RTOS
- 1. RTOS Introduction ŌĆō HARD AND SOFT REAL TIME SYSTEMS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=- VhJHrnhSrY&list=PLOuGMjEXHeeAcJAO_LFw vP6N_IEIoUpFm&index=1 Video link
- 2. Introduction A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system that guarantees a certain capability within a specified time constraint. Difference between a general purpose and Real time system is General purpose OS: Accuracy or performance oriented Real Time OS: Time or deadline oriented
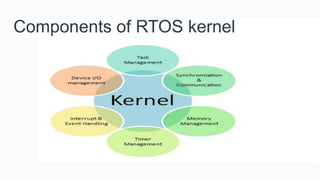
- 4. Components of RTOS kernel
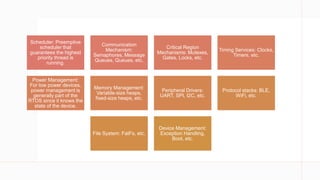
- 5. Scheduler: Preemptive scheduler that guarantees the highest priority thread is running. Communication Mechanism: Semaphores, Message Queues, Queues, etc. Critical Region Mechanisms: Mutexes, Gates, Locks, etc. Timing Services: Clocks, Timers, etc. Power Management: For low power devices, power management is generally part of the RTOS since it knows the state of the device. Memory Management: Variable-size heaps, fixed-size heaps, etc. Peripheral Drivers: UART, SPI, I2C, etc. Protocol stacks: BLE, WiFi, etc. File System: FatFs, etc. Device Management: Exception Handling, Boot, etc.
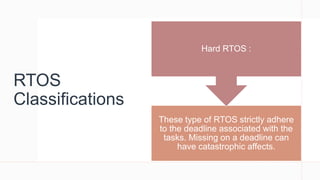
- 6. RTOS Classifications These type of RTOS strictly adhere to the deadline associated with the tasks. Missing on a deadline can have catastrophic affects. Hard RTOS :
- 7. Firm RTOS : These type of RTOS are also required to adhere to the deadlines because missing a deadline may not cause a catastrophic affect but could cause undesired affects, like a huge reduction in quality of a product which is highly undesired.
- 8. Soft RTOS : In these type of RTOS, missing a deadline is acceptable.
- 9. Features of RTOS Occupy very less memory Consume fewer resources Response times are highly predictable Unpredictable environment The Kernel saves the state of the interrupted task ad then determines which task it should run next. The Kernel restores the state of the task and passes control of the CPU for that task.
- 10. TERMS THAT WE USE Task ŌĆō A set of related tasks that are jointly able to provide some system functionality. Job ŌĆō A job is a small piece of work that can be assigned to a processor, and that may or may not require resources. Release time of a job ŌĆō It's a time of a job at which job becomes ready for execution. Execution time of a job: It is time taken by job to finish its execution. Deadline of a job: It's time by which a job should finish its execution. Maximum It is the allowable response time of a job is called its relative deadline. Response time of a job: It is a length of time from the release time of a job when the instant finishes. Absolute deadline: This is the relative deadline, which also includes its release time.