Rouault sfn2014
- 1. INTEGRATION OF VALUES AND INFORMATION IN DECISION-MAKING 1 Marion ROUAULT, Jan DRUGOWITSCH and ├ētienne KOECHLIN Laboratoire de Neurosciences Cognitives INSERM U960, Ecole Normale Sup├®rieure, Paris
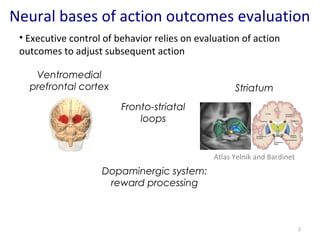
- 2. Neural bases of action outcomes evaluation 2 ŌĆó Executive control of behavior relies on evaluation of action outcomes to adjust subsequent action Fronto-striatal loops Striatum Atlas Yelnik and Bardinet Ventromedial prefrontal cortex Dopaminergic system: reward processing
- 3. Working hypothesis Action outcomes may convey two types of value signals: - ŌĆ£RewardingŌĆØ value : valorisation for the action outcome over an axis of subjective preferences - ŌĆ£InformationalŌĆØ value : information transmitted by the action outcome about choice reliability (probability that, in the current situation, the chosen action was the most appropriate) 3 Reinforcement learning Simple, rapid, phylogenetically old Bayesian inference Sophisticated, rapidly saturated How are processed rewarding and informational aspects of action outcomes? What are their neural and functional interaction?
- 4. Probabilistic reversal learning task Correct state is rewarded 80 % of the time + reversals ŌĆó States : 4 ŌĆó Values : 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 Ōé¼ before decision, range 1:11 Ōé¼ after decision ŌĆó Minimal instructions
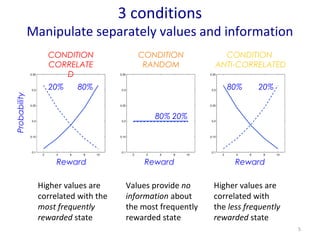
- 5. 3 conditions Manipulate separately values and information CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM 20% 80% 80% 20% Values provide no information about the most frequently rewarded state Higher values are correlated with the most frequently rewarded state Higher values are correlated with the less frequently rewarded state 5 Reward 80% 20% Probability Reward Reward CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED
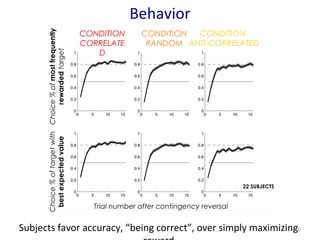
- 6. Behavior Choice % of most frequently rewarded target CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM Subjects favor accuracy, ŌĆ£being correctŌĆØ, over simply maximizing 6 reward Choice % of target with best expected value Trial number after contingency reversal 22 SUBJECTS
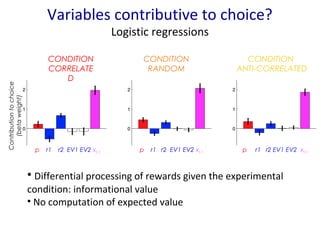
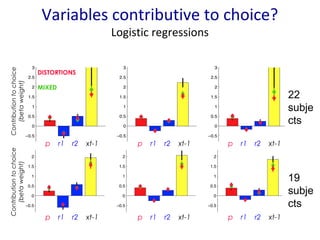
- 7. Variables contributive to choice? Logistic regressions Contribution to choice (beta weight) CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED CONDITION RANDOM p r1 r2 EV1 EV2 xt-1 p r1 r2 EV1 EV2 xt-1 p r1 r2 EV1 EV2 xt-1 ŌĆó Differential processing of rewards given the experimental condition: informational value ŌĆó No computation of expected value
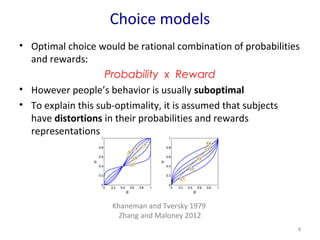
- 8. Choice models ŌĆó Optimal choice would be rational combination of probabilities and rewards: Probability x Reward ŌĆó However peopleŌĆÖs behavior is usually suboptimal ŌĆó To explain this sub-optimality, it is assumed that subjects have distortions in their probabilities and rewards representations 8 Khaneman and Tversky 1979 Zhang and Maloney 2012
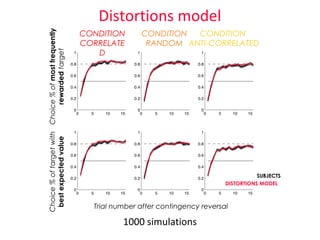
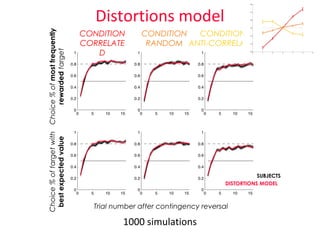
- 9. 1000 simulations SUBJECTS DISTORTIONS MODEL Distortions model CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM Choice % of most frequently rewarded target Choice % of target with best expected value Trial number after contingency reversal
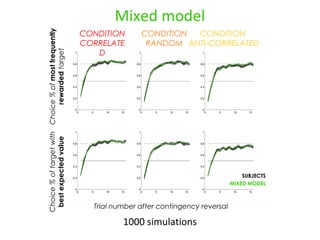
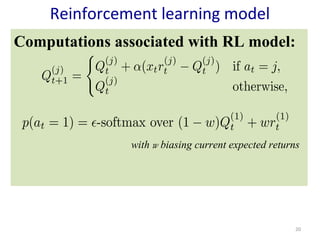
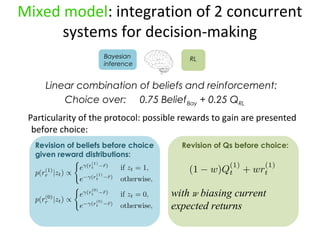
- 10. Mixed model: integration of 2 concurrent systems for decision-making Bayesian RL inference Combination of beliefs and reinforcement: Choice over: 0.75 BeliefBay + 0.25 QRL Particularity of the protocol: possible rewards to gain are presented before choice: Revision of beliefs before choice Revision of Qs before choice: given reward distributions: Qt+1 = Qt + ╬▒ (Rt ŌĆō Qt) (1 ŌĆō w)Qt + wRt with w biasing current expected returns
- 11. 1000 simulations SUBJECTS MIXED MODEL Mixed model CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM Choice % of most frequently rewarded target Choice % of target with best expected value Trial number after contingency reversal
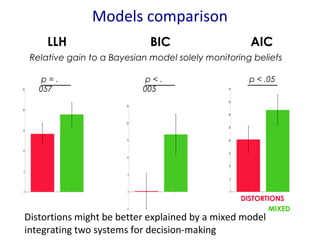
- 12. LLH BIC AIC Relative gain to a Bayesian model solely monitoring beliefs DISTORTIONS MIXED p = . 057 Models comparison p < . 005 p < .05 Distortions might be better explained by a mixed model integrating two systems for decision-making
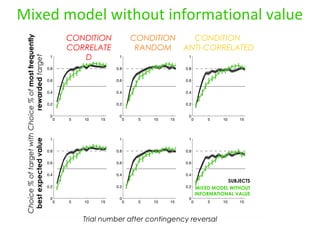
- 13. Mixed model without informational value Choice % of most frequently rewarded target Choice % of target with best expected value CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED Trial number after contingency reversal SUBJECTS MIXED MODEL WITHOUT INFORMATIONAL VALUE
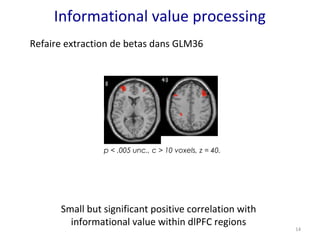
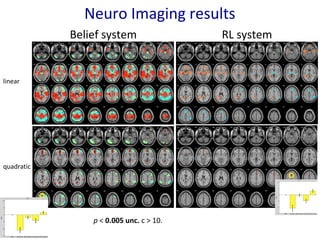
- 14. 14 Informational value processing Refaire extraction de betas dans GLM36 p < .005 unc., c > 10 voxels, z = 40. Small but significant positive correlation with informational value within dlPFC regions
- 15. p < 0.005 unc. c > 10. linear quadratic Neuro Imaging results Belief system RL system
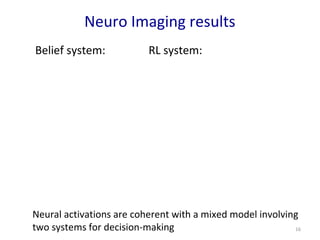
- 16. Neuro Imaging results 16 Belief system: RL system: Neural activations are coherent with a mixed model involving two systems for decision-making
- 17. Summary ŌĆó The product of the distortions is actually explained by an integration of two systems for decision-making ŌĆó Rewarding value: network involving ŌĆó Informational value: network involving dlPFC, 17 Reinforcement learning Simple, rapid, phylogenetically old Bayesian inference Sophisticated, rapidly saturated
- 18. Acknowledgments Frontal lobe functions team 18
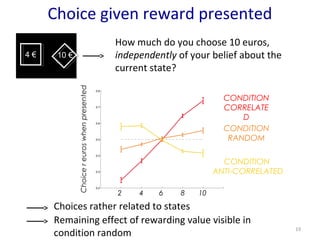
- 19. Choice given reward presented CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED Choice r euros when presented 19 4 Ōé¼ 10 Ōé¼ How much do you choose 10 euros, independently of your belief about the current state? 2 4 6 8 10 Choices rather related to states Remaining effect of rewarding value visible in condition random
- 20. 20 Reinforcement learning model Computations associated with RL model: with w biasing current expected returns
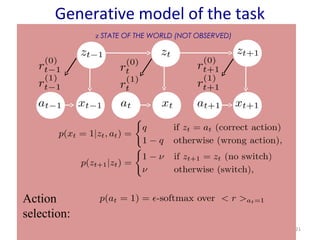
- 21. 21 Generative model of the task Action selection: z STATE OF THE WORLD (NOT OBSERVED)
- 22. Variables contributive to choice? Logistic regressions p r1 r2 xt-1 p r1 r2 xt-1 p r1 r2 xt-1 Contribution to choice (beta weight) Contribution to choice (beta weight) DISTORTIONS MIXED 22 subje cts 19 subje cts p r1 r2 xt-1 p r1 r2 xt-1 p r1 r2 xt-1
- 23. 1000 simulations SUBJECTS DISTORTIONS MODEL Distortions model CONDITION ANTI-CORRELATED CONDITION CORRELATE D CONDITION RANDOM Choice % of most frequently rewarded target Choice % of target with best expected value Trial number after contingency reversal
- 24. Mixed model: integration of 2 concurrent systems for decision-making Bayesian RL inference Linear combination of beliefs and reinforcement: Choice over: 0.75 BeliefBay + 0.25 QRL Particularity of the protocol: possible rewards to gain are presented before choice: Revision of beliefs before choice given reward distributions: Revision of Qs before choice: with w biasing current expected returns
Editor's Notes
- #3: Executive control of behavior relies on evaluation of action outcomes for immediate and future choices of actions Two main brain regions are known to be involved in this evaluation process: ventromedial prefrontal cortex, and a basal ganglium: the striatum. These two structures are linked by recurrent fronto-striatal loops that link the neurons of the two structures. These structures are also a target of the dopaminergic system, involved in positive and negative outcomes processing. However, the respective roles of these two regions are not clear yet and their functional interaction is not understood, since these two regions generally activate together in protocols
- #4: We have been working on the hypothesis that action outcomes may convey two types of value signals: - Rewarding value, representing the valorisation of an action outcome over an axis of subjective preferences, such as sugary or monetary values Informational value, modulating subjectsŌĆÖ belief about the appropriate action in a given situation We think in previous studies these two aspects have been intrinsically linked, and protocols were not able to dissociate them, and probably in natural settings these two values usually come together (obtaining a reward informs you that you have chosen an appropriate action) These two values are the product of two distinct adaptive computational models : We developed a paradigm that allows dissociation of both value signals
- #5: Healthy human subjects had to make a decision between two targets representing two underlying states. The potential rewards to gain for each target were displayed before each choice: Subjects were told to maximize rewards and were instructed that one of the two targets led to obtain the target more frequently than the other shape, and the more frequently rewarded shape would change from time to time along the experiment A key point of the protocol was to decorrelate rewarding value frominformational value, by manipulating the reward distributions underlying each target
- #6: First condition : reward is uninformative about the hidden state Second condition : ╬│ &gt; 0 implies that choosing the high reward is better Third condition : ╬│ &lt; 0 implies that choosing a low reward is better
- #7: On a total of 25 subjects so far, 3 subjects were removed for systematically choosing the highest of the 2 displayed rewards in all conditions DETAIL WHAT IS PLOTTED HERE
- #8: Subsample of 19 subjects to remove outlier responses to xt-1
- #9: In this kind of economic task, optimal choice would be a rational combination of probabilities and rewards: p x r and choose the maximum quantity However, the observed behavior is usually suboptimal But it is often assumed to explain this sub-optimality that people have distortions in their representations of probabilities and reward, which can have different shapes given of each subjects individual deformations
- #10: We can see on this learning curves, and on other behavioral measures, that our distortions model consists of a good phenomenological description of behavior The problem with this model is that it does not provide a psychological explanation for the origin of distortions. As shown by our logistic regressions, subjects combine beliefs about states and rewards in another manner, not in the form of the calculation of expected value
- #11: Model used for GLM32 : BAY3_StdRL_combined_normQ_uniqw_sls3SPIVI_noini_bornw_borngamma
- #13: Paired t tests
- #14: Simus th├®oriques
- #15: Regions within dlPFC show small but significant positive correlation with informational value
- #22: You have a belief about the current state. You observe evidence (xt). You update your belief about the world using bayesian inference Bayes theorem allows to formally incorporate prior knowledge into computing statistical probabilities STATE OF THE WORLD (NOT OBSERVED) REWARD ARE OBSERVED BEFORE DECISION SEQUENCE OF FEEDBACKS (OBSERVED)
- #24: Distortions model consists of a good phenomenological description of behavior, but it does not provide a psychological explanation for the origin of distortions.
- #25: Model used for GLM32 : BAY3_StdRL_combined_normQ_uniqw_sls3SPIVI_noini_bornw_borngamma