Role of manager_129
- 1. What Is Organizational Behavior?
- 2. Managers Organization Individuals who achieve goals through other people. A consciously coordinated social unit, composed of two or more people, that functions on a relatively continuous basis to achieve a common goal or set of goals. What Managers Do
- 3. Management Functions Planning- Includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities. Organizing - Determining what tasks are to be done, who is to do them, how are tasks to be grouped, who reports to whom and where decisions are to be made. Leading - Includes Motivating subordinates, directing others, selecting the most effective communication channels, and resolving conflicts. Controlling- Monitoring activities to ensure they are being accomplished as planned and correcting any significant deviations.
- 4. Managements Roles Based on a study, Henry Mintzberg concluded that managers performed 10 different roles. These ten roles can be grouped into: 1. Interpersonal Roles 2. Informational Roles 3. Decisional Roles
- 5. Interpersonal Roles Acknowledgment of mail external board work Maintains a network of outside contacts who provide favors and information Liaison Virtually all managerial activities involving subordinates. Responsible for the motivation and direction of subordinates Leader Ceremonies status requests, solicitations Symbolic head; required to perform a number of routine duties of a legal or social nature Figurehead Examples Description Role
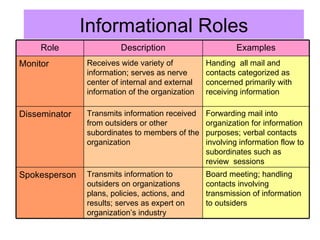
- 6. Informational Roles Board meeting; handling contacts involving transmission of information to outsiders Transmits information to outsiders on organizations plans, policies, actions, and results; serves as expert on organizationĪ»s industry Spokesperson Forwarding mail into organization for information purposes; verbal contacts involving information flow to subordinates such as review sessions Transmits information received from outsiders or other subordinates to members of the organization Disseminator Handing all mail and contacts categorized as concerned primarily with receiving information Receives wide variety of information; serves as nerve center of internal and external information of the organization Monitor Examples Description Role
- 7. Decisional Roles Contract negotiation Responsible for representing the organization at major negotiations Negotiator Scheduling ; requests for authorization; budgeting, the programming of subordinates work Making or approving significant organizational decisions Resource allocator Strategy and review sessions involving disturbances and crises Responsible for corrective action when organization faces important, unexpected disturbances Disturbance handler Strategy and review sessions involving initiation or design of improvement projects Searches organization and its environment for opportunities and initiates projects to bring about change Entrepreneur Examples Description Role
- 8. Management Skills Robert Katz The mental ability to analyze and diagnose complex situations. CONCEPTUAL SKILLS The ability to work with, understand, and motivate other people both individually and in group HUMAN SKILLS The ability to apply specialized knowledge expertise. TECHNICAL SKILLS
Editor's Notes
- #4: According to Henri Fayol every manager perform 5 functions they Plan, organize, command, coordinate and control.