second messenger
- 1. About Second messengers Dr. Yasser Ashour By Dr.Darine Ashraf Dr.Alaa Mamdouh
- 2. Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell to trigger physiological changes such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, andapoptosis. Secondary messengers are therefore one of the initiating components of intracellular signal transduction cascades.
- 4. Examples of second messenger molecules includecyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol trisphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. The cell releases second messenger molecules in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules— the first messengers.
- 7. CAMP PATHWAY Ligands : Epinephrine Ach Primary Effector : Adenyl cyclase Secondary messenger : cAMP
- 9. CGMP PATHWAY Ligands : ANP & NO Primary Effector : Guanylate cyclase Secondary messenger : cGMP
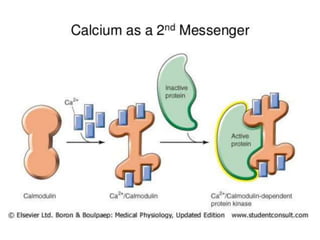
- 14. CALCIUM AS SECOND MESSENGER Calcium ions – once they enter the cytoplasm exert allasteric regulatory effects on many enzymes & protien . Calcium acts as a second messenger by indirect signal transduction pathways such as via G protein – coupled receptors .
- 16. EICOSANOIDS This class of llipids act as signaling molecules that binds to cell surface molecules . They include : Prostaglandins Prostacyclin Thromboxanes Leukotrienes
- 19. GENERAL SCHEMATIC OF SECOND MESSENGER MECHANISM