Robbins_OB13_INS_PPT02.ppt
- 1. Chapter Learning Objectives ’āś After studying this chapter, you should be able to: ŌĆō Contrast the two types of ability. ŌĆō Define intellectual ability and demonstrate its relevance to OB. ŌĆō Identify the key biographical characteristics and describe how they are relevant to OB. ŌĆō Define learning and outline the principles of the three major theories of learning. ŌĆō Define shaping, and show how it can be used in OB. ŌĆō Show how culture affects our understanding of intellectual abilities, biographical characteristics, and learning. 2-0 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 2. Ability An individualŌĆÖs capacity to perform the various tasks in a job. ’āśMade up of two sets of factors: ŌĆō Intellectual Abilities ŌĆó The abilities needed to perform mental activities. ŌĆó General Mental Ability (GMA) is a measure of overall intelligence. ŌĆó Wonderlic Personnel Test: a quick measure of intelligence for recruitment screening. ŌĆó No correlation between intelligence and job satisfaction. ŌĆō Physical Abilities ŌĆó The capacity to do tasks demanding stamina, dexterity, strength, and similar characteristics. 2-1 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 3. Nine Basic Physical Abilities ’āś Strength Factors ŌĆō Dynamic strength ŌĆō Trunk strength ŌĆō Static strength ŌĆō Explosive strength ’āś Flexibility Factors ŌĆō Extent flexibility ŌĆō Dynamic flexibility ’āś Other Factors ŌĆō Body coordination ŌĆō Balance ŌĆō Stamina E X H I B I T 2ŌĆō2 2-2 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 4. Biographical Characteristics Objective and easily obtained personal characteristics. ’āśAge ŌĆō Older workers bring experience, judgment, a strong work ethic, and commitment to quality. ’āśGender ŌĆō Few differences between men and women that affect job performance. ’āśRace (the biological heritage used to identify oneself) ŌĆō Contentious issue: differences exist, but could be more culture-based than race-based. 2-3 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 5. Other Biographical Characteristics ’āś Tenure ŌĆō People with job tenure (seniority at a job) are more productive, absent less frequently, have lower turnover, and are more satisfied. ’āś Religion ŌĆō Islam is especially problematic in the workplace in this post- 9/11 world. ’āś Gender Orientation ŌĆō Federal law does not protect against discrimination (but state or local laws may). ŌĆō Domestic partner benefits are important considerations. ’āś Gender Identity ŌĆō Relatively new issue ŌĆō transgendered employees. 2-4 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 6. Learning Any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience ’āśLearning components: Involves Change Is Relatively Permanent Is Acquired Through Experience 2-5 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 7. Theories of Learning ’āś Classical Conditioning ŌĆō A type of conditioning in which an individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. ’āś Operant Conditioning ŌĆō A type of conditioning in which desired voluntary behavior leads to a reward or prevents a punishment. ’āś Social-Learning Theory ŌĆō People can learn through observation and direct experience. 2-6 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 8. Classical Conditioning ’āś PavlovŌĆÖs Dog Drool ’āś Key Concepts: ŌĆō Unconditioned stimulus ŌĆó A naturally occurring phenomenon. ŌĆō Unconditioned response ŌĆó The naturally occurring response to a natural stimulus. ŌĆō Conditioned stimulus ŌĆó An artificial stimulus introduced into the situation. ŌĆō Conditioned response ŌĆó The response to the artificial stimulus. This is a passive form of learning. It is reflexive and not voluntary ŌĆō not the best theory for OB learning. 2-7 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 9. Operant Conditioning ’āś B. F. SkinnerŌĆÖs concept of Behaviorism: behavior follows stimuli in a relatively unthinking manner. ’āś Key Concepts: ŌĆō Conditioned behavior: voluntary behavior that is learned, not reflexive. ŌĆō Reinforcement: the consequences of behavior which can increase or decrease the likelihood of behavior repetition. ŌĆō Pleasing consequences increase likelihood of repetition. ŌĆō Rewards are most effective immediately after performance. ŌĆō Unrewarded/punished behavior is unlikely to be repeated. 2-8 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 10. Social-Learning Theory ’āś Based on the idea that people can also learn indirectly: by observation, reading, or just hearing about someone elseŌĆÖs ŌĆō a modelŌĆÖs ŌĆō experiences. ’āś Key Concepts: ŌĆō Attentional processes ŌĆó Must recognize and pay attention to critical features to learn. ŌĆō Retention processes ŌĆó ModelŌĆÖs actions must be remembered to be learned. ŌĆō Motor reproduction processes ŌĆó Watching the modelŌĆÖs behavior must be converted to doing. ŌĆō Reinforcement processes ŌĆó Positive incentives motivate learners. 2-9 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 11. Shaping: A Managerial Tool Systematically reinforcing each successive step that moves an individual closer to the desired response. ’āśFour Methods of Shaping Behavior: ŌĆō Positive reinforcement ŌĆó Providing a reward for a desired behavior (learning) ŌĆō Negative reinforcement ŌĆó Removing an unpleasant consequence when the desired behavior occurs (learning) ŌĆō Punishment ŌĆó Applying an undesirable condition to eliminate an undesirable behavior (ŌĆ£unlearningŌĆØ) ŌĆō Extinction ŌĆó Withholding reinforcement of a behavior to cause its cessation (ŌĆ£unlearningŌĆØ) 2-10 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 12. Schedules of Reinforcement: A Critical Issue ’āś Two Major Types: ŌĆō Continuous Reinforcement ŌĆó A desired behavior is reinforced each time it is demonstrated ŌĆō Intermittent Reinforcement ŌĆó A desired behavior is reinforced often enough to make the behavior worth repeating but not every time it is demonstrated ŌĆó Multiple frequencies 2-11 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 13. Types of Intermittent Reinforcement ’āś Ratio ŌĆō Depends on the number of responses made. ’āś Interval ŌĆō Depends on the time between reinforcements. ’āś Fixed ŌĆō Rewards are spaced at uniform time intervals or after a set number of responses. ’āś Variable ŌĆō Rewards that are unpredictable or that vary relative to the behavior. 2-12 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
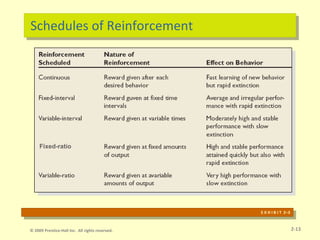
- 14. Schedules of Reinforcement E X H I B I T 2ŌĆō3 Fixed-ratio 2-13 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 15. Behavior Modification (OB Mod) The application of reinforcement concepts to individuals in the work setting ’āśFollows the Five-Step Problem-Solving Model 1 ŌĆó Identify critical behaviors 2 ŌĆó Develop baseline data 3 ŌĆó Identify behavioral consequences 4 ŌĆó Develop and apply intervention 5 ŌĆó Evaluate performance improvement 2-14 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
- 16. Problems with OB Mod and Reinforcement ’āś OB Mod ignores thoughts and feelings. ’āś OB Mod may not explain complex behaviors that involve thinking and feeling. ’āś Stimuli may not be consciously given as a means of shaping behavior. Modern managers and OB theorists are using cognitive approaches to shaping behavior. 2-15 ┬® 2009 Prentice-Hall Inc. All rights reserved.