Semantic Web
- 1. Moving From Noise to Signal Semantic Web
- 2. Agenda Introduction Semantic Web What is Semantic Web? Why it matters? How to Semantify the Web? Web 3.0 Linked Data
- 3. Introduction 1.3+ billion people connected to the web 2006 161 EB of information created/replicated (1 EB = 1 billion GB) Technical information doubled every 2 years By 2010 six times to 988Eb (approx = 1 ZB) Technical information will double every 72 hours Computers, mobile phones, intelligent devices Internet is broken â not one web â unable to communicate
- 4. Information Overload Is that really how the Web experience is supposed to feel? Key Problem â how to share meaning? Filtering, not aggregating. Not more, just smarter.
- 5. Semantics? Related to Syntax Syntax â How you say something (letters, punctuation, grammar) eg. HTML Semantics â Meaning behind what you say Example: I Love Technology I Technology
- 6. Whatâs the big deal? Internet std way to communicate Parrot â mimic w/o understanding The Web Store and retrieve docs on the internet syntax to display the doc (HTML) Search Engines Find any website that we want Life is good!!! Can we make it any better?? How??
- 7. The Answer â Semantic Web Understand the meaning behind webpages Web of Things vs Web of Documents Things can be ANYTHING â people, places, pets, events, music, movies, organizationsâĶ. Not only identify these things but also relationships (Human-like!!!) Embed semantics in html docs â microformats, RDF Itâs not about the futureâĶitâs about Today!!!
- 9. Ėý
- 10. Why Semantic Web? Spend less time searching Spend less time looking at things that do not matter Spend less time explaining what we want to computers Bottomline â improve the online experience!!!
- 11. Cartoon by Geek and Poke
- 12. Itâs all about the noiseâĶ Web 1.0: Get (hear & see) âNoiseâ Web 2.0: Make Noise Web 3.0: Filter the Noise Web 4.0: Going deafâĶ.or SmartNoise
- 13. Semantifying the Web - Approaches Bottom Up Annotating information in web pages with machine readable tags Technical Challenges Representational Complexity How to create â manual/automatic? How much can be transformed? Standard Issue Business Challenges Itâs primitive Consumer Value? How to market? Recent Wins: Yahoo search engine to support RDF, MF Dapper â automated annotation tool
- 14. Annotation Technologies Trade-off between simplicity and completeness RDF Graph based â things, attributes, relationships Precise but complex Triple Microformats Uses specific CSS styles Compact Embedded in HTML gaining popularity because of their simplicity Popular microformats: hCard: describes personal and company contact information hReview: adds meta information to review pages hCalendar: used to describe events Limitations no way to described type hierarchies somewhat cryptic, because the focus is to keep the annotations to a minimum Flickr, Eventful, and LinkedIn
- 15. Semantifying the Web - Approaches Top Down Focused on leveraging information in existing web pages As â is NLP Tools (entity extraction) Calais & TextWise â APIs that recognize people, companies, places in docs Vertical Search Engines â ZoomInfo, Spock & Retrevo Dapper, BlueOrganizer, ClearForest â recognize objects in web pages & annotate them Yahoo! Shortcuts, Snap, Smartlinks â recognize objects in text and links Challenges Not 100% perfect, has ambiguities May not scale well
- 16. Map+ add-on for Firefox vertical search engine Spock
- 17. More Annotations ï Structured Web ï More Precise Top-Down
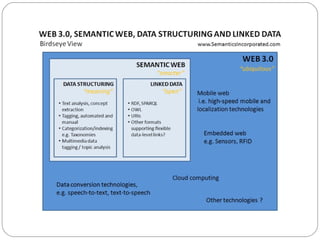
- 18. Web 3.0 = Semantic Web = Linked Data Are They Equal??
- 19. Ėý
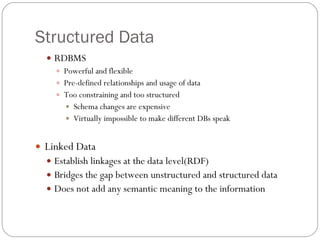
- 20. Structured Data RDBMS Powerful and flexible Pre-defined relationships and usage of data Too constraining and too structured Schema changes are expensive Virtually impossible to make different DBs speak Linked Data Establish linkages at the data level(RDF) Bridges the gap between unstructured and structured data Does not add any semantic meaning to the information
- 21. Linked Data Medium for the semantic web It does not create smart data, only enables it Relies on clean, granular, structured data Pre-Structured Pre-Connected
- 22. Further Reading RDF, OWL, Microformats, FOAF Linked Data Semantic APIs