sinaps
- 1. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaps ´ü« Bir n├Âron ile di─ƒer efekt├Âr aras─▒ndaki fizyolojik ba─ƒlant─▒lard─▒r. ´ü« ─░letim sadece bir y├Ânde ger├ºekle┼ƒir. ´ü« 1. n├Âron aksonu presinaptik u├º, 2. n├Âronun dendritik ucu ise postsinaptik u├º olarak adland─▒r─▒l─▒r. ´ü« Sinaptik iletim kimyasal kap─▒l─▒ kanallar ile ger├ºekle┼ƒir. ´ü« Presinaptik n├Âron ucundan n├Ârotransmitter maddeler (NT) sal─▒n─▒r.
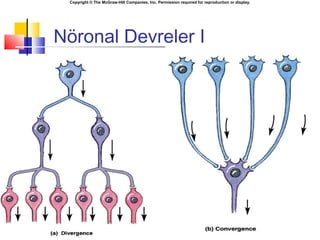
- 2. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. N├Âronal Devreler I
- 3. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. N├Âronal Devreler II
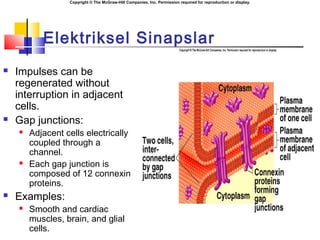
- 4. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Elektriksel Sinapslar ´ü« Impulses can be regenerated without interruption in adjacent cells. ´ü« Gap junctions: ´ü« Adjacent cells electrically coupled through a channel. ´ü« Each gap junction is composed of 12 connexin proteins. ´ü« Examples: ´ü« Smooth and cardiac muscles, brain, and glial cells.
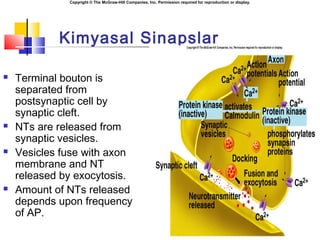
- 5. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Kimyasal Sinapslar ´ü« Terminal bouton is separated from postsynaptic cell by synaptic cleft. ´ü« NTs are released from synaptic vesicles. ´ü« Vesicles fuse with axon membrane and NT released by exocytosis. ´ü« Amount of NTs released depends upon frequency of AP.
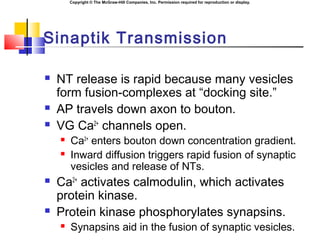
- 6. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaptik Transmission ´ü« NT release is rapid because many vesicles form fusion-complexes at ÔÇ£docking site.ÔÇØ ´ü« AP travels down axon to bouton. ´ü« VG Ca2+ channels open. ´ü« Ca2+ enters bouton down concentration gradient. ´ü« Inward diffusion triggers rapid fusion of synaptic vesicles and release of NTs. ´ü« Ca2+ activates calmodulin, which activates protein kinase. ´ü« Protein kinase phosphorylates synapsins. ´ü« Synapsins aid in the fusion of synaptic vesicles.
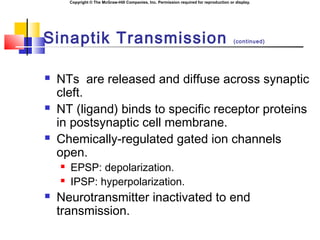
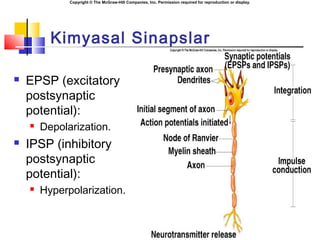
- 7. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaptik Transmission (continued) ´ü« NTs are released and diffuse across synaptic cleft. ´ü« NT (ligand) binds to specific receptor proteins in postsynaptic cell membrane. ´ü« Chemically-regulated gated ion channels open. ´ü« EPSP: depolarization. ´ü« IPSP: hyperpolarization. ´ü« Neurotransmitter inactivated to end transmission.
- 8. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaptik Transmission (continued)
- 9. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaptik Transmission (continued)
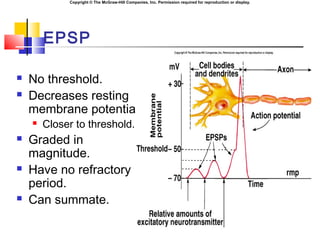
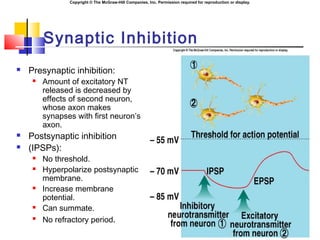
- 10. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. EPSPs ve IPSPs ´ü« If the transmitter opens a cation influx, the resulting depolarization is called an Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP). ´ü« These individual potentials are sub-threshold. ´ü« If the transmitter opens an anion influx, the resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP ´ü« All these potentials are additive.
- 11. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. EPSP ´ü« No threshold. ´ü« Decreases resting membrane potential. ´ü« Closer to threshold. ´ü« Graded in magnitude. ´ü« Have no refractory period. ´ü« Can summate.
- 12. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Long-Term Potensilizasyon ´ü« May favor transmission along frequently used neural pathways. ´ü« Neuron is stimulated at high frequency, enhancing excitability of synapse. ´ü« Improves efficacy of synaptic transmission. ´ü« Neural pathways in hippocampus use glutamate, which activates NMDA receptors. ´ü« Involved in memory and learning.
- 13. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Electrical Activity of Axons ´ü« All cells maintain a resting membrane potential (RMP): ´ü« Potential voltage difference across membrane. ´ü« Largely the result of negatively charged organic molecules within the cell. ´ü« Limited diffusion of positively charged inorganic ions. ´ü« Permeability of cell membrane: ´ü« Electrochemical gradients of Na+ and K+. ´ü« Na+ /K+ ATPase pump. ´ü« Excitability/irritability: ´ü« Ability to produce and conduct electrical impulses.
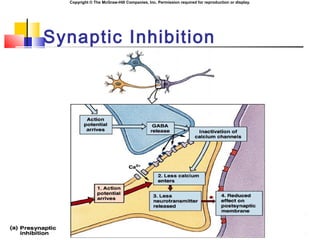
- 14. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Synaptic Inhibition ´ü« Presynaptic inhibition: ´ü« Amount of excitatory NT released is decreased by effects of second neuron, whose axon makes synapses with first neuronÔÇÖs axon. ´ü« Postsynaptic inhibition ´ü« (IPSPs): ´ü« No threshold. ´ü« Hyperpolarize postsynaptic membrane. ´ü« Increase membrane potential. ´ü« Can summate. ´ü« No refractory period.
- 15. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Synaptic Inhibition
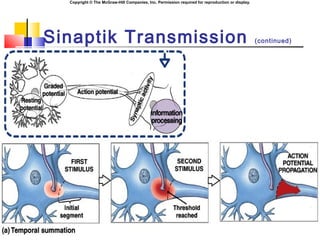
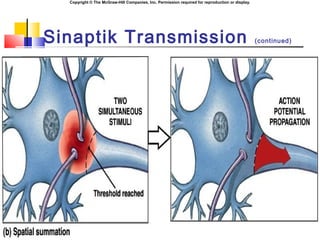
- 16. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Sinaptik Integrasyon ´ü« EPSPs can summate, producing AP. ´ü« Spatial summation: ´ü« Numerous boutons converge on a single postsynaptic neuron (distance). ´ü« Temporal summation: ´ü« Successive waves of neurotransmitter release (time).
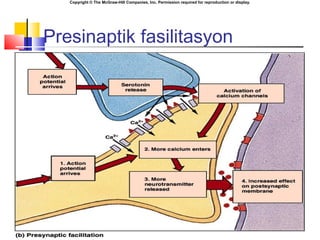
- 17. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Presinaptik fasilitasyon
- 18. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Kimyasal Sinapslar ´ü« EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential): ´ü« Depolarization. ´ü« IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential): ´ü« Hyperpolarization.
- 19. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Acetylcholine (ACh) as NT ´ü« ACh is both an excitatory and inhibitory NT, depending on organ involved. ´ü« Causes the opening of chemical gated ion channels. ´ü« Nicotinic ACh receptors: ´ü« Found in autonomic ganglia and skeletal muscle fibers. ´ü« Muscarinic ACh receptors: ´ü« Found in the plasma membrane of smooth and cardiac muscle cells, and in cells of particular glands.
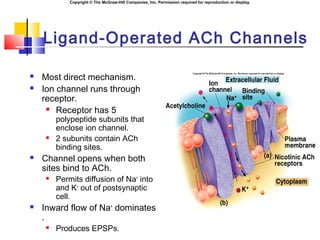
- 20. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Ligand-Operated ACh Channels ´ü« Most direct mechanism. ´ü« Ion channel runs through receptor. ´ü« Receptor has 5 polypeptide subunits that enclose ion channel. ´ü« 2 subunits contain ACh binding sites. ´ü« Channel opens when both sites bind to ACh. ´ü« Permits diffusion of Na+ into and K+ out of postsynaptic cell. ´ü« Inward flow of Na+ dominates . ´ü« Produces EPSPs.
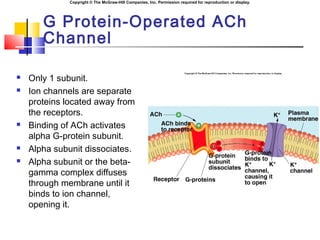
- 21. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. G Protein-Operated ACh Channel ´ü« Only 1 subunit. ´ü« Ion channels are separate proteins located away from the receptors. ´ü« Binding of ACh activates alpha G-protein subunit. ´ü« Alpha subunit dissociates. ´ü« Alpha subunit or the beta- gamma complex diffuses through membrane until it binds to ion channel, opening it.
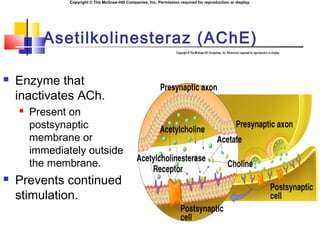
- 22. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Asetilkolinesteraz (AChE) ´ü« Enzyme that inactivates ACh. ´ü« Present on postsynaptic membrane or immediately outside the membrane. ´ü« Prevents continued stimulation.
- 23. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ACh in CNS ´ü« Cholinergic neurons: ´ü« Use ACh as NT. ´ü« Axon bouton synapses with dendrites or cell body of another neuron. ´ü« First VG channels are located at axon hillock. ´ü« EPSPs spread by cable properties to initial segment of axon. ´ü« Gradations in strength of EPSPs above threshold determine frequency of APs produced at axon hillock.
- 24. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ACh in PNS ´ü« Somatic motor neurons synapse with skeletal muscle fibers. ´ü« Release ACh from boutons. ´ü« Produces end-plate potential (EPSPs). ´ü« Depolarization opens VG channels adjacent to end plate.
- 25. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Monoamines as NT ´ü« Monoamine NTs: ´ü« Epinephrine. ´ü« Norepinephrine. ´ü« Serotonin. ´ü« Dopamine. ´ü« Released by exocytosis from presynaptic vesicles. ´ü« Diffuse across the synaptic cleft. ´ü« Interact with specific receptors in postsynaptic membrane.
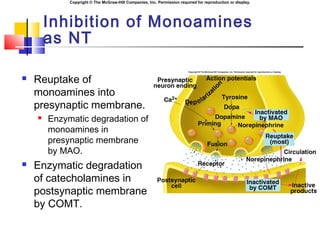
- 26. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Inhibition of Monoamines as NT ´ü« Reuptake of monoamines into presynaptic membrane. ´ü« Enzymatic degradation of monoamines in presynaptic membrane by MAO. ´ü« Enzymatic degradation of catecholamines in postsynaptic membrane by COMT.
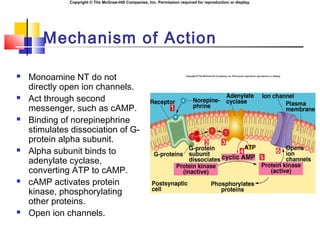
- 27. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Mechanism of Action ´ü« Monoamine NT do not directly open ion channels. ´ü« Act through second messenger, such as cAMP. ´ü« Binding of norepinephrine stimulates dissociation of G- protein alpha subunit. ´ü« Alpha subunit binds to adenylate cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. ´ü« cAMP activates protein kinase, phosphorylating other proteins. ´ü« Open ion channels.
- 28. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Serotonin as NT ´ü« NT (derived from L-tryptophan) for neurons with cell bodies in raphe nuclei. ´ü« Regulation of mood, behavior, appetite, and cerebral circulation. ´ü« SSRIs (serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors): ´ü« Inhibit reuptake and destruction of serotonin, prolonging the action of NT. ´ü« Used as an antidepressant. ´ü« Reduces appetite, treatment for anxiety, treatment for migraine headaches.
- 29. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dopamine an NT ´ü« NT for neurons with cell bodies in midbrain. ´ü« Axons project into: ´ü« Nigrostriatal dopamine system: ´ü« Nuerons in substantia nigra send fibers to corpus straitum. ´ü« Initiation of skeletal muscle movement. ´ü« ParkinsonÔÇÖs disease: degeneration of neurons in substantia nigra. ´ü« Mesolimbic dopamine system: ´ü« Neurons originate in midbrain, send axons to limbic system. ´ü« Involved in behavior and reward. ´ü« Addictive drugs: ´ü« Promote activity in nucleus accumbens.
- 30. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Norepinephrine (NE) as NT ´ü« NT in both PNS and CNS. ´ü« PNS: ´ü« Smooth muscles, cardiac muscle and glands. ´ü« Increase in blood pressure, constriction of arteries. ´ü« CNS: ´ü« General behavior.
- 31. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Amino Acids as NT ´ü« Glutamic acid and aspartic acid: ´ü« Major excitatory NTs in CNS. ´ü« Glutamic acid: ´ü« NMDA receptor involved in memory storage. ´ü« Glycine: ´ü« Inhibitory, produces IPSPs. ´ü« Opening of Cl- channels in postsynaptic membrane. ´ü« Hyperpolarization. ´ü« Helps control skeletal movements. ´ü« GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid): ´ü« Most prevalent NT in brain. ´ü« Inhibitory, produces IPSPs. ´ü« Hyperpolarizes postsynaptic membrane. ´ü« Motor functions in cerebellum.
- 32. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Polypeptides as NT ´ü« CCK: ´ü« Promote satiety following meals. ´ü« Substance P: ´ü« Major NT in sensations of pain. ´ü« Synaptic plasticity (neuromodulating effects): ´ü« Neurons can release classical NT or the polypeptide NT.
- 33. Copyright ┬® The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Polypeptides as NT ´ü« Endogenous opiods: ´ü« Brain produces its own analgesic endogenous morphine-like compounds, blocking the release of substance P. ´ü« Beta-endorphin, enkephalins, dynorphin. ´ü« Neuropeptide Y: ´ü« Most abundant neuropeptide in brain. ´ü« Inhibits glutamate in hippocampus. ´ü« Powerful stimulator of appetite. ´ü« NO: ´ü« Exerts its effects by stimulation of cGMP. ´ü« Macrophages release NO to helps kill bacteria. ´ü« Involved in memory and learning. ´ü« Smooth muscle relaxation.