Scour around bridge piers
- 1. Scour around Bridge Piers. Mohammad saeed khawam 201401379 Walid Omairi 201401485 Ayman Mansour 201400917
- 2. Basic Components of a Bridge The two basic parts are: • Substructure - includes the piers, the abutments and the foundations. • Superstructure - consists of the deck structure itself, which support the direct loads due to traffic and all the other permanent and variable leads to which the structure is subjected. • The connection between the substructure and the superstructure is usually made through bearings. However, rigid connections between the piers (and sometimes the abutments) may be adopted, particularly in frame bridges with tall (flexible) piers.
- 3. Substructure : Piers Piers are of two basic types: • Column piers - Concrete column piers may have a solid cross-section, or a box section may be the shape chosen for the cross-section for structural and aesthetic reasons. • Wall piers - generally less economical and less pleasing from an aesthetic point of view. They are very often adopted in cases where particular conditions exist, e.g. piers in rivers with significant hydrodynamic actions or in bridges with tall piers where box sections are adopted.
- 4. Basic Types of Bridge Piers
- 5. Bridge scour Bridge scour is the removal of sediment such as sand and rocks from around bridge abutments or piers. Scour, caused by swiftly moving water, can scoop out scour holes, compromising the integrity of a structure. In the United States, bridge scour is one of the three main causes of bridge failure where 46 of 86 major bridge failures resulted from scour near piers from 1961 to 1976.
- 6. Some photos of bridges failed due to the scour of foundation material. Effects of Scour ÔÇûLowering the river bed level around Pier ÔÇûDestabilize the Foundation(Pier)
- 8. Piles exposed to river due to large scour
- 9. Mechanism of Scour Development scour hole: Vortex system formed in front of the obstruction, and has the form of horseshoe River flow and boundary condition give rise to the energy of the vortex Increased shear stress commence local sediment transport
- 10. Local Scour at Piers • Occurs due to the acceleration of flow around the pier and the formation of flow vortices.
- 12. A bridge in the dry season in Sudan
- 14. Protection : Gravel bags : put around pies used for filter function to reduce flow but disadvantages handling cost and potential damage to bags during installation and after a time loose rock due to flow
- 15. Rock Channel Protection at Bridges
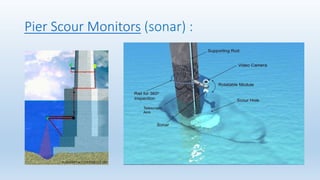
- 17. Pier Scour Monitors (sonar) :
- 19. Thank you Mohammad saeed khawam ---Walid Omairi --- Ayman Mansour