Sensorcomm3 t sullivan
- 1. A Smart City-Smart Bay Project: Establishing an integrated water monitoring system for decision support in Dublin Bay Fiona Regan, Timothy Sullivan, Ciprian Briciu, Helen Cooney, Dian Zhang*, Edel OâConnor*, Noel OâConnor*, Alan Smeaton* Marine and Environmental Sensing Technology Hub (MESTECH), National Centre for Sensor Research Dublin City University *CLARITY Centre for Sensor Web Technologies, Dublin City University Dublin, Ireland
- 2. Project  Ra+onale  Design,  deployment  and  integra2on  of  an  autonomous  real-Ââ2me  mul2modal  sensing  network  for  improved  decision  making  Research  Objec+ves   âĒâŊ Improve  Water  quality  monitoring  âĒâŊ Improve  discrete  sampling  regimes   âĒâŊ Iden+fy  and  Improve  detec+on  of  Security  threats  âĒâŊ Iden2fy  threats  to  health  (microbial  and  other  pollutants)  âĒâŊ Enhanced  Signal  processing:  Develop  surrogate  measurements  âĒâŊ Produce  Baseline  datasets  on  water  quality     Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Study  site   Methods   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions Â
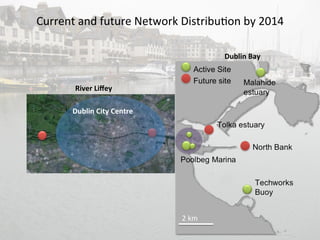
- 4. Current  and  future  Network  Distribu+on  by  2014  River  LiïŽey  Dublin  Bay  Dublin  City  Centre  2  km Â
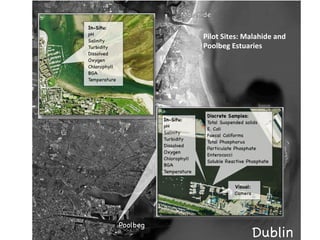
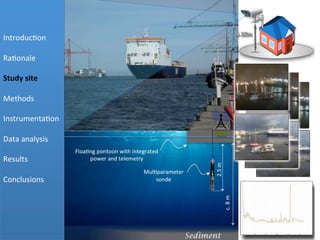
- 5. Pilot  Sites:  Malahide  and  Poolbeg  Estuaries Â
- 6.    Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Study  site   Methods   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions Â
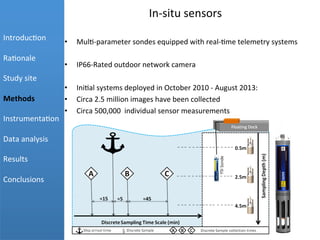
- 7. In-Ââsitu  sensors  âĒâŊ Mul+-Ââparameter  sondes  equipped  with  real-Ââ+me  telemetry  systems   âĒâŊ IP66-ÂâRated  outdoor  network  camera   âĒâŊ Ini+al  systems  deployed  in  October  2010  -Ââ  August  2013:  âĒâŊ Circa  2.5  million  images  have  been  collected  âĒâŊ Circa  500,000   individual  sensor  measurements     Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Study  site   Methods   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions Â
- 8.    Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Study  Site   Methods   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions  Duc+ng  of  marina  structure  220V  power  supply  Commercial  telemetry  solu+on  box Â
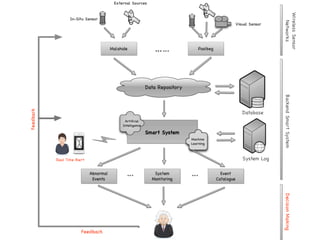
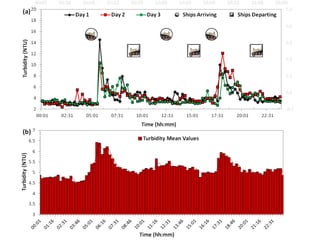
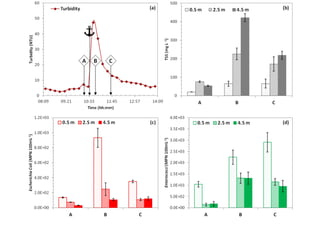
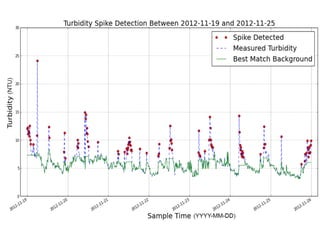
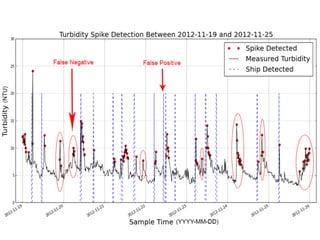
- 9.  Data  Analy+cs  âĒâŊ Machine  learning  objec+ves:  automated  detec+on  and  trajectory  of  vessels  âĒâŊ Automated  Turbidity  event  detec+on  â  pixel-Ââbased  adap+ve  segmenter  method  âĒâŊ Salinity  predic+on  using  mul+ple  data  sources  (+de,  ïŽow,  weather  data)  using  regression  tree  approach  âĒâŊ Shipping  ac+vity  +  turbidity:  predic+on  of  sampling  +mes  and  microbial  contamina+on  â  separa+ng  natural  events  from  anthropogenic  events  âĒâŊ Water  level  predic+on  âĒâŊ Security  Threats:  Unauthorized  shipping     Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Methods   Study  Site   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions Â
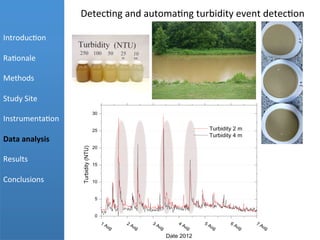
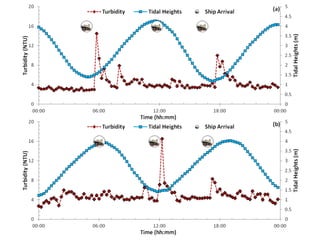
- 10. 1 Aug 2 Aug 3 Aug 4 Aug 5 Aug 6 Aug 7 Aug 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Turbidity 2 m Turbidity 4 m Turbidity(NTU) Date 2012 Detec+ng  and  automa+ng  turbidity  event  detec+on     Introduc+on   Ra+onale   Methods   Study  Site   Instrumenta+on   Data  analysis   Results   Conclusions Â
- 17. Conclusions  âĒâŊ An  extensive  network  of  both  in-Ââsitu  aqua+c  sensors  and  visual  sensing  systems  have  been  and  are  in  process  of  deployment  in  Dublin  Bay   âĒâŊ The  network  has  already  had  demonstrable  impact  on  monitoring  and  understanding  dynamic  processes  in  Dublin  Bay  âĒâŊ Incorpora+on  of  visual  sensing  nodes  into  the  network  has  proven  advantageous  âĒâŊ Machine  learning  and  increased  compu+ng  power  has  aided  in  data  analysis  â  future  work  will  emphasize  data  analy+cs    âĒâŊ Challenges  remain:  Increased  spa+al  coverage,  Biofouling!,  Cost,  Transla2on  of  data  into  knowledge    Â
- 18. Thank  You!  Ques+ons?  Contacts:  +m.sullivan@dcu.ie;  ïŽona.regan@dcu.ie  Â