Sindromul de malabsobéÈie
The document discusses malabsorption syndrome in pediatrics. It defines normal gastrointestinal function and malabsorption as the disruption of absorption of one or more nutrients ingested. Malabsorption can lead to secondary complications like malnutrition and specific nutrient deficiencies. The diagnosis of malabsorption syndrome involves considering when to think about malabsorption, clinical evaluation, biological evaluation, investigations to demonstrate what is not being absorbed and what disease caused the malabsorption. A minimum set of investigations includes blood tests, stool examination, digestive tests, and tests to evaluate if the intestinal mucosa is affected. Further tests evaluate absorption of lipids, proteins, disaccharides and xylose to identify the underlying cause. Biopsy of the intestine may also be performed.















Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot (7)
Similar to Sindromul de malabsobéÈie (8)
Recently uploaded (20)
Sindromul de malabsobéÈie
- 1. SINDROMUL DE MALABSORBTIE CURS DE PEDIATRIE Dr. Alina Stanescu
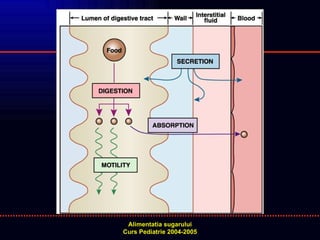
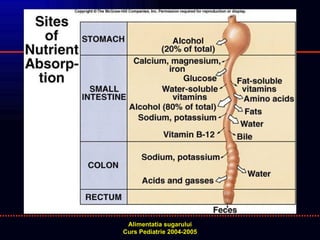
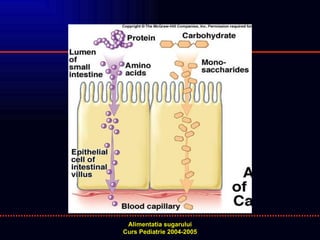
- 2. FUNCTIONAREA NORMALA A TUBULUI DIGESTIV FLUX SECRETOR NORMAL TRAIECT NEINTRERUPT / NEDEVIAT LUNGIME SI MOTILITATE INTESTINALA NORMALA MUCOASA NORMALA CIRCULATIE APTA PENTRU PRELUAREA SUBSTANTELOR ABSORBITE
- 3. ä»
- 4. ä»
- 5. ä»
- 6. ä»
- 7. ä»
- 8. ä»
- 9. MALABSORBTIE PERTURBAREA ASIMILARII UNEIA SAU MAI MULTOR SUBSTANTE NUTRITIVE INGERATE ELIMINARE FECALA EXCESIVA
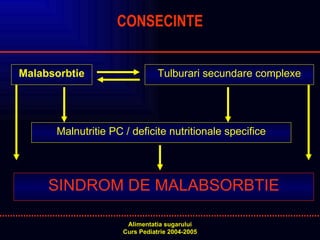
- 10. Malabsorbtie CONSECINTE Tulburari secundare complexe Malnutritie PC / deficite nutritionale specifice SINDROM DE MALABSORBTIE
- 11. DIAGNOSTICUL SINDROMULUI DE MALABSORBTIE CAND NE GANDIM LA MALABSORBTIE? ANAMNEZA EVALUARE CLINICA EVALUARE BIOLOGICA MALABSORBTIE? CE NU SE ABSOARBE? INVESTIGATII PENTRU DEMONSTRARE CE BOALA A GENERAT MALABSORBTIA? INVESTIGATII PENTU INCADRAREA ETIOPATOGENICA
- 12. CAND NE GANDIM LA MALABSORBTIE? SCADERE PROGRESIVA IN GREUTATE DEFICIT DE CRESTERE SI DEZVOLTARE SLABICIUNE / ASTENIE DIAREE CRONICA DISTENSIE ABDOMINALA MANIFESTARI ALE DEFICITELOR NUTRITIONALE SPECIFICE (PALOARE, EDEME, SANGERARI, TETANIE, PARESTEZII, DURERI OASOASE / FRACTURI)
- 13. SET MINIM DE INVESTIGATII ã SINDROM BIOLOGIC CARENTIAL ã HEMOGRAMA : NR ERITOCITE, Hb, Ht, FROTIU BIOCHIMIC : SIDEREMIE, CALCEMIE PROTEINEMIE, COLESTEROLEMIE TIMP DE PROTROMBINA MALABSORBTIE? PIERDERI PRIN FECALE? EXAMEN SCAUN : MACRO / MICROSCOPIC pH PROBA DE DIGESTIE EXAMEN PARAZITOLOGIC ESTE AFECTATA MUCOASA INTESTINALA ? TEST LA D-XILOZA
- 14. MALABSORBTIE? MACROSCOPIC GRASOS (STEATOREE) APOS, SPUMOS MICROSCOPIC LEUCOCITE (INFLAMATIE) EOZINOFILE (ALERGIE) pH-ACID ( <5,5) MALABSORBTIE DIZAHARIDE PROBA DE DIGESTIE LIPIDE 25-30g - 3 ZILE EX. MICROSCOPIC: AG - CRISTALE, TG - col Sudan III, FIBRE MUSCULARE ( INSUFICIENTA PANCREATICA) AMIDON (TRANZIT ACCELERAT)
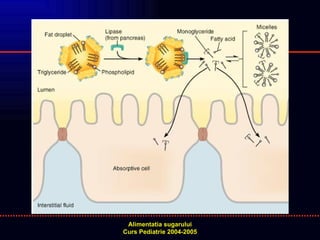
- 15. TESTE DE ABSORBTIE A LIPIDELOR (L) DETERMINAREA CANTITATIVA A L IN FECALE APORT LIPIDIC CALCULAT PT VARSTA TIMP DE 8 ZILE COLECTARE FECALE IN ULTIMELE 3 ZILE NORMAL: L FECALE ãÊ 7% DIN LIPIDELE INGERATE TEST ABSORBTIE VITAMINA A SOLUTIE ULEIOASA: ABSORBTIE ã SOLUTIE ALCOOLICA: ABSORBTIE NORMALA
- 16. TESTE DE ABSORBTIE A PROTEINELOR (P) DETERMINARE AZOT IN FECALE: APORT PROTEIC CALCULAT ã 3 ZILE COLECTARE FECALE NORMAL: ELIMINARE 1-2g AZOT / 24 ORE TESTE INDIRECTE: ABSORBTIE AA ã ÿ NIVEL PLASMATIC ã TESTE CU AA, PEPTIDE MARCATE RADIOACTIV: DUPA ADM. P.O. ÿ RADIOACTIVITATE SERICA SI FECALA DETERMINARE ENZIME: ENZIME PANCREATICE / ENTEROKINAZA INTESTINALA IN SUCUL DUODENAL
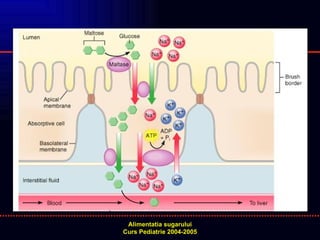
- 17. TESTE DE ABSORBTIE A DIZAHARIDELOR DIZAHARIDE (DZ): LACTOZA -> GLUCOZA + GALACTOZA SUCROZA -> GLUCOZA + FRUCTOZA MALTOZA -> GLUCOZA + GLUCOZA 2 TEHNICI - DZ - 2g/kgcorp p.o. CURBA GLICEMIEI LA 30 MIN ã 2 ORE: NORMAL: GLICEMIE MAXIMA BAZALA > 20 mg/dl TEST RESPIRATOR NORMAL: HIDROGEN EXPIRAT < 20ppm
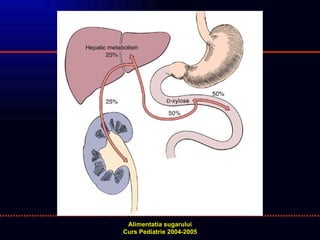
- 18. TESTUL D-XILOZA D-XILOZA = PENTOZA CU ABSORBTIE JEJUNALA ACTIVA INDEPENDENTA DE ENZIME 3 TEHNICI: 0,5g D-XILOZA/kg ELIMINARE IN URINA - 5 ore (NORMAL- 15-20%) CONCENTRATIA SERICA LA 1 ORA DUPA INGESTIE (NORMAL>25mg/dl) TEST RESPIRATOR ã CONCENTRATIA HIDROGENULUI EXPIRAT LA 10 ã 200 MIN. DUPA INGESTIE (NORMAL < 20 ppm)
- 19. ä»
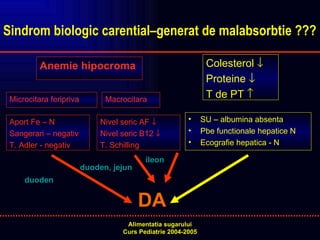
- 20. Sindrom biologic carentialãgenerat de malabsorbtie ??? Anemie hipocroma Microcitara feripriva Macrocitara Colesterol ÿ₤ Proteine ÿ₤ T de PT ÿÙ Aport Fe ã N Sangerari ã negativ T. Adler - negativ Nivel seric AF ÿ₤ Nivel seric B12 ÿ₤ T. Schilling SU ã albumina absenta Pbe functionale hepatice N Ecografie hepatica - N DA duoden duoden, jejun ileon
- 21. BIOPSIA INTESTINALA CAPSULA WATSON ã BIOPSIE JEJUNALA ENDOSCOPIE ã BIOPSIE DUODENALA LEZIUNI SPECIFICE: LIMFANGIECTAZIA CONGENITALA A- û LIPOPROTEINEMIA MALADIA WHIPPLE LEZIUNI NESPECIFICE ATROFIA VILOZITARA
- 22. ATROFIA VILOZITARA PRODUCTIE ENTEROCITE MUCOASA SUBTIRE INDICE MITOTIC ã MPC SEVERA AGENTI CITOTOXICI AVITAMINOZA B12 ANTIFOLICE IRADIERE Rx DISTRUCTIE ENTEROCITE BOALA CELIACA SD. POSTGASTROENTERITIC SPRUE TROPICAL GIARDIA DEFICITE IMUNE IPLV
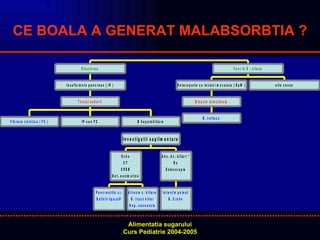
- 23. CE BOALA A GENERAT MALABSORBTIA ?
- 24. SM LA GRUPELE DE VARSTA NOU NASCUT INTOLERANTA CONGENIATALA DZ/MZ ATREZIE CAI BILIARE HEPATITA NEONATALA SUGAR SI COPIL MIC BOALA CELIACA FIBROZA CHISTICA DEFICIT DE DIZAHARIDAZE (CONGENITAL/DOBANDIT) ATREZIE CAI BILIARE MALNUTRITIE PROTEIN ã CALORICA PESTE VARSTA DE 2 ANI BOALA CELIACA FIBROZA CHISTICA PANCREATITA CRONICA PARAZITOZE INTESTIN SCURT BOALA CROHN A ûLIPOPROTEINEMIA