*Sampling technics pend biologi 13 unp
- 1. SAMPLING TECHNICS BY : Darma Yeliza Putra Yulia Nirwana Fatwa Utami Basic Competence Can Understand about Vegetation sampling Technics Indicator Explain the kinds of vegetation samplingtechnics Do the vegetation sampling with plot or without plot Main Material Vegetation sampling technics 1. Technics with plot 2. Technics without plot
- 3. Sampling technics Defenition Function Mind Map Material Test Type Supporting component With Plot method Without plot method 2 form method Forming of sampling unit
- 4. Sampling technics Defenition Function Mind Map Material Test Type Supporting component With Plot method Without plot method 2 form method Forming of sampling unit
- 6. Defenition The technics use to measure, to know, to get information about a vegetation with fast, easy, less need money, and less need energy. Because we just take some data to represent all data in a vegetation Diferent with Sensus method We must take all of data information about a vegetation and that must invetarisation
- 7. Function To get the validation data with : Easy Fast No more need money No more need the energy
- 8. Supporting component Morphology (life form) of plant Agihan/ persebaran Experiment purpose Prize and energy that need
- 9. Form of sampling unit 1. Quadrat 2. Line/ jalur 3. Point
- 10. Form of sampling unit 1. Quadrat 2. Line/ jalur 3. Point ŌĆó Like square, ŌĆ£long squareŌĆØ, cycle 1. Smanll quadrat for homogen vegetation 2. Big quadrat for heterogen vegetation Characteristic of quadrat /plot 1. Must compose of all plant in a community 2. That habitat in quadrat must homogen By oosting, quadrat can devide into 3 1. Quadrat 10 x 10 m for trees strate 2. 4 x 4 m fot lignosus vegetation strate at undergrowt until 3 m tall 3. 1x 1 m for under vegetation
- 11. PARA PENELITI EKOLOGI HUTAN UMUMNYA MEMBEDAKAN POHON DALAM BEBERAPA TINGKAT PERTUMBUHAN, YAITU : ’ü▒ SEMAI (PERMUDAAN TINGKAT KECAMBAH SAMPAI TINGGI <1,5 M). UKURAN PLOT 1 X 1 ATAU 2 X 2 M ’ü▒ PANCANG (PERMUDAAN DENGAN TINGGI >1,5 M SAMPAI POHON MUDA DENGAN DIAMETER <10 CM). UKURAN PLOT 5 X 5 M. ’ü▒ TIANG (POHON MUDA DENGAN DIAMETER 10 ŌĆō 20 CM). UKURAN PLOT 10 X 10 M ’ü▒ POHON DEWASA (DIAMETER BATANG >20 CM). UKURAN PLOT 20 X 20M (KUSMANA, 1997) Form of sampling unit 1. Quadrat 2. Line/ jalur 3. Point
- 12. Type With plot method Without plot method METODE SPECIES AREA CURVE (MINIMAL AREA) METODE KUADRAT Metode Point Intercept (Metode Titik Sentuh) Metode Line Intercept (Metode Garis Sentuh) Metode Point-Centered Quartered Distance Method (Metode Jarak)
- 13. METODE SPECIES AREA CURVE (MINIMAL AREA) The technics with plot where, we must see the ŌĆ£LUAS TERKECILŌĆØ that represent all of a vegetation characteristic
- 14. METODE KUADRAT The sampling technics like square or cycle with a wide that support by vegetation form Type Base on sum of plot Single plot Multiply plot others Metode jalur/transek Metode garis berpetak Metode kombinasi
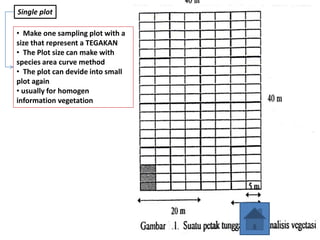
- 15. Single plot ŌĆó Make one sampling plot with a size that represent a TEGAKAN ŌĆó The Plot size can make with species area curve method ŌĆó The plot can devide into small plot again ŌĆó usually for homogen information vegetation
- 16. Multiply plot ŌĆó Use many plot that in area will observe ŌĆó The plot can arrange with sistematis or random
- 18. Metode garis berpetak Modification of technic from multiply plot or jalur method that jump of plots in jalur rintis make the plot and another plot have same distance. 20m x 20m : trees 10m x 10m : poles 5m x 5m : sapling 2m x 2m : seedling/ tumbuhan bawah.
- 19. Metode kombinasi ŌĆó This method is combination between jalur method and line with plot ŌĆó Trees can measure with jalur method with wide 20 m ŌĆó And for poles, sapling, seedling use line with plot method
- 20. Without plot method At the basic concept, this technics use the measure of distance between one plant and anothers plant that have small distance that mean the vegetation is re-peattedly Some advantages : ŌĆó save the time ŌĆó decrease of mistake when make the sampling ŌĆó Decrease of mistake when we say the plant at inner place or outer place
- 21. Metode Point Intercept (Metode Titik Sentuh) ŌĆó Special for herba plant that very rough arrangement ŌĆó Use the point frecuency frame and quadrat point tools ŌĆó The process, with write the plant that first touch by pin of tools How use the point intercept methods? Choose the vegetation we will observe Take the point frecuency frame tools with re- peattedly Write the first plant that have been pin
- 22. Metode Line Intercept (Metode Garis Sentuh) ŌĆó Agree with determine the cover and frecuency at perdu layers ŌĆó Transek change with line form ŌĆó All of tajuk daun that struck by the line must measure the length ŌĆó If the line use 100 m size, so the cover is per 100 m ŌĆó So, if we use the point intercept methods and line intercept methods will get 2 parameters, such as : ŌĆóCover ŌĆófrecuency
- 23. Metode Point-Centered Quartered ŌĆó Special for trees vegetation measure ŌĆó this methods so easy to get information about trees, aspecially for kinds composition, Dominancy level, ŌĆ£menaksirŌĆØ trees volume ŌĆó Character this methods, the trees must in random distribution arrange ŌĆó Make one point at centre and some imagination line that make 4 quadran ŌĆó Chooce one trees for each quadran that near with point and measure the distance between trees and point ŌĆóAnd measure the braest high of trees
- 24. Distance Method (Metode Jarak) ŌĆó Can measure the 3 parameters, such as : cover, frecuency and density ŌĆó Sum of individu can determine with measure distance between for each individu or between sampling point and plant By Grant Cottam dan John Curtis from wisconsin univercity at 1950-an ŌĆó Metode individu terdekat (nearest individual method) ŌĆó Metode titik pusat kuadrat (point-centered quarter method) ŌĆó Metode tetangga terdekat (nearest neighbor method) ŌĆó Metode berpasangan acak (random pairs method)