Scaling with mongo db (with notes)
- 1. Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter 2011 @schmichael Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
- 2. What is MongoDB? Community ŌĆó Developer by 10gen ŌĆó AGPL Database ŌĆó Apache drivers ŌĆó JIRA issue tracking ŌĆó On GitHub Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
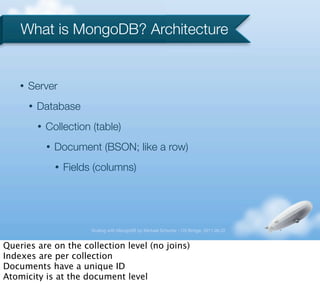
- 3. What is MongoDB? Architecture ŌĆó Server ŌĆó Database ŌĆó Collection (table) ŌĆó Document (BSON; like a row) ŌĆó Fields (columns) Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Queries are on the collection level (no joins) Indexes are per collection Documents have a unique ID Atomicity is at the document level
- 4. What is MongoDB? Documents (2) ŌĆó BSON ŌĆó Open standard: bsonspec.org ŌĆó Binary JSON or protobufs without the schema ŌĆó Objects/Sub-documents/mappings ŌĆó Arrays ŌĆó UTF-8 Strings ŌĆó Floats, Integers (32 or 64 bit) ŌĆó Timestamps, DateTimes ŌĆó Booleans ŌĆó Binary ŌĆó Assorted others speci’¼üc to Mongo's use case (Regex, ObjectID) Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
- 5. What is MongoDB? Querying ŌĆó Querying ŌĆó Dynamic queries (JavaScript code or objects) ŌĆó Map/Reduce (JavaScript functions) ŌĆó Secondary indexes (B-tree, R-tree for simple geospatial) Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
- 6. What is MongoDB? Querying (2) ŌĆó Search by value or inside an array: ŌĆó db.collection.find({tags: "some tag"}) ŌĆó ŌćÆ [{...}, {...}, ...] ŌĆó Update tag lists: ŌĆó update({app: "...", $addToSet: {tags: "another tag"}) ŌĆó No escaping values ŌĆó Declarative┬Āsyntax makes for easy┬Ācomposition Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Must escape keys and insure values arenŌĆÖt objects
- 7. What is MongoDB? Operations ŌĆó Replication ŌĆó Master/Slave ŌĆó Replica Pairs Sets ŌĆó Auto-sharding (data partitioning) ŌĆó Tools ŌĆó mongo shell, mongostat ŌĆó mongo{dump,restore,export,import} Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Multi-master slaves mongo shell is javascript mongostat is *amazing*
- 8. What is(nŌĆÖt) Mongo? Durability ŌĆó Single server durability added in 1.8 (off by default) ŌĆó Preference is Replica Sets ŌĆó No guarantee your data was written with safe=True ŌĆó Use safe=True ŌĆó No guarantee your data was replicated without w=1 ŌĆó If a server goes down, trash itŌĆÖs data and use a slave Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Unknown performance hit for durability Probably worse than systems that ship WALs/journals as part of replication safe=False is literally ’¼üre and forget
- 9. What is MongoDB? Performance ŌĆó I hear itŌĆÖs fast ŌĆó It is until: ŌĆó Your data no longer ’¼üts in memory ŌĆó Your indexes no longer ’¼üt in memory ŌĆó You miss the index (full collection scan) ŌĆó You use safe=True ŌĆó You use w>0 ŌĆó You turn on journaling/durability Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Oodles of marketing Anecdote: Cassandra vs. Memcache
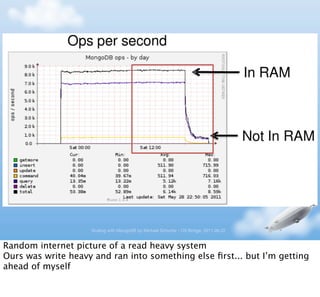
- 10. Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Random internet picture of a read heavy system Ours was write heavy and ran into something else ’¼ürst... but IŌĆÖm getting ahead of myself
- 11. MOAR RAM Rinse; repeat. Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 RAM is probably your single most important resource SSDs would be great Sharding essentially buys you the ability to add RAM forever lol voltdb
- 12. In the beginning ŌĆó Project at YouGov prior to Urban Airship ŌĆó User/group database ŌĆó Was custom datastore, migrated to MongoDB 1.2 ŌĆó Highly recommended to Michael Richardson ŌĆó Single PostgreSQL instance dying under load ŌĆó I snuck into Urban Airship before anything blew up Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 ŌĆó User permissions and profiles were relatively complex ŌĆó Initially stored in a BDB-backed CouchDB-inspired Python service. o Worked fine, a bit slow, major NIH-Syndrome ŌĆó MongoDB (1.2?) to the rescue! o Perfect fit for a small read-heavy, write-light dataset
- 13. Early perf. issue: syncdelay ŌĆó The theory: Durability within a certain time-frame. (default: 60s) ŌĆó Barely documented ŌĆó Never worked for us ŌĆó Syncs would cause infinite block loops: block for 30s, apply backed up writes, block another 30s, never catch up. ŌĆó Just let the kernel handle flushing Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 syncdelay useless with journaling? No hints in docs There are proc tunables for how the kernel handles dirty pages
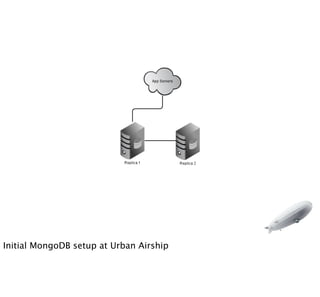
- 14. Initial MongoDB setup at Urban Airship
- 15. Replication ŌĆó Streaming asynchronous replication ŌĆó Streams an oplog; no con’¼éict resolution ŌĆó Master accepts writes, can read from slaves ŌĆó Master + Slaves or... ŌĆó Replica Sets (auto-election & failover) ŌĆó Non-idempotent operations like $inc/$push/etc are changed to their idempotent form: {devices: 1,560} ŌåÆ {$inc: {devices: 1}} ŌćÆ┬Ā{devices: 1,561} Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 But we were using replica pairs which were deprecated before replica sets were even officially released Had a driver + replica sets issue where writes with safe=False went to slave (safe=False means we never saw an error)
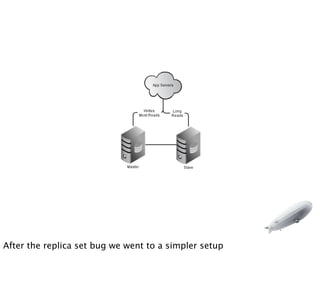
- 16. After the replica set bug we went to a simpler setup
- 17. Locked In ŌĆó MongoDB only has Global (per-server) locks ŌĆó Early versions (~1.2) locked server on every query ŌĆó Later (~1.4) separate read & write locks ŌĆó Present (>=1.6) updates use read lock while seeking ŌĆó Future (1.9?) Per collection locks ŌĆó Moral: Do not run long queries on your master Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Similar to dynamic programming languages Keep indexes in memory to keep read locks short Have fast disks - NOT EBS (See GavinŌĆÖs talk http://bit.ly/j6pR21) https://jira.mongodb.org/browse/SERVER-1240
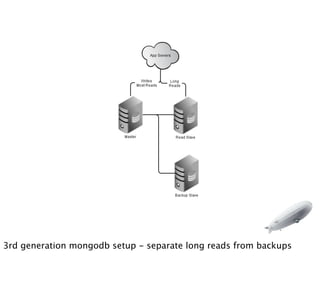
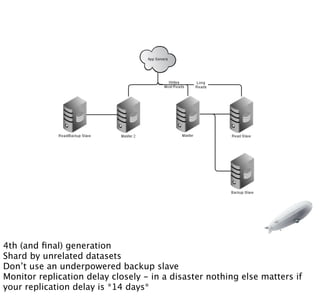
- 18. 3rd generation mongodb setup - separate long reads from backups
- 19. Double (Up)Dating ŌĆó Cause: update(..., {$push: {big object}}) ŌĆó Effect: ŌĆó Big object exceeds document padding ŌĆó Document is moved to end of data ŌĆó Update comes along and re-updates all documents Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Changing your schema can avoid this ... how do you change schemaless dataŌĆÖs schema? not easily IsnŌĆÖt guaranteed to hit all documents, so you canŌĆÖt just $pop once
- 20. Flip/Flop for the Win ŌĆó Data ’¼üles get sparse as documents are moved ŌĆó Indexes could get sparse (getting better & better) ŌĆó Sparse indexes new in 1.8 (have to recreate old indexes) ŌĆó The Solution: Take slave of’¼éine, resync, failover ŌĆó Requires downtime without Replica Sets ŌĆó Future (1.9) - In-place compaction Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Docs are padded to avoid moving; but when they are moved, gaps can grow Poor data locality in disk / in memory Schemaless means lots of space wasted repeating ’¼üeld names / structure In-place - *not* online. Queries & replication stopped before compaction
- 21. When adding RAM isnŌĆÖt enough ŌĆó More RAM doesnŌĆÖt alleviate pain of full server locks ŌĆó You have to write to disk someday ŌĆó Solution: Partition the cluster ŌĆó Good old days: manually shard your data ŌĆó Brave new world (1.6): auto-sharding Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
- 22. Auto-Sharding ŌĆó We donŌĆÖt use it ŌĆó CouldnŌĆÖt get it to work in any of the 1.5 dev releases ŌĆó CouldnŌĆÖt pay me enough to use 1.6.0, maybe safe post 1.8.1 ŌĆó Auto-shards based on a shard-key per collection ŌĆó Order preserving partitioner ŌĆó Querying anything other than the shard-key spams the cluster ŌĆó Each shard should be a Replica Set ŌĆó Run 1 mongos per app server Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Early adopters seemed to all have 10gen support & ŌĆ£special buildsŌĆØ Took down 4sq because adding shards & rebalancing incurs expenses in any distributed system (most? maybe there are clever ways to mitigate...) Much larger ops burden Make the right decisions initially (not totally schemaless)
- 23. 4th (and ’¼ünal) generation Shard by unrelated datasets DonŌĆÖt use an underpowered backup slave Monitor replication delay closely - in a disaster nothing else matters if your replication delay is *14 days*
- 24. Disaster Recovery So what happens when things go *really* wrong?
- 25. EBS Goes on Strike ŌĆó EBS volumes grind to a halt (or at least 1 per RAID) ŌĆó Restore from backup in a different Availability Zone! ŌĆó 4 hours later the restore is still building indexes ŌĆó Wait for EBS to come back or use stale backup data? ŌĆó In the end: EBS came back before restore ’¼ünished. Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 When your HDD locks, MongoDB locks
- 26. mongorestore --indexesLast ŌĆó Always use it ŌĆó Should be On by default ŌĆó Lock database and copy ’¼üles (snapshot) is best Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 Waiting for indexes to build takes approximately as long as it takes AWS engineers to EBS issues.
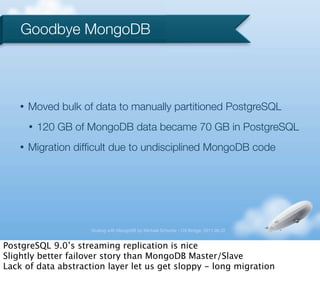
- 27. Goodbye MongoDB ŌĆó Moved bulk of data to manually partitioned PostgreSQL ŌĆó 120 GB of MongoDB data became 70 GB in PostgreSQL ŌĆó Migration dif’¼ücult due to undisciplined MongoDB code Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 PostgreSQL 9.0ŌĆÖs streaming replication is nice Slightly better failover story than MongoDB Master/Slave Lack of data abstraction layer let us get sloppy - long migration
- 28. Moral ŌĆó Test MongoDB for your use case ŌĆó If you canŌĆÖt get auto-sharding working, probably run ŌĆó That goes double for Replica Sets ŌĆó Choose your schema well (especially with sharding) ŌĆó Use short key names + a data abstraction layer ŌĆó {created_time: new DateTime()} 27 bytes ŌĆó {created: new DateTime()} 22 bytes ŌĆó {ct: new DateTime()} 17 bytes Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22 With Auto-sharding *and* Replica Sets, MongoDBŌĆÖs scaling and durability stories are just too scary to trust. YouŌĆÖll thank me when your data ’¼üles are 1/3 smaller.
- 29. Questions? Content, text & diagrams, public domain (steal away) ║▌║▌▀Ż template copyright Urban Airship (sorry) Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22




![What is MongoDB? Querying (2)
ŌĆó Search by value or inside an array:
ŌĆó db.collection.find({tags: "some tag"})
ŌĆó ŌćÆ [{...}, {...}, ...]
ŌĆó Update tag lists:
ŌĆó update({app: "...", $addToSet: {tags:
"another tag"})
ŌĆó No escaping values
ŌĆó Declarative┬Āsyntax makes for easy┬Ācomposition
Scaling with MongoDB by Michael Schurter - OS Bridge, 2011.06.22
Must escape keys and insure values arenŌĆÖt objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalingwithmongodbwithnotes-110623004318-phpapp02/85/Scaling-with-mongo-db-with-notes-6-320.jpg)