Seismicretrofitmethods 100415085521-phpapp01
- 1. Seismic Retrofit: Criteria, Weakness & Methods Seismic Retrofit: Criteria, Weakness & Methods by Paul W. McMullin, SE, PhD CRSA Green Brains Seminar June 26, 2008
- 3. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Life Safety Through the Eyes of an SE GET PEOPLE OUT THE DOOR ALIVE GET PEOPLEGET PEOPLE OUT THEOUT THE DOOR ALIVEDOOR ALIVE
- 4. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Life Safety Through the Eyes of an SE The purpose of this code is to establish the minimum requirements to safeguard the public health, safety and general welfare… (IBC 2006, 101.3) The purpose of this code is to establish the minimum requirements to safeguard the public health, safety and general welfare… (IBC 2006, 101.3)
- 5. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Life Safety Through the Eyes of an SE Structural Code generally does not consider: Building economics Business interruption losses Sustainability Structural Code generally does not consider: Building economics Business interruption losses Sustainability
- 6. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Building State After a Major Earthquake Northridge Earthquake Magnitude 6.7 Estimated Economic Loss $49.3 billion Northridge Earthquake Magnitude 6.7 Estimated Economic Loss $49.3 billion PEER (2000)
- 7. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Building State After a Major Earthquake: Northridge SDEDC (1994)
- 8. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Building State After a Major Earthquake: Northridge FEMA (2000)
- 9. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Performance Based Seismic Design: Basics Next generation seismic design methodology Originally developed by FEMA for existing buildings Applicable for new design Considers each element’s energy dissipation capacity Next generation seismic design methodology Originally developed by FEMA for existing buildings Applicable for new design Considers each element’s energy dissipation capacity
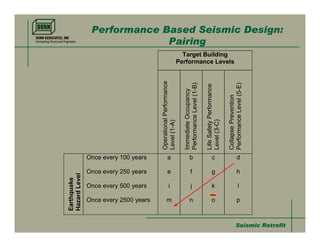
- 10. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Performance Based Seismic Design: Pairing Target Building Performance Levels OperationalPerformance Level(1-A) ImmediateOccupancy PerformanceLevel(1-B) LifeSafetyPerformance Level(3-C) CollapsePrevention PerformanceLevel(5-E) Earthquake HazardLevel Once every 100 years Once every 250 years Once every 500 years Once every 2500 years a e i m b f j n c g k o d h l p
- 11. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Performance Based Seismic Design: Levels & Acceleration Performance levels Operational Immediate Occupancy Life Safety (IBC) Collapse Prevention Performance levels Operational Immediate Occupancy Life Safety (IBC) Collapse Prevention Acceleration Options Typical 50%/50 (1/100 year) 20%/50 (1/250 year) 10%/50 (1/500 year) 2/3 of 2%/50 (IBC) 2%/50 (1/2500 year) Any probability between those listed above Acceleration Options Typical 50%/50 (1/100 year) 20%/50 (1/250 year) 10%/50 (1/500 year) 2/3 of 2%/50 (IBC) 2%/50 (1/2500 year) Any probability between those listed above
- 12. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Damage
- 13. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Damage
- 14. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Masonry Unreinforced Masonry: Everything Reinforced Masonry: (generally perform well) Under-reinforced Ungrouted cells Connections Unreinforced Masonry: Everything Reinforced Masonry: (generally perform well) Under-reinforced Ungrouted cells Connections
- 15. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Concrete Ductility is big issue: Continuous beam reinforcing Hoop spacing Lap splices Under-reinforced (primary) Ductility is big issue: Continuous beam reinforcing Hoop spacing Lap splices Under-reinforced (primary)
- 16. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Concrete EQE (1999 Taiwan)
- 17. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Timber DETAILING Cross grain bending Continuity Shear transfer Undersized Elements Nail pattern too far apart DETAILING Cross grain bending Continuity Shear transfer Undersized Elements Nail pattern too far apart
- 18. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Steel Constraint Full penetration welds Redundancy Material Over strength Constraint Full penetration welds Redundancy Material Over strength FEMA (2000)
- 19. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Common Weaknesses: Steel Constraint Full penetration welds Redundancy Material Over strength Constraint Full penetration welds Redundancy Material Over strength FEMA (2000)
- 20. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Masonry Unreinforced Masonry Post Tensioning Adding Perforations Vertical Wall Coring Slotting Shotcrete Fiber Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Reinforced Masonry Shotcrete FRP Unreinforced Masonry Post Tensioning Adding Perforations Vertical Wall Coring Slotting Shotcrete Fiber Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Reinforced Masonry Shotcrete FRP
- 21. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Masonry
- 22. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Masonry
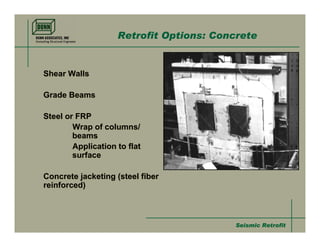
- 23. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Concrete Shear Walls Grade Beams Steel or FRP Wrap of columns/ beams Application to flat surface Concrete jacketing (steel fiber reinforced) Shear Walls Grade Beams Steel or FRP Wrap of columns/ beams Application to flat surface Concrete jacketing (steel fiber reinforced)
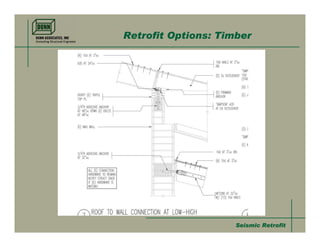
- 24. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Timber Structural Panel overlay Increased nailing Sheet metal blocking Steel Connectors (Simpson is our friend) Structural Panel overlay Increased nailing Sheet metal blocking Steel Connectors (Simpson is our friend)
- 25. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Timber
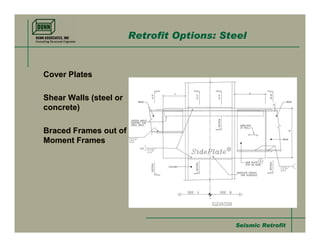
- 26. Seismic RetrofitSeismic Retrofit Retrofit Options: Steel Cover Plates Shear Walls (steel or concrete) Braced Frames out of Moment Frames Cover Plates Shear Walls (steel or concrete) Braced Frames out of Moment Frames