Rickettsial diseases
- 1. RICKETTSIAL ZOONOSES Saleem Sayed, Final year part-I. NIMRA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Saleemsayed092@gmail.com
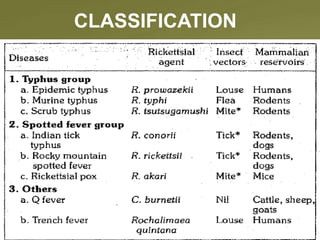
- 3. Rickettsial diseases ? • Group of specific communicable diseases. • Caused by :Rickettsial organisms. • Transmitted to man by : Arthropod vectors.
- 4. Diagnosis ? • These are under-diagnosed and they contribute to the.. • Acute febrile illness (Rapid onset of fever)
- 6. INDIAN TICK TYPHUS AGENT :caused by Rickettsiaconorii. RESERVOIR OF INFECTION: The tick is the reservoir of infection (infective at all stages of its life cycle) VARIOUS TICK GENERA: • Rhipicephalus, • Boophilus, • Haemaphysalis.
- 7. MODE OF TRANSMISSION : • Acquires infection by bite of an infected tick. • Contamination of skin with crushed tissues • Faeces of an infected tick. INCUBATION PERIOD:3-7 days. CLINICAL FEATURES : Acute onset of fever, • Headache & Malaise . • *A maculopapular rash appearson the 3rd day. • *Clinical syndrome may be confusedwithatypical measles.
- 8. CONTROLL MEASURES: • TREATMENT : Broad spectrum antibiotics. • PERSONAL PROPHYLAXIS: Daily inspection of the body for ticks is important.
- 9. Q FEVER AGENT :caused by Coxiellaburnetti. RESERVOIR OF INFECTION: cattle ,sheep, ticks. •Placenta of infected cows and sheep contains agent. MODE OF TRANSMISSION: 1. Inhalation of infected dust from soil (previously contaminated by urine and faeces) 2.Ingestion of contaminated meat and milk.
- 10. INCUBATION PERIOD:2-3 weeks. CLINICAL FEATURES : Acute onset of fever, chills, Headache & Malaise . *There will be no rash or local lesion. CONTROLL MEASURES: 1.TREATMENT :Prolonged treatment over 18 months *Doxycycline is the drug of choice.
- 12. RICKETTSIAL POX • Man gets infection through bite of mites found on infected mice (Musmusculus) • Rickettsial pox may be confused withatypical cases of chicken pox. TRENCH FEVER • Limited to central europe. • Vector is louse and transmitted by faeces of same.
- 13. RICKETTSIAL POX CHICKEN POX