Safe netizens
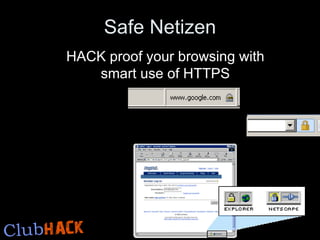
- 1. Safe Netizen HACK proof your browsing with smart use of HTTPS
- 2. SSL / HTTPS Supposedly Secure Layer HTTPS uses SSL to create a unique set of keys called Public & Private key used to encrypt the communication This can°Øt be forged BUT impersonated There is no perfect impersonation & slightest of change will through a warning. User MUST NOT ignore these warnings
- 8. ?
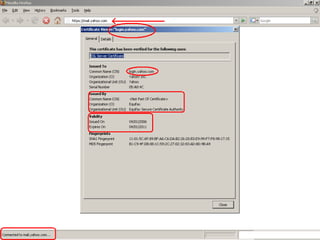
- 9. How to check ?
- 10. ?
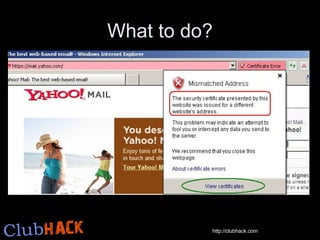
- 11. What to do?
- 12. ?
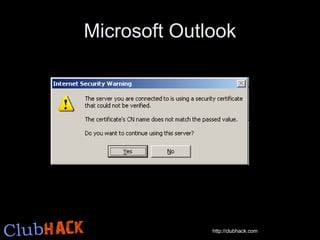
- 13. Am I getting HACKED? Someone might be trying to do a MITM attack Attacker will capture the traffic between your computer & server Can°Øt decrypt HTTPS traffic if it uses valid certificate Will impersonate the certificate Encrypt your data with HIS certificate, decrypt the same at his end, encrypt again with original server certificate & send to server YOU ARE HACKED!
- 14. OK, I get valid certificates But you are still not secure Most of the websites uses only password authentication over HTTPS Your mails/traffic still goes in plain text. WHY ??? Its an expensive mechanism (time & effort) A trade-off between speed & security
- 15. So what to do? Try using mail clients (thunderbird / outlook / whatever) rather than web browser Atleast all the traffic is encrypted, it adds a little latency though, but on the other hand gives me ease to manage my mails Change the URL & force it to go over HTTPS That°Øs for emails, what for other apps? Use client applications as much as possible
- 16. Nothing is 100% secure But a smart netizen can atleast be 80-90% safe ? ? Q & 42