Shoulder Arthroscopy positioning and preparation
- 1. SETUP AND POSITIONING FOR SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY Dr Rishi Kiran Doshi Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Kolhapur Institute Of Orthopaedics and Trauma Knee Arthroscopy Fellow, Sportsmed Clinic Mumbai Shoulder Arthroscopy Fellow, Italy
- 2. Today, apart from Shoulder Replacement and major Shoulder Fractures, nearly all Shoulder Pathology can be treated With arthroscopic techniques
- 3. Shoulder Arthroscopy the evolution of the technique Diagnostic Tool Final Treatment From tool of the devil , the treatment of choice of most shoulder pathologies
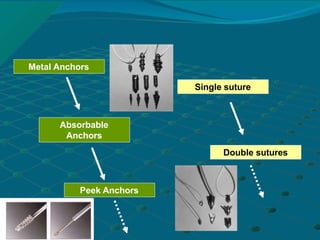
- 4. Metal Anchors Absorbable Anchors Peek Anchors Single suture Double sutures
- 8. BASIC ARTHROSCOPIC KIT • Arthroscope • Light source and cable • Camera system and monitor with recorder • Arthroscopic probe • Arthroscopic grasper • Arthroscopic scissor • Arthroscopy FMS pump • Arthroscopy RF • Arthroscopic Punches (basket forcepes 2.7 mm upcutting right and left Rotatory ) • Motorized shaver
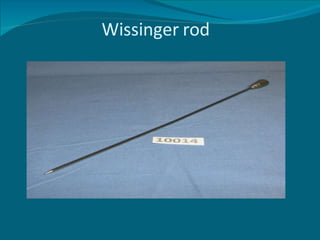
- 10. Wissinger rod
- 12. Shoulder Arthroscopy may be done in either the Beachchair, or lateral decubitus positions. Recently there have been modifications of both.
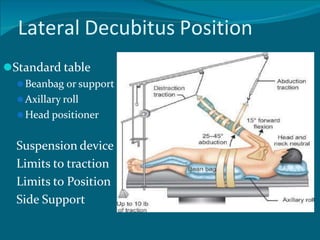
- 13. Lateral Decubitus Position âš«Standard table âš«Beanbag or support âš«Axillary roll âš«Head positioner Suspension device Limits to traction Limits to Position Side Support
- 15. By tilting the patient 20 to 30 degrees posteriorly, glenoid will be parallel to the floor 1. Less traction: Decrease the risk of neurapraxia of the brachial plexus 2. Accentuation of tears in the glenoid labrum as it pulled away from their beds 3. Improved arthroscopic access to the inferior third of the glenoid labrum and capsule. Canale, S T, James H. Beaty, and Willis C. Campbell. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013
- 16. Vertical and longitudinal traction, with most of the traction applied vertically to distract the glenohumeral joint without subluxing it inferiorly • 4 to 6 kgs of traction is applied • 30 to 60 degrees of abduction • 20 to 30 degrees of forward flexion • 23% and 30%: neurapraxia after excessive arm traction. Canale, S T, James H. Beaty, and Willis C. Campbell. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013
- 17. All pressure points Padded with a pillow Acromion, ASIS, Below knee, lateral malleolus and one or more pillows between the knees and ankles. Canale, S T, James H. Beaty, and Willis C. Campbell. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013
- 18. Beach Chair âš«Standard table with back support âš«Head positioner
- 19. BEACH CHAIR POSITION The benefits of the “beach chair” position 1. Interscalene block 2. Faster and easier positioning 3. Reduced risk of neurapraxia 4. Less distortion of intra articular capsular anatomy, 5. Improved mobility of the patient’s arm 6. Ease in orientation 7. Surgical manipulation in the subacromial space 8. Ease in conversion to an open surgical procedure.
- 20. COMPLICATIONS 1. Difficulty in working from posterior portals 2. Stroke 3. Death due to hypotensive episodes Canale, S T, James H. Beaty, and Willis C. Campbell. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013
- 22. LATERAL DECUBITUS BEACH CHAIR