Rotylenchus
- 1. Reniform nematode R. reniformis Prepared by R MOHANAPRIYA Assisstant Professor (Plant Pathology) JSA College of Agriculture and Technology, Ma. Podaiyur, Cuddalore district, Tamilnadu
- 2. First recorded in India is cotton by Seshadri & Sivakumar 1963 Systematic position Phylum : Nematoda Class : Secernentea Order : Tylenchida Suborder : Tylenchina Super family : Tylenchoidea Family : Hoplolaimidae Sub-family : Rotylenchulinae Genus : Rotylenchulus Species : R. reniformis (reniform/kidney shape of mature females) Major hosts : Cotton, cowpea, castor, papaya and vegetables Type of parasitism : Semiendoparasite
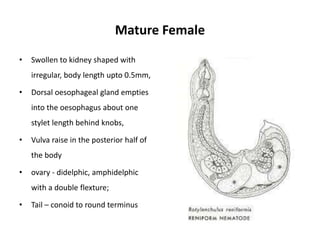
- 3. Mature Female ŌĆó Swollen to kidney shaped with irregular, body length upto 0.5mm, ŌĆó Dorsal oesophageal gland empties into the oesophagus about one stylet length behind knobs, ŌĆó Vulva raise in the posterior half of the body ŌĆó ovary - didelphic, amphidelphic with a double flexture; ŌĆó Tail ŌĆō conoid to round terminus
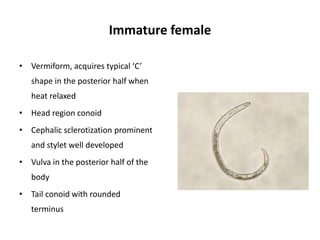
- 4. Immature female ŌĆó Vermiform, acquires typical ŌĆśCŌĆÖ shape in the posterior half when heat relaxed ŌĆó Head region conoid ŌĆó Cephalic sclerotization prominent and stylet well developed ŌĆó Vulva in the posterior half of the body ŌĆó Tail conoid with rounded terminus
- 5. Juvenile Resembling immature female but shorter, lacking vulva and genital tracts. Head of female
- 6. Male ŌĆó Vermiform ŌĆó Cephalic sclerotization ŌĆó Stylet and oesophagus reduced, ŌĆó Weak median bulb; ŌĆó Tail ŌĆō curved, pointed, ŌĆó Bursa absent sometimes present but not reaching upto tail tip Tail Head
- 7. Biology and life cycle ’é¦ Sedentary semiendoparasite on roots ’é¦ The pre-adult female(immature female) is infective stage. ’é¦ Vermiform females insert their anterior most region of the body into the root and start swelling, becoming kidney shaped(mature female). ’é¦ Gelatinous matrix is secreted by the female around the body in which eggs are deposited. ’é¦ Second stage juveniles undergo three moults in the soil. ’é¦ Third and fourth stage juveniles do not shed the old cuticle.
- 8. ’é¦ The nematode can feed upon cortical, pericycle, endodermis and phloem cells and results in the formation of syncytium due to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the cells ’é¦ Life cycle- 25 days 25-30oC ’é¦ Lomy and clay loam soils are favourable for reproduction of reniform nematode ’é¦ Males are non parasitic, but reproduction is by amphimixis ’é¦ Reniform namatode plays an imporatant role in the Fusarium & Verticillium wilts of cotton
- 10. Control ŌĆó Deep Summer Ploughing during May/June 2-3 times at 10-15 days interval can be effective in killing most of the nematode population. ŌĆó Grow non hosts such as Onion, Garlic, Turnip, Carrot etc., for 1- 2years in rotation ŌĆó In bold seeded crops nematicidal seed coating with Carbosulfan 3% w/w, Fensulfothion 2% and Oxamyl has been found effective