:- Source: https://www.bioenergyconsult.com/tag/paddy-wastes/
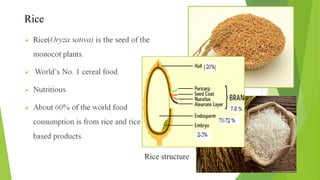
- 6. Paddy grain and its products after husking
- 7. Loss of nutrients due to paddy straw burning (per ton basis) ïĩ Nitrogen 5.5 kg ïĩ Sulphur 1.2 kg ïĩ Phosphorus 2.3 kg ïĩ Potash 25.0 kg ïĩ Organic Carbon 400 kg
- 8. Rice husk uses Fuel Gaseous fuel Husk briquette Silicon tetra chloride Husk board Furfural Rice bran uses Edible grade oil Industrial grade crude oil Free fatty acid manufacture Plasticizers Tocoferol Rice bran wax Husk ash uses Carrier for bio fertilizer organisms Sodium silicate Activated carbon Rice straw uses Mulch Mushroom Production Packing Material Briquettes Ropes Vermi compost Pellets Paper Bio gas production Animal feeding
- 9. The straw fuel or biofuel of biomass pellet mill machine uses corn stalk, wheat straw, rice straw, peanut shell, cob, cotton bar, soybean rod, weeds, branches, leaves, sawdust, bark and other solid wastes as raw materials. After crushing, pressing, increasing density and forming, they become small solid pellets fuel. Delivery and storage for biomass pellet fuel is very convenient and at the same time, its combustion performance is greatly improved. The technological process of biomass pellet mill is: collecting raw materials, crushing raw materials, pelletize raw materials and finally packaging and selling. Pellets Structure of the screw extruder Piston-type briquetting Ring die-type pelletizing machine
- 10. compressed rice straws ï This is done to produce homogenous fuel with a high energy density in square, rectangle, cubed shapes with dimension of 50Ã50Ã50mm3 (LooVan S et al.,2004a). Compressed rice straws Different size of straws Machine for compressed straws
- 11. Degradable Disposal ï These products are not only reduce the problem of agricultural waste but also diminish the dependence on non-renewable petroleum based, melanin products that are non- biodegradable and well existing for hundreds of years8. ï Materials: Agricultural crop residues as rice husk and wheat husk, lemon juice and carboxy methyl cellulose. a) before water resistant coating, b) after water resistant coating as final products Sample Preparation Washing Drying Crushing Preparation of Husk paste ï§Weighed 3.5g carboxy methyl cellulose and mixed it with 100ml of distilled water to make 3.5% edible glue. ï§Then mixed thoroughly the husk powder with edible glue in the ratio of 96.5:3.5% and some lemon juice was also added. ï§After that the mixture was saturated with steam in the autoclave for 20min at the temperature of 120oC. ï§As a result uniform husk paste material was formed which was then further sterilized with UV light for 15min by using UV lamp. ï§Rolling the husk paste ï§Primary shaping ï§Secondary shaping and drying ï§Surface treating and 2nd drying
- 12. To Make Paper Straw is a competitive, alternative source of fiber for paper making to reduce the pressures on forests. Rice straw can be used not only to make paper but various paper products (i.e., newsprint, copier paper, bond paper, etc.). Paper manufacturing process flow chart white liquor (80:20 NaOH and NaS) and steamed for about two to three hours at high temperature and pressure (162 - 168o C and 7-8 kg/cm2 ).bleaching agents are used to bleach the pulp like chlorine, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen peroxide, oxygen and calcium hypo chlorite. Jordan is used in mechanical pulp preparation method in which a conical plug rotates in conical shell. Paddy straw pulps are blended with 10-15% of high strength
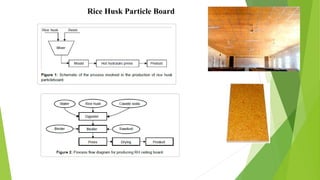
- 13. Rice Husk Particle Board
- 14. Mushroom Production Oyster mushroom production ïChopping of paddy straw ï Sterilize ( Baviston + Pharmaline ) ï Drying (Mc = 15-20%) ï Spawn-run ï Packing ïWatering ïHarvesting ïMarketing
- 15. Vermin compost Paddy waste is used for making vermin compost, various methods are:- Size of worm compost heaps Wide = 1-2 m High = 30-50 cm Length = As long as desired Worm used = Eisenia fetida Location Distributed b/w rows of trees Housed in shelters Climate Tem. = 20 -25 degree Humidity = 80% Bedding Feed Worms Watering Covering the compost heap Monitoring Harvesting of vermin compost Eisenia fetida Vermin compost
- 16. Silica ï One ton of paddy milled generates 200 kg of husk ï 200 kg of husk give 50 kg of ash ïThe ash contains 60~80% Silica (i.e.) 40 kg silica per ton of paddy Uses of Precipitated silica in products : ïRubber reinforcement (Tyre industry) ïPlastic reinforcement ïAgriculture (Animal food) ïFood, Healthcare, Cosmetics ïCatalyst; Coatings ïPulp and Paper processing
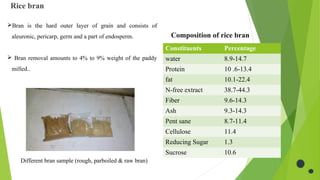
- 17. Rice bran Different bran sample (rough, parboiled & raw bran) ïBran is the hard outer layer of grain and consists of aleuronic, pericarp, germ and a part of endosperm. ï Bran removal amounts to 4% to 9% weight of the paddy milled.. Constituents Percentage water 8.9-14.7 Protein 10 .6-13.4 fat 10.1-22.4 N-free extract 38.7-44.3 Fiber 9.6-14.3 Ash 9.3-14.3 Pent sane 8.7-11.4 Cellulose 11.4 Reducing Sugar 1.3 Sucrose 10.6 Composition of rice bran
- 18. Preparatory unit HOPPER ROTERY SCREEN SCREW CONVEYOR BUCKET ELEVATOR FEED CONVEYOR PALETTIZATION COOLING BRAN PELLET SEND TO SOLVENT UNIT THROUGH CONVEYOR STEAM HEATING Preparatory unit. Palletization machine
- 19. Hopper (dry pallet) Extraction (Hexane + oil) Fine separation Miscella tank Economiser(45-50 C) Heater-A (85-90C) Heater-B (100C) Final heater (110C) Storage For refinery Hexane liquid Condenser Hexane vapour Hexane storage Direct roasting Hexane Oil Oil less pallets Packaging Solvent extraction unit-
- 20. FFA and smell Solid wax Fine wax Mud, earth Colour Waste water Moisture FFA, gum, pigments Gum Crude oil Degumming Neutralization Hydration tank (80C) Separator (100C) Bleaching tank Leaf filter (PLF) Crystallizer Plate filter (frame) Deodorizer (200-250C) Packaging unit Refinery unit- Separator
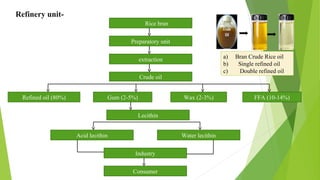
- 21. Rice bran extraction Crude oil FFA (10-14%)Wax (2-3%)Gum (2-5%)Refined oil (80%) Lecithin Water lecithinAcid lecithin Industry Consumer Preparatory unit Refinery unit- a) Bran Crude Rice oil b) Single refined oil c) Double refined oil
- 22. Rice bran oil Rice bran oil benefits- ïĩNutritionally superior. ïĩLonger shelf life. ïĩBetter protection for heart & related blood vessels. ïĩEconomic-15% less absorption of oil during frying. ïĩMore stable at higher temperature. ïĩGives better taste & flavor to food items. ïĩOil is less sticky-easy to wash and lower soap consumption. ïĩUsed as a health heart oil, control diabetes, improve the immune system, cholesterol control. ïĩPromotes heart helps burn fat. ïĩRice bran oil is use in cosmetics.
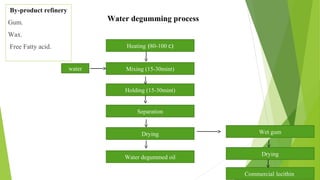
- 23. Heating (80-100 c) water Drying Wet gum Mixing (15-30mint) Holding (15-30mint) Separation Drying Commercial lecithin Water degummed oil Water degumming process By-product refinery Gum. Wax. Free Fatty acid.
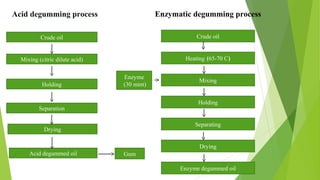
- 24. Crude oil Mixing (citric dilute acid) Holding Separation Drying GumAcid degummed oil Acid degumming process Enzyme degummed oil Crude oil Heating (65-70 C) Mixing Holding Separating Drying Enzyme (30 mint) Enzymatic degumming process
- 25. Lecithin- ï Lecithin can be obtained from a source such as extracted oil of plant seeds, and vegetable oil, by using a process known as degumming. ï Degumming is the treatment of oil with water to remove phosphorus containing compounds, waxes and other impurities from oil. Crude lecithinï Emulsifiers ï Viscosity Modifiers ï Separating Agents ï Extrusion Aids ï Anti-Dusting Agents ï Shelf- Life Aids ï Supplements ï Dispersing agent ï Beverage industry Properties & uses of lecithin
- 26. 2-3% wax is obtained during refining of RBO Usage of waxes: ï Chewing gums ï Coating over fruits ï Polishing of floor and leather etc. Wax ïFor food wraps ïCarbon paper RICE BROKEN ïMaking Flour ïUsed for Idli ready mix ïUsed for upma, and other ready mixes like dosa etc ïFor brewery ïFor animal feed etc.
- 27. ï Packing Materials: The compaction resistance and resiliency of rice straw makes it a very good packing material. ï Erosion control and soil stabilization: Rice straw is an effective material both in commercial erosion control practices and in rice field erosion control. Bales of rice straw can be shredded on site and blown into roadside cuts and fills to provide soil stabilization. ï Frost control: layers of rice straw can be used for frost control in areas with low temperatures. These uses are usually closely allied with mulching and composting and it is difficult to determine which one of the practices is dominant. ï Sewage sludge mixing: Rice straw would be a suitable bulking agent for sewage sludge composting and disposal. It would appear that chopped or fiberized straw would increase both absorbency and acceleration of decomposition. Other Uses for Rice Straw
- 28. Thanks