Road To War Pacific
- 1. War in the Pacific* SEQ Examinable
- 2. What is an Expansionist Power?A state that takes over countries & keeps extending territory whenever & wherever it can.Imperialism - the policy of extending the power and dominion of a nation especially by direct territorial acquisitions The revamped Jp military was hungry for more action
- 3. Japanese Imperialism before 19301st Sino-Jp War (1894-95) – Gained Formosa or TaiwanRusso – Jp War (1905) – Gained Port Arthur in Manchuria, S. Sakhalin & Liaotung1910 – Annexed Korea1919 – Gained Shantung Peninsula from WW I settlementKorea as the “dagger pointing to the heart of Japan”
- 4. Japan’s Foreign Policy AimsTo build an empire in the Asia – PacificTo free Asians from western controlTo find room for Jp’s growing populationTo control resources & raw materialsBy the 1930s, the Japanese military was one of the most advanced in the world & was ready for action
- 5. Building an Empire in the PacificJp wanted to become the leading power in the Asia Pacific regionTo do this, it needed to build an empireJp was casting glances over territories in the Far East.
- 6. To “Liberate” AsiaMost of SEA under western colonial controlJp initiated propaganda to “liberate” them“Asia for Asians” – Asians should stand up against western imperialism“Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere” – Resources should be for the benefit of Asia, not westerners.Jp as the leader of Asia, should lead the fight against western colonial powers.A propaganda poster on Asian cooperation
- 8. Find Room for PopulationPopulation in 1870: 30 millionPopulation in 1930: 70 millionJp could no longer find living space & food for its exploding populationNeeded to resettle its population elsewhereTokyo in the early 1900s. Japan was fast becoming over-crowded
- 9. Control Natural ResourcesThe Great Depression made it hard for Jp to import resources & exports its goodsOverseas territories would provide resources & give Jp a market to sell its goods.Manchuria was a prime target:Cheap abundant manpowerRaw materials like coal, timber, iron, grain & goldAn overseas market
- 10. Where in the world is Manchuria?Manchuria was extremely rich in natural resources which Jp coveted. Only problem: it belonged to China
- 11. Mukden Incident, 1931A bomb exploded on the S. Manchurian Railway track in Mukden which was owned by JpThe Jp army accused the Chinese govt of sabotage.Events shrouded with controversyThe scene of the railway “sabotage”
- 12. Kwantung Army ActsIn retaliation, the Kwantung Army stationed in Manchuria attacks Chinese positionsIt’s excuse was to “defend Jp interests” in the regionManchuria is soon capturedThey established the state of Manchukuo with the last Qing emperor, Pu Yi, installed as its puppet rulerKwantung Army marches into Manchurian citiesHenry Pu Yi, The last Emperor of China
- 13. Japanese Govt PowerlessKwantung army acted independently of Japanese GovtPM Ki Inukai protested against the invasion, but was powerless to do anythingPM Inukai’s opposition to the Kwantung Army would cost him dearly.
- 14. League of Nation’s Response (or lack of)Convened the Lytton commission to Manchuria to investigateCommission declared Manchurian invasion illegal & that Japan should withdraw immediatelyJp did withdraw… but from the LON in 1932LON took no further action & Jp was convinced the west were too weak to prevent it’s expansionist ambitions
- 15. League of Nation’s Response (or lack of)West were too busy recovering from Great Depression to care about Manchuria LON also had no army to force Japan to do anythingNewspaper article on the Mukden Incident
- 16. Fascists Unite!Anti – Comintern Pact (1936)Nazi Germany & Japan pledge to fight communismHowever, Japan was concerned with the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact in 1940.Tripartite Pact (1940)Italy, Germany & Japan become alliesAxis representatives signing the Tripartite Agreement.
- 17. Why did War break out in the Pacific?Japan’s desire to conquer ChinaJapan’s neutrality with the SovietsEuropeans more worried about Hitler Worsening relations with the U.S.Appointment of Hideki Tojo as PM.
- 18. Jp’s Desire to Conquer China Historically, Japan had always been China’s tributary.Wanted to assert its dominance over China once & for all.Wanted access to China’s rich port cities & resourcesChina was also weak, having civil war.Zaibatsus were also pushing for war to gain assess to lucrative Chinese markets, industries & resources
- 19. China in TurmoilThe Chinese were too busy fighting among themselves than to worry about the Jp threat. Left: Mao Zedong leads the Chinese Communist Party while Chiang Kai shek on the right leads the Nationalists.
- 20. Marco Polo Bridge Incident – 7th July 1937A misunderstanding led to an exchange of fire between both sides at Marco Polo Bridge.Jp demanded that Chinese troops withdraw but the latter refused.Became a full-scale invasion of ChinaThe Pacific War had begunChinese troops engage Jp forces at MP bridge
- 21. Neutrality with SovietsJp initially coveted Soviet lands as well. However they were defeated in battles at Changkufeng & Nomonhan.Sued for peace & signed neutrality pact with Soviets in 1941 to concentrate on ChinaThe Imperial Jp Army took a beating at Nomonhan by the Soviets.
- 22. European pre-occupation with HitlerHitler had been re-arming Germany since the mid 1930s Britain, France & Holland were more concerned about defending their own countries.Could spare little resources to defend SEA colonies.The west obviously gave priority to Europe rather than Asia. This would come back to bite them later.
- 23. General Tojo Becomes PMWith the appointment of a general as PM, it was obvious that Jp would pursue an aggressive foreign policy stanceTojo, a former Kwantung Army commander, believed war with the U.S. could not be avoided.General (later PM) Hideki Tojo – 1884 – 1948
- 24. Worsening Relations with the U.S.U.S. declared Chinese invasion illegal.Placed trade embargo on oil, steel & scrap iron to Japan.Forced Jp to look at SEA for for resources.Despite this, both sides were keen to avoid war & had last ditch talksHowever, Jp refused American demands to withdraw from China & talks broke down.
- 25. American Pacific FleetU.S. had a powerful fleet stationed at Pearl Harbour, HawaiiThis posed a huge obstacle to Japanese advance into SEA.The solution was obvious…..American President Franklin Roosevelt pushed for a tough stance on Jp aggression in the Pacific.
- 27. Pearl Harbour – 7 Dec 1941Without warning, Jp bombers attacked the Pacific Fleet in Pearl Harbour.2400 killed, 1200 wounded3 cruisers, 3 destroyers, 188 planes destroyedDespite heavy losses for the Americans, the Jp failed to knock out fuel storage & maintenance capabilitiesThis enabled America to rebuild their fleet later on.
- 28. “A Date Which Will Live in Infamy”Mitsubishi Zero Fighters, preparing to launch from their aircraft carrier.Sinking of the USS ArizonaUSS Arizona Memorial today
- 29. American Response1st ever attack on AmericaAmerica declare war on the AxisHitler & Mussolini declare war on America.U.S. enters WW II on the side of the AlliesFormally ends American policy of isolationismAllies against the Axis: From left, Winston Churchill (PM of Britain), Franklin Roosevelt (American President), Joseph Stalin (Soviet Leader)
- 30. A Very Brief Summary of the Pacific War*Non-examinable
- 31. Japan vs. ChinaAfter M.P. bridge, Jp forces pour into ChinaHowever, realised China was too huge for Jp to conquer.Had to settle for China’s rich coastal cities like Beijing, Nanjing, Shanghai etc...Jp rule was extremely brutalJp forces march into Nanjing, the capital of the Nationalist govt.
- 32. Rape of NanjingWanton looting, murder & rape by Jp armyCasualties ranged from 100,000 – 300,000Even infants & elderly women were not spared rape Jp textbooks today play down the Nanjing Massacre, a source of contention between Jp & China.These 2 Jp Officers had a contest to see who can collect 100 Chinese heads first
- 33. Sons were forced to rape their mothers, fathers were forced to rape daughters. One pregnant woman who was gang-raped by Japanese soldiers gave birth only a few hours later; although the baby appeared to be physically unharmed. Monks who had declared a life of celibacy were also forced to rape women. An eye-witness account of the Rape of NanjingMass graves containing massacred Chinese infants
- 34. Japan Sweeps into SEAAttack on Pearl Harbour coordinated with advance into SEA.1941 – Hong Kong, Malaya, Philippines & Burma fell1942 – Singapore & Dutch East Indies fellThailand signed alliance with Jp to avoid being conqueredFrench Indo-China became Jp ally as well. SEA came under Jp control by 1942
- 35. At the height of its empire…
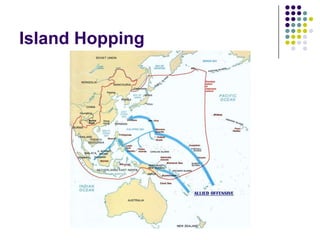
- 37. The Tide Turns…America rebuilds Pacific Fleet by 1943 & was out for revenge.Naval battles at Coral Sea & Midway saw America cripple Jp Navy.U.S. marines begin the “island-hopping” strategy hatched by Gen. Douglas McArthur.American navy wins a decisive battle against the Jp at the Pacific island of Midway
- 38. Island Hopping
- 39. By early 1945…Allied forces had retaken Philippines, fighting to retake Burma, & preparing to retake Malaya.Island hopping brought U.S. marines within striking range of Japan.General Douglas Macarthur – “I have returned!”
- 40. Approaching JapanCostly battles at Iwo Jima & Okinawa convinced Americans that invasion of Japan would result in high casualties.Jp kamikaze tactics showed desperationThe solution?The iconic American flag raising at Iwo Jima. The battle gave the U.S. marine corps its highest casualty rate in any battle in history.Kamikaze plane in action
- 41. Truman drops the BombTop & left: Hiroshima flattened.Right: Radiation burns from survivors
- 42. AftermathEmperor Hirohito declares unconditional surrenderJp comes under American occupationHirohito absolved from all blame.Tojo & many Jp tried & executed for war crimes.Zaibatsus & military dismantledJp becomes staunch U.S. ally in Cold WarHirohito with Macarthur, who was the Supreme Allied Commander for occupation forces in Japan.
- 43. Why did Japan Lose?Economic CollapseUS submarines sank more than 75% of Japan’s merchant shipsUS bombing destroyed Japanese homes & factories1945 - people starving & collapse of industrial production
- 44. Why did Japan Lose?Resources Over-stretchedRapid conquests ==> had too large an area to control & defend.No allies & not enough troopsMany of the conquered territories were vulnerable by sea & Jp had no more control of the seas after 1943.How do you defend an empire as large as this?
- 45. Why did Japan Lose?Air & Sea power of USABattles of Coral Sea, Midway and Leyte Gulf, Americans gained command of sea & air.Essential for successful operations in Pacific Islands.Superior ResourcesUS able to produce more aircraft, aircraft carriers and weapons than Japan due to its industrial power.Jp factories constantly bombed, diff to sustain productionIncendiary bombing of Tokyo – bombed to the stone age.
- 46. Why did Japan Lose?Atomic BombShowcased firepower of USThe destruction shocked the Jp military & EmperorNo way Jp could compete with such weaponry.