Short Overview of HELMINTHS(Microbiology)
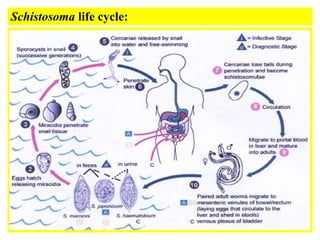
- 1. Helminthes: Trematodes (flukes): SCHISTOSOMES: Schistosomes are unisexual blood flukes that have worldwide distribution, Three species arc known to affect man: 1- Schistosoma hematobium: • Found in Middle East, Africa, Portugal and Cyprus • Definitive host: man • Intermediate host: snail • It causes urinary bilharziasis (female deposits eggs in the vesical and pelvic plexus of venous circulation).
- 2. a 2 - Schistosoma mansoni: • Found in Middle East, Africa, Sooth America • Definitive host: man • Intermediate host: snail (Biomphilaria) • It causes intestinal bilharziasis (female deposits eggs in mesenteric venous circulation. 3- Schistosoma Japonicum: • Found in Far East • Definitive host: man, domestic animals (dogs, pig, cats) Intermediate host: Snail (onchomelania) • It causes intestinal bilharziasis (female deposits eggs in mesenteric venous circulation.
- 3. MORPHOLOGY: Male: 10-20 x I mm with short anterior cylindrical pan and posterior flattened part which incurved ventrally to form the gynaeccphoric canal. It has well developed oral and ventral suckers. Female: 15-25 x 0.25 mm:, cylindrical, ovary may "be central, anterior or posterior, uterus may be short or long containing eggs.
- 4. Schistosoma Eggs: S. hematobium : 140x50 µ, oval with terminal spine. Passes in urine and sometimes in stool S. mansoni: 150x60 µ,oval with lateral spine ,passes with feces and sometimes in urine. S. Japonicum : 80x60 µ sub-rounded, spineless with tubercle like projection, Pass with stool.
- 6. CLINICAL PICTURE: The clinical pictures of Schistosoma (Schistosomiasis) is mainly due to egg deposition with tearing action of the spine in early stags and fibrosis around the eggs in late stages. The clinical picture is divided into three stage: 1-Incubation period; (acute Schistosomiasis 6-12 Weeks) : This stage is characterized by skin irritation after coming from water, and coughing. Late in the incubation period, patients complains of enlarged liver, fever, headache, anorexia, loss of weigh. CBC shows Eosinophilia. 2- Stage of egg deposition: (1- 5 years after infection). Urinary bilharziasis: caused by S.hematobium, characterised by terminal haematuria, burning sensation during urination. Intestinal bilharziasis: dysentery with frequent defecation. blood and mucous in stool.
- 7. a 3-Stage of complication: due to a fibrosis around the eggs in bladder, rectum, colon, liver and lung. It occurs 2 to 5 years after infection depending on severity of infection and immunity of the patients. A- Urinary bilharziasis: cystitis, hydronephrosis and Pyonephrosis , sterility in males, renal failure, cancer bladder, pulmonary hypertension and heart failure. B- Intestinal bilharziasis: fever, Jaundice, portal hypertension, and Hepatospleenomegaly.
- 8. Nematoda: Nematodes are cylindrical non-segmented unisexual worms. They have body cavity containing fluids in which organs float. Anal and genital opening are separate in female and united in male (Cloaca). Mouth may be provided with lips, papillae and teeth. Ascaris lumbricoides : Distribution: worldwide Habitat: Free in small intestine D.H.: Man, no intermediate host (direct life cycle). Morphology: Whitish yellow cylindrical worms, male 15-25 cm x 3 mm with posterior curved end, female 20 -40 cm x 5mm with tapering posterior end. it lays around 200000 eggs per day.
- 10. TYPES OF ASCARIS EGGS: 1-Fertilized egg (corticated mamillated egg): 60x45µ, oval, thick walled, shell is covered with a layer of albuminoid mamillation, contains unsegmented fertilized embryo. 2-Decorticated egg: no albuminoid mamillation. 3-Unfertilized egg: elongated 90x45 µ, dark, ill developed mamillation, and contains multiple refractile granules. 4- Embryonated egg: like corticated egg, embryo in form of larva.
- 11. CLINICAL PICTURE: 1- Pulmonary: cough, Sputum production. 2-Intestinal: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension and indigestion. 3- Complication: Light infection: obstruction of bile duct, pancreatic duct and appendix leading respectively to jaundice, pancreatitis and appendicitis. Peritonitis may occur Heavy infection: Intestinal obstruction and bronchopneumonia.
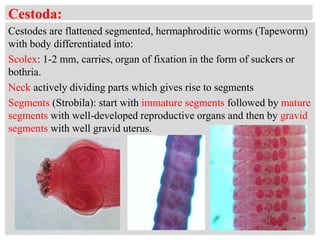
- 12. Cestoda: Cestodes are flattened segmented, hermaphroditic worms (Tapeworm) with body differentiated into: Scolex: 1-2 mm, carries, organ of fixation in the form of suckers or bothria. Neck actively dividing parts which gives rise to segments Segments (Strobila): start with immature segments followed by mature segments with well-developed reproductive organs and then by gravid segments with well gravid uterus.
- 13. FAMILY: TAENDDAE TAENIA WORMS: Two Taenie species are known to affect man: 1- Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm) Distributed all over the world. Definitive host: man Intermediate host: sheep, cattle and camels. 2- Taenia solium (pork tapeworm): Distributed in pig raising countries Definitive host: man Intermediate host: pigs
- 14. LIFE CYCLE: a
- 15. CLINICAL PICTURE: Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, colic, irregular bowel habits, Intestinal obstruction, Loss of weight, and Loss of vitamins. DIAGNOSIS: By finding the eggs or gravid segments in the stool of patient.
- 16. Thank You!