Skin introduction (Part 1- Epidermis)
- 1. INTRODUCTIONTO SKIN Part 1- Epidermis
- 2. SKIN ANATOMY Image source: suggestkeyword.com
- 3. EPIDERMIS Stratum Corneum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale Stratum Lucidum Image source: suggestkeyword.com
- 4. THE RELATION BETWEENTHESE 5 LAYERS Stratum CorneumStratum GranulosumStratum SpinosumStratum Basale Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 1 2 3 4 Image source: amazonnaws.com, usmagazine.com, country1067.com, pixnet.net
- 5. STRATUM BASALE ŌĆó Made up of keratinocyte stem cell. ŌĆó Undergoes mitosis division to constantly renew epidermal cells. ŌĆó Half of the cells differentiate and move to the next layer (stratum spinosum) to begin the maturation process- Keratinisation/ desquamation ŌĆó Other cell in stratum basale: Melanocyte Keratinocyte
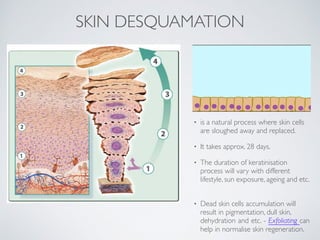
- 6. SKIN DESQUAMATION ŌĆó is a natural process where skin cells are sloughed away and replaced. ŌĆó It takes approx. 28 days. ŌĆó The duration of keratinisation process will vary with different lifestyle, sun exposure, ageing and etc. ŌĆó Dead skin cells accumulation will result in pigmentation, dull skin, dehydration and etc. - Exfoliating can help in normalise skin regeneration.
- 7. MELANOCYTE ŌĆó is a melanin producing cells. ŌĆó melanin is a pigment found in eyes, skin, and hair. ŌĆó Function is to protect skin cells and tissues from harmful UV radiation- transform the UV energy to heat. ŌĆó Almost everyone has the same amount of melanocyte,while the size and amount of melanosomes can be different. ŌĆó Most of the whitening products act on the process of melanogenesis. Image source: palaeo.gly.bris.ac.uk
- 8. STRATUM SPINOSUM ŌĆó Retaining moisture and protect against foreign bodies and substances. ŌĆó Begin to synthesise keratin, which can hold water and retain moisture. ŌĆó Langerhans cells to detect skin penetration by foreign matter and transport the invaders to the lymph node. ŌĆó The malfunction/activation of langerhans cells can lead to sensitive skin. Desmosomes
- 9. STRATUM GRANULOSUM ŌĆó Contain granules, which to bind keratin ’¼ülaments together. ŌĆó Lamellar bodies are formed in the keratinocytes of stratum granulosum. ŌĆó When it matures to the stratum corneum, enzyme degrade the outer layer of lamellar bodies, releasing lipids such as ceramides, essential fatty acids and cholesterol. ŌĆó The lipids fuse with stratum corneum to form a continuous layer of lipids- called lamellar lipid bilayer- which is lipid soluble. ŌĆó impermeable to water soluble substances. Image source: wisegeek.com
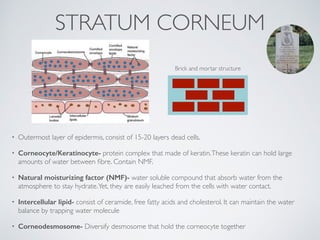
- 10. STRATUM CORNEUM ŌĆó Outermost layer of epidermis, consist of 15-20 layers dead cells. ŌĆó Corneocyte/Keratinocyte- protein complex that made of keratin.These keratin can hold large amounts of water between ’¼übre. Contain NMF. ŌĆó Natural moisturizing factor (NMF)- water soluble compound that absorb water from the atmosphere to stay hydrate.Yet, they are easily leached from the cells with water contact. ŌĆó Intercellular lipid- consist of ceramide, free fatty acids and cholesterol. It can maintain the water balance by trapping water molecule ŌĆó Corneodesmosome- Diversify desmosome that hold the corneocyte together Brick and mortar structure
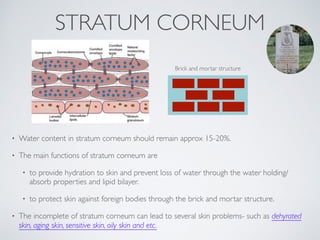
- 11. STRATUM CORNEUM ŌĆó Water content in stratum corneum should remain approx 15-20%. ŌĆó The main functions of stratum corneum are ŌĆó to provide hydration to skin and prevent loss of water through the water holding/ absorb properties and lipid bilayer. ŌĆó to protect skin against foreign bodies through the brick and mortar structure. ŌĆó The incomplete of stratum corneum can lead to several skin problems- such as dehyrated skin, aging skin, sensitive skin, oily skin and etc. Brick and mortar structure
- 12. SEBUM ŌĆó A combination of sebum that secrete by the sebaceous gland and sweat. ŌĆó ItŌĆÖs slightly acidic (pH 4.5-6.5) ŌĆó Function: ŌĆó to inhibit the growth of bacteria due to the acidic environment ŌĆó Prevent water loss from the epidermis due to itŌĆÖs waterproof nature ŌĆó Sebum is odorless, but it breakdown by bacteria can product strong odor ŌĆó The incomplete of sebum can lead to acne skin.Keratinocyte Intercellular matrix Sebum Brick and mortar structure Image source: pinterest.com
- 13. CONTENT OF STRATUM CORNEUM Sebum Corneocyte/ Keratinocyte Intercellular Matrix 41%Triglyceride 21% Wax esters Amino acids Lactic acid Cholesterol 12% Squalane Uric acid 80% Keratin protein 20% amino acids Uric acid NMF Pyrrolidone Carboxylic Acid 55% Ceramides Cholesterol Free fatty acids Keratinocyte Intercellular matrix Sebum Brick and mortar structure
- 14. REVISION Stratum basale ŌĆó Skin regeneration ŌĆó Secrete melanin Stratum spinosum ŌĆó Provide nutrients ŌĆó Detect allegens Stratum granulosum ŌĆó Provide structural protection ŌĆó to create skin barrier Stratum corneum ŌĆó Provide hydration ŌĆó 1st layer to protect skin from foreign bodies. Stratum lucidum ŌĆó Reduces effect of friction ŌĆó Provides protection Image source: rci.rutgers.edu
- 15. REFERENCE ŌĆó https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKosGSm7Ps4 ŌĆó http://dermatology.about.com/ ŌĆó http://www.taiwanlaser.com/ ŌĆó http://www.wisegeek.com/ ŌĆó https://www.wikipedia.org