Rotavirus
- 1. SAURABH WANI PGDPM 10 GARWARE COLLEGE ROTAVIRUS
- 2. INTRODUCTION ïRotaviruses are the major cause of diarrheal illness in human infants in the world ïAdults also get infected because of rotavirus ïYoung animals like calves and piglets are also infected ïRotavirus infection spread easily and outbreaks usually occur in the winter and early spring between about November and April ïRotavirus infections often spread in settings where many children's are together, such as daycare centers
- 3. âTRANSMISSION OF ROTAVIRUSâ ïPrimary mode of rotavirus transmission is fecal to oral ïHighly communicable and transmissible disease ïClose person to person contact and environmental surfaces are common vectors of transmission ïIncubation period is 1-3 days ïLarge quantities of virus are shed in stool from just prior to onset of symptoms until about 10 days after onset ïAmount of virus shed in stool [10-100 billion virion/gram of stool]infection ïAmount of ingested virus required to cause infection as few as 10 infective virions
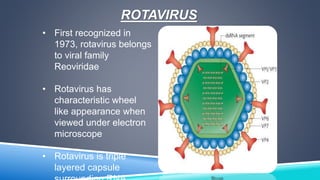
- 4. ROTAVIRUS âĒ First recognized in 1973, rotavirus belongs to viral family Reoviridae âĒ Rotavirus has characteristic wheel like appearance when viewed under electron microscope âĒ Rotavirus is triple layered capsule surrounding RNA
- 5. âĒ The Rotavirus genome consist of 11 double stranded RNA segments each encoding one viral proteins âĒ Scientist have describe seven Rotavirus group [A to G] âĒ Only groups A, B AND C infect humans âĒ Group A which has multiple strains cause majority of childhood infections âĒ Vaccine candidates are designed to protect against group A Rotaviruses âĒ The G type and P type define the serotype âĒ They are critical to a vaccine development because they are the vaccine for stimulating a protective immune response
- 6. â SEROTYPESâ ïSerotypes are described as variations within species of bacteria or viruses or among immune cells of different individuals G1P[8] is the most common serotype worldwide and accounts for over two thirds of rotavirus infections worldwide Infections with G1,G2,G3,G4 AND G9 together comprise almost 95% of rotavirus serotype observed Because the two gene segments that encode these protein can segregate independently, A typing system which consist of both G and P type is used i.e. G1P[8],G2P[4],G3P[8],G4P[8],G9P[8] and G9P[6]
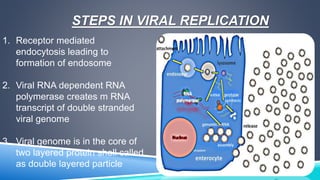
- 7. STEPS IN VIRAL REPLICATION 1. Receptor mediated endocytosis leading to formation of endosome 2. Viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase creates m RNA transcript of double stranded viral genome 3. Viral genome is in the core of two layered protein shell called as double layered particle
- 8. VIRAL REPLICATION 4. Third layer is disrupted 5. By remaining in the core, the viral RNA evades innate host immune responses called RNA interference that are triggered by the presence of double-stranded RNA 6. Viroplasm is formed around the cell nucleus as early as two hours after virus infection, and consists of viral factories thought to be made by two viral nonstructural proteins: NSP5 and NSP2
- 9. 7. In this viroplasm RNA is replicated and the DLPs are assembled 8. The DLPs migrate to the endoplasmic reticulum where they obtain their third, outer layer 9. Progeny viruses are released from the cell by lysis
- 10. WHY ROTAVIRUS INFECTION CAUSES DIARRHEA ïInfection of villus epithelial cells causes cell destruction, decreased absorption of salt and water and decreased dissachridase activity leading to osmotic load in the gut lumen ï The osmotic load in the gut and increased fluid secretion leads to diarrhea and without fluid replacement it will ultimately lead to dehydration and acidosis ï Rotavirus induced gastroenteritis in children with immunodeficiency may cause persistent infections lasting weeks or months
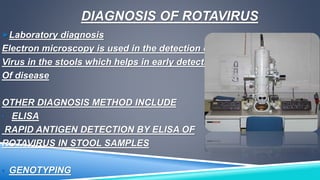
- 11. DIAGNOSIS OF ROTAVIRUS INFECTION Diagnosis of infection with Rotavirus follows diagnosis of gastroenteritis of severe diarrhea Most children's are admitted to hospital with gastroenteritis are tested for Rotavirus A Specific diagnosis of infection with rotavirus A is made by finding the virus in childâs stool by enzyme immunoassay Children with immunodeficiency disorders may be treated with specific rotavirus immunoglobulin preparation
- 12. DIAGNOSIS OF ROTAVIRUS ïLaboratory diagnosis Electron microscopy is used in the detection of Virus in the stools which helps in early detection Of disease OTHER DIAGNOSIS METHOD INCLUDE âĒ ELISA RAPID ANTIGEN DETECTION BY ELISA OF ROTAVIRUS IN STOOL SAMPLES âĒ GENOTYPING
- 13. TREATMENT FOR ROTAVIRUS DIARRHEA ïTherapy for rotavirus induced diarrhea involves replacement of fluid and electrolyte loss during infection ïORAL REHYDRATION THERAPY is recommended in children with mild or moderate dehydration ïFruit juices and soft drinks are not recommended due to there high glucose content low sodium content and high osmolarity ï Antibiotics, antisecretory drugs, antimotility drugs, absorbents and antiemeticâs Do not clear acute infection but it prevents reinfection and reduce fluid losses during rotavirus induced gastroenteritis and hence do not play role in treatment
- 14. INFECTION CONTROL Home and daycare facilities 1.HAND WASHING AREAS 2.Food preparation areas 3.Diaper changing surfaces 4.Diaper disposable containers 5.Toys Hospital areas and clinics 1.HAND WASHING AREAS 2.Medication preparation areas 3.Equipment 4.Patient care areas
- 15. Rotavirus vaccine - Two oral,live,attenuated rotavirus vaccines
- 17. INDIA UNVEILS FIRST INDIGENOUS ROTAVIRUS VACCINE ïRotavirus responsible for approximately 4,53,000 child deaths due to diarrhea globally each year ïThe Phase-III clinical trial of low cost Indian-made rotavirus vaccine Rotavac has demonstrated strong efficacy and excellent safety profile and if approved by the Drugs Controller General of India, it would be available at Rs. 54 per dose. ïClinical study has demonstrated for the first time that Rotavac is efficacious in preventing severe rotavirus diarrhea in low-resource settings in India, and developing countries in Asia and Africa. Strain diversity, too, has not apparently affected its efficacy.
- 18. Rotavirus is responsible for approximately 4,53,000 child deaths due to diarrhea globally each year. It is particularly threatening in India where â according to a recent study â around 1,00,000 children die each year from severe diarrhea and dehydration caused by rotavirus. India accounts for 22 per cent of the estimated global deaths from diarrhea-causing rotavirus. Rotavac is an oral vaccine and is administered to infants in a three-dose course at the ages of 6, 10 and 14 weeks. It is given alongside routine immunizations' in the Universal Immunization Programed (UIP) vaccines recommended at these ages.
- 19. The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase-III clinical trial enrolled 6,799 infants in India (aged six to seven weeks at the time of enrolment) at three sites â the Centre for Health Research and Development, Society for Applied Sciences, in New Delhi; Shirdi Sai Baba Rural Hospital, KEM Hospital Research Centre in Vadu; and Christian Medical College in Vellore. Infants received Rotavac and the UIP vaccines, including the oral polio vaccine (OPV). Result showed that infants receiving OPV at the same time as Rotavac generated comparable immune responses to all three polio serotypes as the infants receiving OPV without Rotavac, supporting the concurrent administration of OPV and Rotavac.
- 20. VACCINATING KIDS AGAINST ROTAVIRUS MAY REDUCE RISK OF SEIZURES ïThe researchers found that children who were fully vaccinated against rotavirus had an approximately 20 percent reduced risk of seizure-related hospitalizations and emergency department visits during the year following vaccination, compared to unvaccinated children ïLatest study estimated that rotavirus vaccination could potentially save more than $7 million in U.S. health care costs each year by preventing approximately 1,000 hospitalizations and 5,000 emergency room visits for seizures among young children. "Caring for children who have seizures can be expensive and emotionally taxing for families," Dr. Payne said. "Seizures sometimes lead to painful procedures, medication regimens, trips to the emergency room, or
- 22. THANKYOU


![âTRANSMISSION OF
ROTAVIRUSâ
ïPrimary mode of rotavirus transmission is fecal to oral
ïHighly communicable and transmissible disease
ïClose person to person contact and environmental
surfaces are common vectors of transmission
ïIncubation period is 1-3 days
ïLarge quantities of virus are shed in stool from just prior
to onset of symptoms until about 10 days after onset
ïAmount of virus shed in stool [10-100 billion virion/gram
of stool]infection
ïAmount of ingested virus required to cause infection as
few as 10 infective virions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-3-320.jpg)
![âĒ The Rotavirus genome consist of 11 double stranded
RNA segments each encoding one viral proteins
âĒ Scientist have describe seven Rotavirus group [A to
G]
âĒ Only groups A, B AND C infect humans
âĒ Group A which has multiple strains cause majority of
childhood infections
âĒ Vaccine candidates are designed to protect against
group A Rotaviruses
âĒ The G type and P type define the serotype
âĒ They are critical to a vaccine development because
they are the vaccine for stimulating a protective
immune response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-5-320.jpg)
![â SEROTYPESâ
ïSerotypes are described as variations within species of
bacteria or viruses or among immune cells of different
individuals
G1P[8] is the most common serotype worldwide and
accounts for over two thirds of rotavirus infections
worldwide
Infections with G1,G2,G3,G4 AND G9 together
comprise almost 95% of rotavirus serotype observed
Because the two gene segments that encode these
protein can segregate independently, A typing system
which consist of both G and P type is used i.e.
G1P[8],G2P[4],G3P[8],G4P[8],G9P[8] and G9P[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-6-320.jpg)