Right to accesible information
- 1. Some thoughts on privacy and information rights with plain language Cheryl Stephens April 2018
- 3. Reading the Legal World
- 4. What is legal literacy? Few people, and only those with high functional literacy, education, and knowledge of context can comprehend legal texts. Legal literacy is the ability to read and familiarity with the legal context. It requires that a person ŌĆó understand the words used in the legal context ŌĆó grasp the potential effects ŌĆó know how to their access rights.
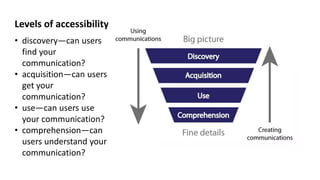
- 5. Levels of accessibility ŌĆó discoveryŌĆöcan users find your communication? ŌĆó acquisitionŌĆöcan users get your communication? ŌĆó useŌĆöcan users use your communication? ŌĆó comprehensionŌĆöcan users understand your communication?
- 6. Indirect discrimination or systemic discrimination a uniform practice or standard which ŌĆó has a negative or adverse effect on a group of persons ŌĆó because it does not accommodate their particular characteristics though this could be done without sacrificing legitimate objectives or incurring undue hardship. ŌĆó occurs even when everyone is treated the same and there is no intent to discriminate. ŌĆó discriminatory in its effect and with the failure to accommodate
- 9. Right to understandable information The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities requires When an institution is required to provide information it needs to be understandable The convention includes plain language as one of the "modes, means and formats of communication".[3]
- 10. 2017 Personal data protection in EU EU General Data Protection Regulation said: The principle of transparency requires that any information and communication relating to the processing of those personal data be easily accessible and easy to understand, and that clear and plain language be usedŌĆ” Given that children merit specific protection, any information and communication, where processing is addressed to a child, should be in such a clear and plain language that the child can easily understand.
- 11. General Data Protection Regulation 2018 In the U.S., legalese has been used to cover up unfair and deceptive practices. A side effect of this new regulation is more plain language in terms of service: ŌĆ£The principle of transparency requires that any information and communication relating to the processing of those personal data be easily accessible and easy to understand, and that clear and plain language be used.ŌĆØ (39) http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF
- 12. General Data Protection Regulation 2018 ŌĆ£The principle of transparency requires that any information addressed to the public or to the data subject be concise, easily accessible and easy to understand, and that clear and plain language and, additionally, where appropriate, visualisation be used.ŌĆØ http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF
- 14. Human rights laws on discrimination International laws, Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the Canada Human Rights Act, or provincial or territorial human rights laws apply to: ŌĆó failing to accommodate people with low literacy skills (may be a form of systemic discrimination) ŌĆó failing to take reasonable steps (to end systemic discrimination)
Editor's Notes
- #2: 14. Courts, Low Literacy, Collateral Effects, and Systemic Discrimination ŌĆō with Cheryl Stephens How are the courts addressing their systemic discrimination against people, including the accused, victims, and witnesses who have literacy challenges? What is systemic discrimination? What are the collateral effects of encounters with the justice system? What has been learned about it? What has been done since the 2008 report on literacy and the justice system (see PoliceABC.ca)? About the Presenter: Since 1989, Cheryl Stephens has consulted on communication and education projects, including plain language and literacy in the justice system. For many years, her work has focused on plain language, legal literacy, and access to justice. In 2008, Stephens was researcher and writer for the Canadian Association of Chiefs of Police on the Literacy and Policing Project, which resulted in the report and website at PoliceABC.ca Also see: Canadian Assoc of Administrative Tribunals literacy training resources Lord Neuberger, recently retired UK Supreme Court president: ŌĆśAccess to justice, and all the other rights we hold so dear, all flow from democracy and the rule of law.ŌĆÖ ŌĆ£ŌĆ”barriers are constantly being erected to prevent ordinary individuals from seeking legal remedies.ŌĆ”access to justice has become inversely proportional to the need for legal advice and representationŌĆ”┬Āresearch by the National Literacy Trust which shows that one in six people in the UK struggle with literacy: ŌĆśThe key thing is to recognise that for all the advantages that court modernisation and technology might provide, while the law remains as complex as it is there is never going to be true equality of arms. That is why it is important that those who are more vulnerable do have access to legal advice and indeed representation.ŌĆÖ Marialuisa Taddia┬Ā, Out of the Loop, Oct 27, 2017 https://www.lawgazette.co.uk/features/out-of-the-loop/5063340.article
- #4: From Reading the Legal World People using the legal system must be able to guide themselves through a process that they understand [...] and, at appropriate places along the way, recognize they have a legal right or responsibility, in order to exercise or assume it; recognize when a problem or conflict is a legal conflict and when a legal solution is available; know how to take the necessary action to avoid problems and where this is not possible, how to help themselves appropriately; know how and where to find information on the law, and be able to find information that is accessible to them, know when and how to obtain suitable legal assistance; have confidence that the legal system will provide a remedy, and understand the process clearly enough to perceive that justice has been done...
- #5: http://www.ccat-ctac.org/CMFiles/Publication/Literacyandjustice.pdf Or Literacy is the ability to draw conclusions from words that are understood and then to use those conclusions to make decisions and to take action.
- #6: Users move down the framework, funnelled from big picture to fine details: they first have to find a communication, then get it, use it, and understand it. Creators of communications move up the framework: they write the content, design it, disseminate it, and finally archive it. Iva Ceung, Four levels to accessible communications http://www.ivacheung.com/2016/09/four-levels-to-accessible-communications/
- #8: Literacy and the Courts, Katherine Alteneder Alaska Justice Forum┬Ā>┬Ā24(2), Summer 2007 http://justice.uaa.alaska.edu/forum/24/2summer2007/a_literacycourts.html
- #9: This is about more than poor reading skills. ItŌĆÖs also about not understanding. And it is about having different thinking strategies and problem-solving approaches. The legal system is structured, hierarchical, rigid, and rule-bound. Many people cannot even understand how this can work. Plain Language is needed in criminal justice for the proper functioning of the justice system, efficiency of court processes, fundamental right to a fair trial, fairness to victims and witnesses success of prosecutions, prevention of risk and losses to police organizations.
- #10: The United Nations┬ĀConvention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities┬Āincludes plain language as one of the "modes, means and formats of communication".[3] ┬ĀUnited Nations General Assembly.┬ĀConvention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities ┬ĀArchived ┬Ā2016-12-02 at the┬ĀWayback Machine., Article 2 - Definitions. 13 December 2006, A/RES/61/106, Annex I. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- #11: Previous to REGULATION (EU) 2016/679 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL, 27 April 2016
- #12: WikiTribune quote: ŌĆ£GDPR strengthens the rights of individuals by giving them more control over how businesses use their personal data. These include the right to be informed, to access and to rectify personal data records if they are inaccurate or incomplete.ŌĆØ┬Ā
- #13: REGULATION (EU) 2016/679 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL, 27 April 2016 WikiTribune quote: ŌĆ£GDPR strengthens the rights of individuals by giving them more control over how businesses use their personal data. These include the right to be informed, to access and to rectify personal data records if they are inaccurate or incomplete.ŌĆØ┬Ā
- #14: A [minimally good human life]* is not possible without access to a rich array of expressions and to knowledge for both practical ends and intrinsic benefits to the human spirit. Guaranteed by countries that sign treaty People have a right to access information, to access quality information. Information quality includes accuracy, completeness, currency, and comprehensibility (Fox 1994)ŌĆ”.Meeting the right to access information requires that we consider in what format the information will be most comprehensible to the people who need itŌĆ” The ŌĆ£knowledge interestŌĆØ is the ŌĆ£fundamental interest in securing reliable information about the conditions required for pursuing oneŌĆÖs aims and aspirationsŌĆØ (229). Without access to such knowledge, individuals and groups will be unable to effectively carry out their aims. International: A UNESCO treaty says Article 7. All are equal before the law and are entitled without any discrimination to equal protection of the law. All are entitled to equal protection against any discrimination in violation of this Declaration and against any incitement to such discrimination. Article 10. Everyone is entitled in full equality to a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal, in the determination of his rights and obligations and of any criminal charge against him. Article 11. (1) Everyone charged with a penal offence has the right to be presumed innocent until proved guilty according to law in a public trial at which he has had all the guarantees necessary for his defence. ┬Ā ŌĆ£Global Trends on the Right to InformationŌĆØ compiled by the Human Rights organization Article 19. The report makes a number of recommendations for governments, civil society, and businesses among which are the following (Article 19, 2001, 155-157): ŌĆ£The right to access public information about oneŌĆÖs economic, social and cultural rights is not only related to these rights ŌĆō it is a precondition for their realization. Without information about the scope and content of their rights to health, housing or work, citizens are unable to determine whether their rights are being respected.ŌĆØ (Article 19, 2007, p. 18).







![Right to understandable information
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of
Persons with Disabilities requires
When an institution is required to provide
information it needs to be understandable
The convention includes plain language as one of the
"modes, means and formats of communication".[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/righttoaccesibleinformation-180411000410/85/Right-to-accesible-information-9-320.jpg)






