Session 1 Globalization and Differences of Political and Economic Systems Among Countries.pdf
- 1. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Muthia Pramesti | Mutiara Baby Admeinasthi | PPJJ
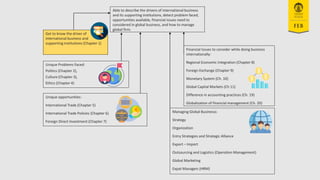
- 2. 2 International Business What will you get from this class? GET TO KNOW THE DRIVER OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS AND SUPPORTING INSTITUTIONS (CH 1) PROBLEM FACED (CH 2,3,4) OPPORTUNITIES (CH 5,6,7) ISSUES (PARTICULARLY FINANCE) TO CONSIDER WHILE DOING BUSINESS INTERNATIONALLY (CH 8-11, 19, 20) MANAGING GLOBAL BUSINESS (STRATEGY, ORGANIZATION, HRM, OPERATION, MARKETING, ETC (CH 12-18)
- 3. Unique opportunities: International Trade (Chapter 5) International Trade Policies (Chapter 6) Foreign Direct Investment (Chapter 7) Managing Global Businesss: Strategy Organization Entry Strategies and Strategic Alliance Export ŌĆō Import Outsourcing and Logistics (Operation Management) Global Marketing Expat Managers (HRM) Unique Problems Faced: Politics (Chapter 2), Culture (Chapter 3), Ethics (Chapter 4) Financial Issues to consider while doing business internationally: Regional Economic Integration (Chapter 8) Foreign Exchange (Chapter 9) Monetary System (Ch. 10) Global Capital Markets (Ch 11) Difference in accounting practices (Ch. 19) Globalization of financial management (Ch. 20) Able to describe the drivers of international business and its supporting institutions, detect problem faced, opportunities available, financial issues need to considered in global business, and how to manage global firm. Get to know the driver of international business and supporting institutions (Chapter 1)
- 5. 5 International Business The World Today Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 6. 6 International Business New Global Business Realities The world flatten 1 Companies got internationalized 2 Trade agreements 3 Rapid and extensive global communication 4 Rapid development and transfer of technologies 5 And so on.. 6 The rapid growth and spread of these drivers led to GLOBALIZATION Chapter 1 : Introduction Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 7. Globalization Refers to the shift toward a more integrated and interdependent world economy.
- 8. 8 International Business Globalization of Markets ŌĆó Falling trade barriers make it easier to sell globally ŌĆó ConsumersŌĆÖ tastes and preferences are converging on some global norm ŌĆó Firms promote the trend by offering the same basic products worldwide 01 Globalization of Production ŌĆó Lower overall cost structure ŌĆó Improve the quality or functionality of their product offering 02 Globalization Common Types Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 9. 9 International Business International Organizations Why do we need international organization? Help manage, regulate, and police the global marketplace. Promote the establishment of multinational treaties to govern the global business system. Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 10. IMF WTO ŌĆó Maintains order in the international monetary system ŌĆó Polices the world trading system ŌĆó Makes sure that nation- states adhere to the rules laid down in trade treaties ŌĆó Promotes lower barriers to trade and investment What do International Organizations do? 11/13/2018 10 10 International Business Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 11. UN World Bank ŌĆó Maintains international peace and security ŌĆó Develops friendly relations among nations ŌĆó Cooperates in solving international problems and in promoting respect for human rights ŌĆó Is a center for harmonizing the actions of nations ŌĆó Promotes economic development What do International Organizations do? 11/13/2018 11 11 International Business Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 12. 12 International Business The Changing Demographics of World GDP and Trade Chapter 1 : Introduction
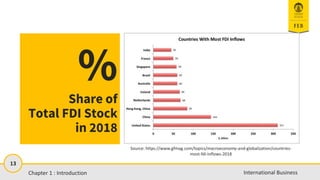
- 13. 13 International Business % Share of Total FDI Stock in 2018 Source: https://www.gfmag.com/topics/macroeconomy-and-globalization/countries- most-fdi-inflows-2018 Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 14. 14 International Business The financial crisis that swept through South East Asia in the late 1990s Globalizations Risks The recent financial crisis that started in the U.S. in 2008, and moved around the world Debates on Globalization Chapter 1 : Introduction
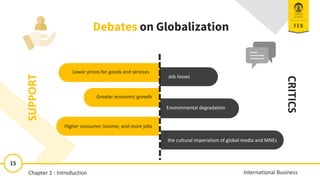
- 15. International Business 15 Lower prices for goods and services Greater economic growth Higher consumer income, and more jobs Job losses Environmental degradation the cultural imperialism of global media and MNEs Debates on Globalization SUPPORT CRITICS Debates on Globalization Chapter 1 : Introduction 11/13/2018 15 15 International Business Chapter 1 : Introduction
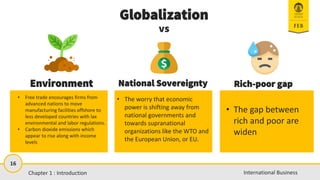
- 16. 16 International Business Environment ŌĆó Free trade encourages firms from advanced nations to move manufacturing facilities offshore to less developed countries with lax environmental and labor regulations. ŌĆó Carbon dioxide emissions which appear to rise along with income levels Rich-poor gap ŌĆó The gap between rich and poor are widen Globalization vs National Sovereignty ŌĆó The worry that economic power is shifting away from national governments and towards supranational organizations like the WTO and the European Union, or EU. Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 17. 17 International Business Multinational Enterprise ŌĆó A multinational enterprise (MNE) is any business that has productive activities in two or more countries International Business Chapter 1 : Introduction 17
- 18. 18 International Business Implication for Managers Managing an international business, or any firm that engages in international trade or investment, will be different from managing a domestic business for several key reasons. Countries differ. Greater and more complex problems Government intervention in markets creates limitations. Deal with exchange rate changes Chapter 1 : Introduction
- 19. SLIDE / 02 NATIONAL DIFFERENCES IN POLITICAL ECONOMY
- 20. 20 ŌĆó This chapter focuses on how the political, economic, and legal systems of countries differ. ŌĆó Collectively, we refer to these system as constituting the political economy of a country INTRODUCTION 11/13/2018 20 20 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
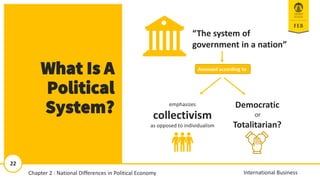
- 21. 21 International Business What Is A Political Economy? The political economy of a nation refers to how the political, economic, and legal systems of a country are interdependent ŌĆó they interact and influence each other ŌĆó they affect the level of economic well- being in the nation Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 22. 22 International Business What Is A Political System? Democratic or Totalitarian? emphasizes collectivism as opposed to individualism Assessed according to ŌĆ£The system of government in a nationŌĆØ 11/13/2018 22 22 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 23. 23 International Business What Is Collectivism? Collectivism stresses the primacy of collective goals over individual goals Today, collectivism is equated with socialists (Karl Marx 1818-1883) advocate state ownership of the basic means of production, distribution, and exchange Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy Photo: Karl Marx
- 24. 24 International Business How Does Modern-Day Look? COMMUNISM SOCIAL DEMOCRATS can only be achieved through violent revolution and totalitarian dictatorship. state-owned enterprises have been privatized Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 25. 25 International Business What Is Individualism? Individualism refers to philosophy that an individual should have freedom in his own economic and political pursuits ŌĆó can be traced to Greek philosopher, Aristotle (384- 322 BC), who argued that individual diversity and private ownership are desirable ŌĆó individual economic and political freedoms are the ground rules on which a society should be based ŌĆó implies democratic political systems and free market economies International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy 25
- 26. 26 International Business Individualism citizens should be directly involved in decision making Representative democracy Citizens periodically elect individuals to represent them What Is Democracy? a political system in which government is by the people, exercised either directly or through elected representatives. 11/13/2018 26 26 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 27. 27 International Business What Is Totalitarianism? Totalitarianism is a form of government in which one person or political party exercises absolute control over all spheres of human life and prohibits opposing political parties Communist totalitarianism Theocratic totalitarianism Tribal totalitarianism Right-Wing totalitarianism Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 28. 28 International Business MARKET ECONOMIES COMMAND ECONOMIES MIXED ECONOMIES ŌĆó Privately owned ŌĆó Production determined by supply and demand ŌĆó Free and fair competition between private producers ŌĆó Production quantity and prices determined by government ŌĆó State-owned ŌĆó ŌĆ£The good of societyŌĆØ ŌĆó Stagnate ŌĆó Governments tend to own firms that are considered important to national security ŌĆó Certain sectors of the economy are left to private ownership WHAT IS AN ECONOMIC SYSTEM? Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 29. 29 International Business 02 03 Common law - based on tradition, precedent, and custom Civic law - based on detailed set of laws organized into codes Theocratic law - law is based on religious teachings 01 LEGAL SYSTEM The legal system of a country refers to the rules that regulate behavior along with the processes by which the laws are enforced and through which redress for grievances is obtained Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 30. 30 International Business How Are Contracts Enforced In Different Legal Systems? ŌĆó Contract law is the body of law that governs contract enforcement ŌĆó Under a common law system, contracts tend to be very detailed with all contingencies spelled out ŌĆó Under a civil law system, contracts tend to be much shorter and less specific because many issues are already covered in the civil code ŌĆó Many countries have ratified the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CIGS) which establishes a uniform set of rules governing certain aspects of the making and performance of everyday commercial contracts between buyers and sellers who have their places of business in different nations 2-30 A contract is a document that specifies the conditions under which an exchange is to occur and details the rights and obligations of the parties involved 11/13/2018 30 30 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
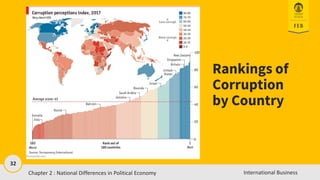
- 31. 31 International Business Property Rights And Corruption Property rights refer to the legal rights over the use to which a resource is put and over the use made of any income that may be derived from that resource Can be violated through 1. Private action ŌĆō theft, piracy, blackmail 2. Public action - legally - ex. excessive taxation or illegally - ex. bribes or blackmailing ŌĆó high levels of corruption reduce foreign direct investment, the level of international trade, and the economic growth rate in a country The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act makes it illegal for U.S. companies to bribe foreign government officials to obtain or maintain business over which that foreign official has authority 2-31 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy 31
- 32. 32 International Business Rankings of Corruption by Country Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 33. 33 International Business 02 03 Patents ŌĆō exclusive rightsfor a defined period to the manufacture, use, or saleof that invention CopyrightsŌĆō the exclusive legal rights of authors, composers, playwrights, artists, and publishersto publish and disperse their work as they see fit TrademarksŌĆō design and names by which merchants or manufacturers designate and differentiate their products 01 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY Property that is the product of intellectual activity. Can be protected using: Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 34. 34 International Business Intellectual Property Protection Protection of intellectual property rights differs from country to country Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property 2-34 11/13/2018 34 34 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 35. 35 International Business How Can Intellectual Property Be Protected? To avoid piracy, firms can: Stay away from countries where intellectual property laws are lax 1 File lawsuits. 2 Lobby governments for international property rights agreements and enforcement. 3 2-35 11/13/2018 35 35 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 36. 36 International Business Product Safety And Liability ŌĆó Product safety laws set certain standards to which a product must adhere ŌĆó Product liability involves holding a firm and its officers responsible when a product causes injury, death, or damage ŌĆó When product safety laws are stricter in a firmŌĆÖs home country than in a foreign country, or when liability laws are more lax, the firm has to decide whether to adhere to home country or host country standards Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 37. 37 International Business Determinants of a CountryŌĆÖs Level Of Economic Development Two ways to measure levels of economic development are GNI PPP ŌĆó Nobel-prize winner Amartya Sen argues economic development should be seen as a process of expanding the real freedoms that people experience ŌĆó the removal of major impediments to freedom like poverty, tyranny, and neglect of public facilities ŌĆó the presence of basic health care and basic education Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 38. 38 International Business Determinants of a CountryŌĆÖs Level Of Economic Development The United Nations used Amartya SenŌĆÖs ideas to develop the Human Development Index (HDI) which is based on: life expectancy at birth educational attainment whether average incomes are sufficient to meet the basic needs of life in a country 02 03 01 Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 39. 39 International Business Countries Compare on Economic Development Source: https://ourworldindata.org/economic-growth Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 40. 40 International Business Political Economy and Economic Progress Innovation and entrepreneurship are the engines of long-run economic growth 1 Innovation and entrepreneurship require a market economy and strong property rights 2 Democratic regimes are probably more conducive to long- term economic growth than dictatorships, even the benevolent kind 3 Subsequent economic growth leads to the establishment of democratic regimes 4 Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 41. 41 International Business Geography, Education and Economic Development Countries with favorable geography are more likely to engage in trade, and so, be more open to market-based economic systems, and the economic growth they promote Countries that invest in education have higher growth rates because the workforce is more productive 2-41 11/13/2018 41 41 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 42. 42 International Business The Changing Political Economy Since the late 1980s, two trends have emerged: 02 Democraticrevolution (late 1980s and early 1990s) A move away from centrally planned and mixedeconomies 01 ŌĆó More countries have shifted toward the market-based model ŌĆó Many totalitarian regimes failed to deliver economic progress to the vast bulk of their populations ŌĆó New information and communication technologies have broken down the ability of the state to control access to uncensored information ŌĆó Economic advances of the last 25 years have led to increasingly prosperous middle and working classes who have pushed for democratic reforms Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 43. 43 HOW FREE ARE COUNTRIES POLITICALLY? Political Freedom in 2017
- 44. 44 HOW FREE ARE COUNTRIES ECONOMICALLY? Distribution of Economic Freedom in 2013
- 45. 45 International Business The Nature Of Economic Transformation The shift toward a market-based system involves Deregulation Privatization Removing legal restrictions to the free play of markets, the establishment of private enterprises, and the manner in which private enterprises operate. Transfers the ownership of state property into the hands of private investors. Legal System The creation of a legal system to safeguard property rights Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 46. 46 International Business What Does The Changing Economy Mean For Managers? ŌĆó Markets that were formerly off-limits to Western business are now open ŌĆó By identifying and investing early in a potential future economic stars, firms may be able to gain first mover advantages and establish loyalty and experience in a country ŌĆó ex. China -1.2 billion people and India ŌĆō 1.1 billion people ŌĆó Potential risks are large ŌĆó It can be more costly to do business in countries with dramatically different product, workplace, and pollution standards, or where there is poor legal protection for property rights Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 47. 47 International Business What Does The Changing Economy Mean For Managers? Political risk - the likelihood that political forces will cause drastic changes in a country's business environment that adversely affects the profit and other goals of a business enterprise Economic risk - the likelihood that economic mismanagement will cause drastic changes in a country's business environment that adversely affects the profit and other goals of a business enterprise Legal risk - the likelihood that a trading partner will opportunistically break a contract or expropriate property rights Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 48. 48 International Business How Can Managers Determine A MarketŌĆÖs Overall Attractiveness? The overall attractiveness of a country as a potential market and/or investment site for an international business depends on balancing the benefits, costs, and risks associated with doing business in that country Other things being equal, the benefit-cost-risk trade-off is likely to be most favorable in politically stable developed and developing nations that have free market systems and no dramatic upsurge in either inflation rates or private sector debt Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 49. Read the Article ŌĆó The new political divide ŌĆó How the West got China wrong ŌĆó Video: How does ChinaŌĆÖs government works 02 01 2-49 11/13/2018 49 49 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 50. Quiz Please check your understanding by answering the chapterŌĆÖs quiz. 2-50 11/13/2018 50 50 International Business Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy
- 51. 51 International Business Source Chapter 1 ŌĆó Hill, Charles W.L, Wee, Chow-Hou & Udayasankar, Krishna. International Business: An Asian Perspective. ŌĆó https://amp.economist.com/leaders/2016/07/30/the-new-political-divide#top ŌĆó https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xPD477FuqtY&t=45s Chapter 2 ŌĆó Hill, Charles W.L, Wee, Chow-Hou & Udayasankar, Krishna. International Business: An Asian Perspective. ŌĆó https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2018/02/22/corruption-is-still-rife-around-the-world ŌĆó https://www.economist.com/leaders/2018/03/01/how-the-west-got-china-wrong ŌĆó https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fgor9fmA6po Chapter 2 : National Differences in Political Economy