Rn grand rounds may 2012
- 1. RN GRAND ROUNDS May 16th, 2012 Thursday, May 17, 12
- 2. CASE 1 22 yo M , college student CC: Nausea / Vomiting PMH: ADHD/ Anxiety Meds: Adderall HPI: 3 day hx of N/V, this is his third visit for same Thursday, May 17, 12
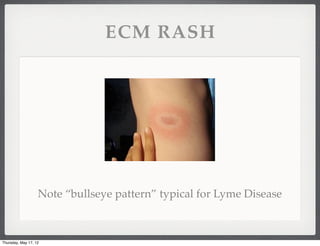
- 3. CASE 1- N/V Vitals: 152/81, P 103, RR 16, T 97.5, Sat 100% RA Pt seen two other times for same and sent home IVF, Zofran IV, Compazine PR, CT head neg, K+ was 3.0 Rash on back noted by RN, did not look like Erythema chronicum migrans ŌĆ£bullseyeŌĆØ Maybe there for several months according to the ID consult Lyme titer added to labs Thursday, May 17, 12
- 4. WORKUP Admitted to medicine for workup CT abdomen was neg ID consulted for positive Lyme titer ( ELISA) Western blot added (con’¼ürmatory test) Thursday, May 17, 12
- 5. ECM RASH Note ŌĆ£bullseye patternŌĆØ typical for Lyme Disease Thursday, May 17, 12
- 6. LAB TESTS Laboratory blood tests are helpful if used correctly and performed with validated methods. Laboratory tests are not recommended for patients who do not have symptoms typical of Lyme disease. Just as it is important to correctly diagnose Lyme disease when a patient has it, it is important to avoid misdiagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease╠²when the true cause of the illness is something else. Source: cdc.gov Thursday, May 17, 12
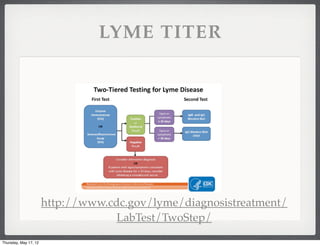
- 7. LYME TITER http://www.cdc.gov/lyme/diagnosistreatment/ LabTest/TwoStep/ Thursday, May 17, 12
- 8. WESTERN BLOT The con’¼ürmatory test for a positive Lyme titer Many false positives occur with with the Lyme titer This clari’¼ües equivocal or positive tests Western Blot sub-fractionates the IgG and IgM Thursday, May 17, 12
- 9. WESTERN BLOT For Positive Results you must have: An lgG Western Blot must have ’¼üve or more of these bands: 18, 21,28, 30, 39, 41,,45, 58, 66 and 93 kDa. An lgM Western Blot must have two or more these three bands: 23, 39, 41 Source: www.whatislyme.com Thursday, May 17, 12
- 10. OUR PATIENTŌĆÖS WB IgG - Negative overall only 2 bands pos Prob no chronic infection IgM- 2 of 3 are positive presumes acute infection Thursday, May 17, 12
- 11. WB DISCLAIMER Thursday, May 17, 12
- 12. SUMMARY False positives on the initial Lyme titer and Western blot can occur Routine testing without actual symptoms causes unnecessary concern, further testing and treatments Much controversy exists on the actual interpretation of Western blot Thursday, May 17, 12
- 13. WESTERN BLOT False-positive reactions may occur with patients with other spirochetal diseases (syphilis, yaws, pinta, relapsing fever, or leptospirosis), in’¼éuenza, autoimmune disorders, multiple sclerosis, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. http://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/ interpretive-guide Thursday, May 17, 12
- 14. CASE 2 22yo F Status post delivery of twins 6 days ago CC: Headache/ HTN since yesterday Pain 6/10 PMH: Asthma, Migraine, Pre ecclampsia (RN note) Arrival 1414hrs, PA time 1448 hrs in FT BP:144/69 in triage Thursday, May 17, 12
- 15. MD NOTE 2 days of HA Hx migraines, this was ŌĆ£more severeŌĆØ BP running high, repeat in ER at 1651 hrs at 175/99, 1705 hrs Gyn consulted 1739hrs at 189/114 1740 hrs Labetalol 10mg IV 1849hrs Hydralazine ordered IV ? in MD note, not RN 1911 Magnesium IV ordered 4 grams over 15 mins Thursday, May 17, 12
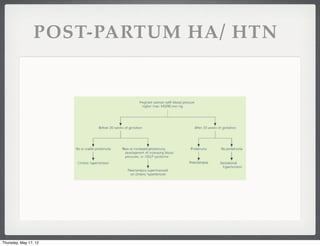
- 16. POST-PARTUM HA/ HTN Thursday, May 17, 12
- 17. HTN IN PREGNANCY Gestational HTN: found late in pregnancy, no other ’¼ündings for preeclampsia, ŌĆ£transientŌĆØ , clears by post partum week 12 Chronic HTN Preceding Pregnancy- Ōēź140/90, before 20 wks, persists beyond 12 weeks Chronic HTN with PIH ( preeclamsia or eclampsia) highest risk Thursday, May 17, 12
- 18. PREGNANCY INDUCED HTN Preeclampsia- mild/ BP Ōēź 140/90, > 20 wks gestation, no end organ damage, >300mg protein/ 24hrs. Severe Preeclampsia- SBP Ōēź160/110, proteinuria > 5gr/ 24hr, Headache, Epigastric pain, Low PLT, Oligouria < 400mg/ 24hr, Pulmonary edema Thursday, May 17, 12
- 19. PREECLAMPSIA RISK FACTORS Nulliparity Previous gestational hypertensive disorders Diabetes Malnutrition Hydatiform mole Low social status Chronic Nephritis Thursday, May 17, 12
- 20. PREECLAMPSIA SIGNS & SYMPTOMS CNS: Headache, visual disturbances, altered mental status, blindness, weakness & malaise Edema Epigastric Pain Dyspnea Seizures- on top of the criteria for preeclampsia de’¼üne Eclampsia Thursday, May 17, 12
- 21. MANAGEMENT Delivery is the only ŌĆ£cureŌĆØ HTN management Hydralazine/ Labetalol IV/ Sodium nitroprusside IV Magnesium - seizure prevention ŌĆ£eclampsiaŌĆØ IV Fluids, patients are intravascularly depleted Thursday, May 17, 12
- 22. HELLP SYNDROME H- Hemolysis EL- Elevated Liver Enzymes LP- Low platelets Occurs in 10-20% of women with Preeclampsia or Ecclampsia Women usually have HTN/ Preeclampsia before HELLP syndrome is noted. Thursday, May 17, 12
- 23. HELLP SYNDROME Fatigue Headache N/V Blurry vision RUQ pain Fluid retention/ edema Thursday, May 17, 12
- 24. LABS All women with new onset HTN: CBC, AST/ALT, BMP, Uric acid, LDH, Indirect Bilirubin, PT/PTT HELLP: check Spot Protein (prot/creat ratio) > 0.3, Proteinuria > 300mg/ 24hr, Uric Acid> 5.6, Creat> 1.2 Also for HELLP: PLT < 100k, Elevated PT/ PTT, Decreased Fibrinogen, Hemolysis markers ( peripheral smear, Indirect Bili > 1.2, LDH>600) Thursday, May 17, 12
- 25. OUR CASE Pt was seen in triage. BP was144/69, RN noted home BP of 170/110 Pt had Headache, got Reglan (no note of vomiting on chart), had leg edema Sent to Fast Track MD involved after PA presentation Thursday, May 17, 12
- 26. PREECLAMPSIA Lessons learned....... Thursday, May 17, 12
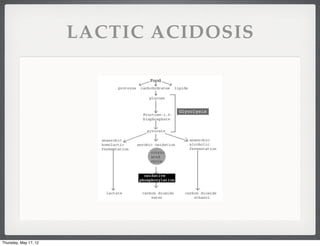
- 27. LACTIC ACIDOSIS The product of anaerobic metabolism Number one cause of metabolic acidosis Causes anion gap AG= NaŌü║ - (ClŌü╗ + HCO3Ōü╗) Bicarb (HCO3Ōü╗) will be low Lactate above 4meq/L is abnormal Thursday, May 17, 12
- 28. LACTIC ACIDOSIS Thursday, May 17, 12
- 29. METABOLIC ACIDOSIS MUDPILES Methanol- metabolized to Formic Acid via liver enzymes, cellular hypoxia, blindness Uremia- increased bicarb wasting leads to acidosis DKA- ketone formation in the absence of insulin from fatty acid breakdown Paraldehyde- sedative no longer in use INH- inhibits lactate dehydrogenase Lactic Acidosis- type A ( hypoperfusion) and type B ( DM, toxins, Ethylene glycol- antifreeze degradation produces glycolic acid and oxalate Salicylates- ie ASA overdose Thursday, May 17, 12
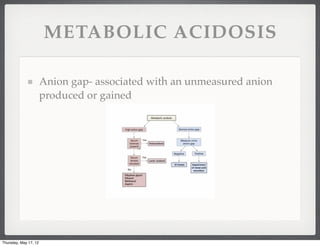
- 30. METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Anion gap- associated with an unmeasured anion produced or gained Thursday, May 17, 12
- 31. TYPES OF LACTIC ACIDOSIS Type A: from tissue hypoperfusion/ hypoxia Type B- Drugs, DM, Liver disease, malignancy, inborn errors of metabolism Thursday, May 17, 12
- 32. LACTIC ACIDOSIS When to order? Think of the situation. Hypoxia- asthma, COPD, CHF Increased Metabolic Activity- seizure, exercise, shivering ( doesnŌĆÖt change management) Sepsis- dead bowel, overwhelming infection, fever Thursday, May 17, 12
- 33. SEPSIS SIRS de’¼ünition- Systemic In’¼éammatory Response Syndrome Essentially a cytokine storm with abnormal Thursday, May 17, 12
- 34. SEPSIS SIRS due to an infection is SEPSIS Non Sepsis Causes- trauma, burns, pancreatitis, ischemia and hemorrhage Also- anaphylaxis, tamponade, PE, Adrenal insuff., complications of surgery, Overdoses Complications- organ failure Thursday, May 17, 12