Routing Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks.pptx
- 1. ROUTING TECHNIQUES IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS: A SURVEY Presented By: Abbas Kazerouni EE 360 paper presentation, winter 2014, EE Department, Stanford University JAMAL N. AL-KARAKI, AHMED E. KAMAL, 2004 1
- 2. OUTLINE ïĒ Challenges in WSNs ïĒ Categorization based on Network Structure ïĒ Flat-Based Routing ïĒ Hierarchical-Based Routing ïĒ Location-Based Routing ïĒ Categorization based on Protocol Operation ïĒ Summary 2
- 3. CHALLENGES IN WSNS ïĒ No global ID addressing ïĒ IP-based protocols do not apply ïĒ Stationary nodes ïĒ Constraints on energy, storage and processing capacity ïĒ High redundancy in different sensorsâ data 3
- 4. NETWORK STRUCTURE CATEGORIZATION 4 Routing Protocols Flat-Based Hierarchical-Based Location-Based
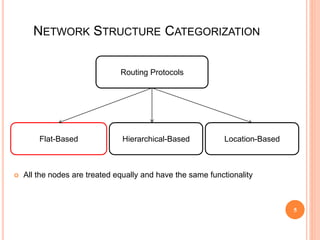
- 5. 5 NETWORK STRUCTURE CATEGORIZATION 5 Routing Protocols Flat-Based Hierarchical-Based Location-Based ïĒ All the nodes are treated equally and have the same functionality
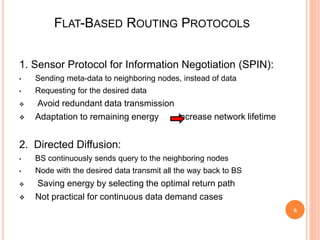
- 6. FLAT-BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS 1. Sensor Protocol for Information Negotiation (SPIN): âĒ Sending meta-data to neighboring nodes, instead of data âĒ Requesting for the desired data ïķ Avoid redundant data transmission ïķ Adaptation to remaining energy increase network lifetime 2. Directed Diffusion: âĒ BS continuously sends query to the neighboring nodes âĒ Node with the desired data transmit all the way back to BS ïķ Saving energy by selecting the optimal return path ïķ Not practical for continuous data demand cases 6
- 7. 7 FLAT-BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS 3. Rumor Routing: âĒ Variation of Directed Diffusion âĒ Each node has an event table âĒ Event agent flooding instead of query flooding ïķ Significant energy saving ïķ Good for when number of events is less than queries 4. Minimum Cost Forwarding Algorithm (MCFA): âĒ Each node knows the least cost path between itself and BS âĒ Least cost path can be acquired via initialization ïķ Saving energy by selecting the optimal return path ïķ Good for small networks 7
- 8. 8 NETWORK STRUCTURE CATEGORIZATION 8 Routing Protocols Flat-Based Hierarchical-Based Location-Based ïĒ Higher energy nodes for transmission, lower energy nodes for sensing ïĒ Two layer routing ïĒ Increasing the life time
- 9. HIERARCHICAL ROUTING 9 1. Low Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy(LEACH): âĒ Random and variation Cluster Head (CH) selection âĒ Compression and transmission of arriving data at CHs ïķ Constant monitoring applications ïķ Good for small networks ïķ Extra overhead because of clustering 2. Self Organizing Protocol (SOP): âĒ Mobile sensors to probe the environment âĒ Stationary nodes as the routers âĒ LML algorithm for routing ïķ Energy consumption is less than SPIN
- 10. 10 HIERARCHICAL ROUTING 10 3. Virtual Grid Architecture âĒ Symmetric, non-overlapping clusters with optimal CH âĒ Local and global data aggregation ïķ NP-hard to find the optimal global aggregators 4. Hierarchical power-aware routing âĒ Proximate nodes form zones âĒ Routes through the zones which has maximum minimum residual energy ïķ Dijkstra algorithm can be exploited
- 11. 11 11 NETWORK STRUCTURE CATEGORIZATION 11 Routing Protocols Flat-Based Hierarchical-Based Location-Based ïĒ Sensor nodes are addressed based on their location ïĒ Location are acquired by GPS or via coordination among nodes
- 12. 12 LOCATION-BASED ROUTING 12 1. Geographical Adaptive Fidelity (GAF): âĒ Network divided into zones âĒ Only one node is awake in each zone, the rest sleep ïķ Conserves energy by turning off unnecessary nodes ïķ Increases the network life time 2. SPAN: âĒ Some nodes are selected as coordinators based on their positions âĒ Enough coordinators such that network is three-hop reachable ïķ Not energy efficient as the others
- 13. ROUTING PROTOCOLS BASED ON PROTOCOL OPERATION 1. Multipath routing âĒ Increases fault tolerance âĒ Sophisticated case: have back up paths 2. Query-based routing âĒ Query transmitted and the date is sent back 3. Negotiation-based routing âĒ High-level data description âĒ Elimination of redundant data transmission 4. QoS-baed routing âĒ Balance between data quality and energy consumption 13
- 14. SUMMARY ïĒ WSNs needs have specific characteristics. ïĒ WSNs need specific routing algorithm. ïĒ Large number of algorithms has been designed, but no optimal one! ïĒ Based on the network structure, routing algorithms can be categorized into 3 main groups. ïĒ We briefly discussed some examples of each group. 14