1 of 23
Downloaded 12 times














Ad
Recommended
Unit 4 human reproduction by alex and ivan s
Unit 4 human reproduction by alex and ivan sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the human reproductive system and process. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then explains the male and female reproductive systems and organs. It outlines the process of fertilization, pregnancy, and labor, including how the embryo develops into a fetus and baby over trimesters until birth.Unit 5 energy deborah and ana s
Unit 5 energy deborah and ana sCrelgo
╠²
Energy can exist in multiple forms including mechanical, light, sound, thermal, electrical, chemical, and nuclear. It can be renewable sources like water, wind, sun, biomass, or waves and tides, or non-renewable sources like fuels or uranium and plutonium. Our bodies transform the chemical energy from food into mechanical energy for movement. Electricity is a form of energy that can be easily transported through power lines and transformed into other types of energy like light. Static electricity occurs when an object accumulates an electrical charge, which can be neutral, positive, or negative. Electrical current is the movement of electrical charges through a conducting material. Producing and using electricity can cause problems to the environment likeUnit 2 nutrition david
Unit 2 nutrition davidCrelgo
╠²
We eat food to obtain nutrients and vitamins that our bodies need, and our digestive system extracts these substances. In addition to digestion, respiration or breathing is also part of nutrition by providing oxygen. The circulatory system is essential for nutrition as it transports the nutrients we eat and oxygen we breathe to our organs, bones, brain, and muscles. Our blood contains three types of cells that each perform specific functions. Vitamins are essential nutrients our bodies need. Junk food contains high levels of sugar and fat, and if consumed in excess can accumulate in our bodies, causing weight gain and potential illness.Unit 1 interaction alvaro s
Unit 1 interaction alvaro sCrelgo
╠²
The nervous system has three main parts: the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The brain receives information and sends messages to the body via the spinal cord and nerves. The brain is made up of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system and are composed of axons, dendrites, and a cell body. The five senses - sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste - allow us to perceive the world around us. Each sense has specialized sensory organs that detect stimuli and relay this information to the brain via nerves.Unit3 nutrition monica s
Unit3 nutrition monica sCrelgo
╠²
Nutrients provide cells with energy and four body systems work together to carry out nutrition: the digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients, the respiratory system inhales oxygen and exhales carbon dioxide for cellular respiration, the excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through sweat and urination, and the circulatory system transports blood to circulate nutrients and oxygen to cells and remove waste.Unit 3 nutrtion tomas s
Unit 3 nutrtion tomas sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses four body systems involved in nutrition: the digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, and excretory system. The digestive system breaks down food and the respiratory system breathes in oxygen. The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells through blood and blood vessels. It also removes waste from cells. The excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through sweat and urine.Usal 2012Maria Jesus Silvo
╠²
Este documento describe las instrucciones para un examen de geometr├Ła m├®trica y sistemas di├®dricos. El examen consta de 3 partes con 2 opciones cada una. Los estudiantes deben completar todas las preguntas de una opci├│n. Se evaluar├Ī la comprensi├│n conceptual y la presentaci├│n formal, dando m├Īs peso a la comprensi├│n. Tambi├®n se proporciona una nomenclatura estandarizada para los elementos geom├®tricos en sistemas di├®dricos.Unit 4 human reproduction alberto and diego s
Unit 4 human reproduction alberto and diego sCrelgo
╠²
Human reproduction involves the joining of male and female sex cells through sexual reproduction. The primary sexual characteristics are the reproductive systems which differ between males and females and are present at birth. Fertilization occurs when an ovum and sperm join inside the fallopian tubes to create a single cell called a zygote, which implants in the uterus wall and becomes an embryo, leading to pregnancy and culminating in labor and birth.Unit 3 nutrition clara s
Unit 3 nutrition clara sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key functions of the digestive, respiratory, excretory, and circulatory systems. It describes how nutrients are broken down and absorbed in the digestive system and carried via the blood. It explains that the respiratory system intakes oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The excretory system filters waste from the blood through sweat glands and the urinary system. The circulatory system transports blood, nutrients, oxygen, and waste throughout the body using the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.Human reproduction by Yulia
Human reproduction by YuliaCrelgo
╠²
The document provides an overview of the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the male and female reproductive cells and systems, including the testes, ovaries, uterus and other organs. It explains fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes. Pregnancy involves development of the embryo and fetus over 9 months as it is nourished through the placenta. Labor concludes pregnancy in three phases as contractions widen the birth canal for delivery of the baby.Unit 4 human reproduction teresa s
Unit 4 human reproduction teresa sCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sex characteristics that develop during puberty to distinguish males and females. It then outlines the male and female reproductive systems and their main organs. It explains that fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes to form a zygote, which implants in the uterus and becomes an embryo, leading to pregnancy. Pregnancy involves different structures that support the development of the embryo over nine months until birth.Human reproduction by Paula Crespo
Human reproduction by Paula CrespoCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the human reproductive system. It describes that reproduction allows living things to create offspring similar to themselves. It then outlines the primary and secondary sexual features that characterize the male and female reproductive systems. The reproductive cells, ovaries, uterus, vagina, vulva, fallopian tubes, testicles, vas deferens, urethra, penis, seminal vesicles and prostate are defined. Fertilization is defined as the union of sperm and ovum in the fallopian tubes, and menstruation occurs if the ovum is not fertilized. The development of an embryo is described including the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac.Unit2 sensitivity and coordination noemi and clara s
Unit2 sensitivity and coordination noemi and clara sCrelgo
╠²
This document discusses the human senses and nervous system. It describes the organs of sight, smell, hearing, touch, and taste, as well as stimuli, responses, neurons, voluntary and involuntary movements, the skeleton, joints, musculature, and tendons. The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system including the brain and peripheral nerves. Neurons are specialized cells that transmit signals in the nervous system. Voluntary movements are controlled by the brain while involuntary movements are controlled by the spinal cord. The skeleton is composed of bones in the head, trunk, and limbs connected by ligaments and joints. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons and located in the head, trunk, and limbs.Unit 5 energy alberto s
Unit 5 energy alberto sCrelgo
╠²
Energy can exist in multiple forms and be obtained from both renewable and non-renewable sources. It transforms from one type to another and can power electrical systems. Producing and using energy has both benefits and environmental impacts. Conservation efforts aim to reduce energy usage and associated problems.Unit 4 human reproduction gonzalo s
Unit 4 human reproduction gonzalo sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then outlines the main organs involved in the male and female reproductive systems. The three phases of labor and birth are defined as dilation, expulsion, and afterbirth. Fertilization is explained as the joining of an ovum and sperm inside the fallopian tubes to form a zygote, which then implants in the uterus wall and develops into an embryo over the course of a typical nine-month pregnancy.Human reproduction by Aadriana Elena Zahira and Rebeca
Human reproduction by Aadriana Elena Zahira and RebecaCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics of males and females. It describes the development and function of reproductive cells and systems in both sexes. Key stages of human reproduction are explained, including fertilization, pregnancy, birth, and the three phases of labor.Human reproduction by Carmen and Alicia
Human reproduction by Carmen and AliciaCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty. It then explains the male and female reproductive systems and cells. Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join to form a zygote. During pregnancy, various structures like the placenta and umbilical cord develop to support the growing embryo and fetus over nine months, until birth occurs in three phases of labor.Human reproduction by Luis
Human reproduction by LuisCrelgo
╠²
The document describes the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that the testicles, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis make up the male reproductive system, while the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva make up the female system. It then discusses pregnancy, noting it lasts 9 months, with the placenta providing nutrients from the mother's blood to the baby via the umbilical cord. The stages of pregnancy and birth are outlined, including fetal development over trimesters and the three stages of labor.Human reproduction by Maria
Human reproduction by MariaCrelgo
╠²
Human reproduction involves the joining of male and female sex cells. During puberty, individuals develop primary and secondary sex characteristics that differentiate males and females for reproduction. The female reproductive system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva. The male system includes testes, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, and prostate. Fertilization occurs when sperm joins an ovum in the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg implants in the uterus and develops over nine months into a fetus with a placenta and umbilical cord, until birth through labor in three stages of dilation, expulsion, and afterbirth.Human reproduction by Julia
Human reproduction by JuliaCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the process of human reproduction, including the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics in males and females during puberty, how fertilization occurs when sperm and eggs join inside the fallopian tubes, the stages of pregnancy over nine months including the roles of the placenta and umbilical cord, and the three stages of labor ending with the delivery of the baby and afterbirth.Human reproduction by Nerea and Alicia
Human reproduction by Nerea and AliciaCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key aspects of human sexual development and reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then explains the male and female reproductive systems and cells, the process of fertilization, pregnancy, fetal development over trimesters, and labor.Unit 3 nutrition pablo and victor s
Unit 3 nutrition pablo and victor sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses the four main body systems involved in nutrition: the digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, and excretory system. The digestive system transforms food into nutrients using the digestive tract and glands. The respiratory system is responsible for breathing in oxygen and out carbon dioxide. The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells using the heart and blood vessels. Finally, the excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through excretion.Human reproduction by Sacha
Human reproduction by SachaCrelgo
╠²
Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction. During puberty, between ages 11-15, secondary sex characteristics develop in both males and females to differentiate the sexes. The male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes which are transported through the vas deferens and urethra. The female reproductive system contains ovaries that produce eggs and a uterus for fetal development. Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes to create an embryo. Pregnancy lasts around 9 months as the embryo develops structures like the placenta and umbilical cord to receive nutrients until birth.Christmas fun lucia villacorta s
Christmas fun lucia villacorta sCrelgo
╠²
The children Elena, Carlota, and Matthew help their grandma decorate the Christmas tree while she tells them the story of Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer. In the story, Rudolph is made fun of by the other reindeer for his shiny red nose until Santa realizes it will be useful for guiding his sleigh and makes Rudolph the lead reindeer. After the story, grandma and the children prepare chicken and biscuits for Christmas dinner and then join with family to eat and retell grandma's story.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (20)
Unit 3 nutrition clara s
Unit 3 nutrition clara sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key functions of the digestive, respiratory, excretory, and circulatory systems. It describes how nutrients are broken down and absorbed in the digestive system and carried via the blood. It explains that the respiratory system intakes oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The excretory system filters waste from the blood through sweat glands and the urinary system. The circulatory system transports blood, nutrients, oxygen, and waste throughout the body using the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.Human reproduction by Yulia
Human reproduction by YuliaCrelgo
╠²
The document provides an overview of the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the male and female reproductive cells and systems, including the testes, ovaries, uterus and other organs. It explains fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes. Pregnancy involves development of the embryo and fetus over 9 months as it is nourished through the placenta. Labor concludes pregnancy in three phases as contractions widen the birth canal for delivery of the baby.Unit 4 human reproduction teresa s
Unit 4 human reproduction teresa sCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sex characteristics that develop during puberty to distinguish males and females. It then outlines the male and female reproductive systems and their main organs. It explains that fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes to form a zygote, which implants in the uterus and becomes an embryo, leading to pregnancy. Pregnancy involves different structures that support the development of the embryo over nine months until birth.Human reproduction by Paula Crespo
Human reproduction by Paula CrespoCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the human reproductive system. It describes that reproduction allows living things to create offspring similar to themselves. It then outlines the primary and secondary sexual features that characterize the male and female reproductive systems. The reproductive cells, ovaries, uterus, vagina, vulva, fallopian tubes, testicles, vas deferens, urethra, penis, seminal vesicles and prostate are defined. Fertilization is defined as the union of sperm and ovum in the fallopian tubes, and menstruation occurs if the ovum is not fertilized. The development of an embryo is described including the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac.Unit2 sensitivity and coordination noemi and clara s
Unit2 sensitivity and coordination noemi and clara sCrelgo
╠²
This document discusses the human senses and nervous system. It describes the organs of sight, smell, hearing, touch, and taste, as well as stimuli, responses, neurons, voluntary and involuntary movements, the skeleton, joints, musculature, and tendons. The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system including the brain and peripheral nerves. Neurons are specialized cells that transmit signals in the nervous system. Voluntary movements are controlled by the brain while involuntary movements are controlled by the spinal cord. The skeleton is composed of bones in the head, trunk, and limbs connected by ligaments and joints. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons and located in the head, trunk, and limbs.Unit 5 energy alberto s
Unit 5 energy alberto sCrelgo
╠²
Energy can exist in multiple forms and be obtained from both renewable and non-renewable sources. It transforms from one type to another and can power electrical systems. Producing and using energy has both benefits and environmental impacts. Conservation efforts aim to reduce energy usage and associated problems.Unit 4 human reproduction gonzalo s
Unit 4 human reproduction gonzalo sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then outlines the main organs involved in the male and female reproductive systems. The three phases of labor and birth are defined as dilation, expulsion, and afterbirth. Fertilization is explained as the joining of an ovum and sperm inside the fallopian tubes to form a zygote, which then implants in the uterus wall and develops into an embryo over the course of a typical nine-month pregnancy.Human reproduction by Aadriana Elena Zahira and Rebeca
Human reproduction by Aadriana Elena Zahira and RebecaCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics of males and females. It describes the development and function of reproductive cells and systems in both sexes. Key stages of human reproduction are explained, including fertilization, pregnancy, birth, and the three phases of labor.Human reproduction by Carmen and Alicia
Human reproduction by Carmen and AliciaCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty. It then explains the male and female reproductive systems and cells. Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join to form a zygote. During pregnancy, various structures like the placenta and umbilical cord develop to support the growing embryo and fetus over nine months, until birth occurs in three phases of labor.Human reproduction by Luis
Human reproduction by LuisCrelgo
╠²
The document describes the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that the testicles, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis make up the male reproductive system, while the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva make up the female system. It then discusses pregnancy, noting it lasts 9 months, with the placenta providing nutrients from the mother's blood to the baby via the umbilical cord. The stages of pregnancy and birth are outlined, including fetal development over trimesters and the three stages of labor.Human reproduction by Maria
Human reproduction by MariaCrelgo
╠²
Human reproduction involves the joining of male and female sex cells. During puberty, individuals develop primary and secondary sex characteristics that differentiate males and females for reproduction. The female reproductive system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva. The male system includes testes, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, and prostate. Fertilization occurs when sperm joins an ovum in the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg implants in the uterus and develops over nine months into a fetus with a placenta and umbilical cord, until birth through labor in three stages of dilation, expulsion, and afterbirth.Human reproduction by Julia
Human reproduction by JuliaCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the process of human reproduction, including the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics in males and females during puberty, how fertilization occurs when sperm and eggs join inside the fallopian tubes, the stages of pregnancy over nine months including the roles of the placenta and umbilical cord, and the three stages of labor ending with the delivery of the baby and afterbirth.Human reproduction by Nerea and Alicia
Human reproduction by Nerea and AliciaCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key aspects of human sexual development and reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then explains the male and female reproductive systems and cells, the process of fertilization, pregnancy, fetal development over trimesters, and labor.Unit 3 nutrition pablo and victor s
Unit 3 nutrition pablo and victor sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses the four main body systems involved in nutrition: the digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, and excretory system. The digestive system transforms food into nutrients using the digestive tract and glands. The respiratory system is responsible for breathing in oxygen and out carbon dioxide. The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells using the heart and blood vessels. Finally, the excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through excretion.Human reproduction by Sacha
Human reproduction by SachaCrelgo
╠²
Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction. During puberty, between ages 11-15, secondary sex characteristics develop in both males and females to differentiate the sexes. The male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes which are transported through the vas deferens and urethra. The female reproductive system contains ovaries that produce eggs and a uterus for fetal development. Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes to create an embryo. Pregnancy lasts around 9 months as the embryo develops structures like the placenta and umbilical cord to receive nutrients until birth.More from Crelgo (12)
Christmas fun lucia villacorta s
Christmas fun lucia villacorta sCrelgo
╠²
The children Elena, Carlota, and Matthew help their grandma decorate the Christmas tree while she tells them the story of Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer. In the story, Rudolph is made fun of by the other reindeer for his shiny red nose until Santa realizes it will be useful for guiding his sleigh and makes Rudolph the lead reindeer. After the story, grandma and the children prepare chicken and biscuits for Christmas dinner and then join with family to eat and retell grandma's story.Unit 3 nutrtion tomas s
Unit 3 nutrtion tomas sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses four body systems involved in nutrition: the digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, and excretory system. The digestive system breaks down food and the respiratory system breathes in oxygen. The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells through blood and blood vessels. It also removes waste from cells. The excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through sweat and urine.Unit 3 nutrition teresa david patricia s
Unit 3 nutrition teresa david patricia sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses the four main systems involved in nutrition: the digestive system, respiratory system, excretory system, and circulatory system. It describes the key parts and functions of each system. The digestive system breaks down food, the respiratory system intakes oxygen and removes carbon dioxide, the excretory system removes waste from the blood, and the circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and waste throughout the body. Together these four systems work to take in nutrients, distribute them to cells, and remove waste from the body.Aladdin & the magic danae s
Aladdin & the magic danae sCrelgo
╠²
Aladdin is a poor boy who is tricked by a man claiming to be his uncle into finding a magic lamp for him. The man imprisons Aladdin but he discovers the lamp contains a genie who grants wishes. Aladdin uses the genie to become rich and rescue the princess from an evil genie, allowing him to marry her as promised by the king. In the end, Aladdin uses the genie to imprison the evil genie forever.Sleeping beauty deborah s
Sleeping beauty deborah sCrelgo
╠²
There was once a magic kingdom with a King and Queen who wished for a child. They had a daughter, Princess Rose, and held a ball to celebrate. All the good fairies in attendance blessed Rose with gifts, but the final fairy had not been invited. She cursed Rose to prick her finger and die on her 16th birthday. Another fairy softened the curse so that Rose would instead fall into a deep sleep for 100 years. On her 16th birthday, Rose pricked her finger and fell asleep along with the entire kingdom for 100 years. A brave prince eventually found and woke Rose with true love's kiss, and they married, breaking the curse and living happily ever after.Unit 4 human reproduction claudia lucia and teresa s
Unit 4 human reproduction claudia lucia and teresa sCrelgo
╠²
The document discusses human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sex characteristics that develop during puberty to distinguish males and females. It explains that sperm and ova are the reproductive cells, and describes the basic structures of the male and female reproductive systems. Fertilization occurs when an ovum and sperm join to form a zygote. Pregnancy lasts about 9 months, during which an embryo develops protected structures like the placenta and umbilical cord, before birth.Unit 3 nutrition sofia lucia ortega s
Unit 3 nutrition sofia lucia ortega sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes several key human body systems including the digestive system, respiratory system, excretory system, circulatory system, blood, and heart. The digestive system transforms food into nutrients using the digestive tract and glands. The respiratory system is responsible for breathing through inhalation and exhalation of air in the lungs. The excretory system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body through sweat glands and the urinary system. The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells using the heart, blood, and three types of blood vessels. Blood contains red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets suspended in plasma. The heart pumps blood around the closed, double circulatory system using rhythUnit 4 human reproduction noemi s
Unit 4 human reproduction noemi sCrelgo
╠²
This document summarizes the key stages of human sexual development and reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females. It then explains the main components of the male and female reproductive systems and their functions. Finally, it provides a brief overview of pregnancy, the structures that develop to support the embryo, and the three phases of labor and childbirth.Unit 3 nutrition patricia s
Unit 3 nutrition patricia sCrelgo
╠²
The document summarizes the key body systems involved in nutrition:
1) The digestive system transforms food into nutrients through the actions of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines and other organs.
2) The respiratory system is responsible for breathing through the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs and diaphragm.
3) The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells through the heart, blood and blood vessels like arteries, veins and capillaries. The hare and the turtle by patricia s
The hare and the turtle by patricia sCrelgo
╠²
The hare and tortoise had an argument about who was faster and decided to settle it with a race. The hare shot ahead and stopped to rest under a tree, falling asleep. While the hare slept, the slow but steady tortoise continued walking and won the race, proving that slow and steady wins the race.The story of santa claus diego s
The story of santa claus diego sCrelgo
╠²
Santa Claus was a carpenter who lived at the North Pole with his wife. As they did not have children of their own, Santa enjoyed making wooden toys but was concerned that children couldn't play outside when it was cold and snowy on Christmas. His wife came up with the idea of Santa delivering the toys to children in their village on Christmas Day. Although Santa did this for many years, one particularly snowy Christmas threatened to prevent him from reaching all the children. An angel then gave Santa magic reindeer, a red sleigh, a red coat, and some elves to help deliver all the toys, allowing Santa to continue bringing presents to children everywhere even in heavy snow.Ad
Sleeping beauty patricia s
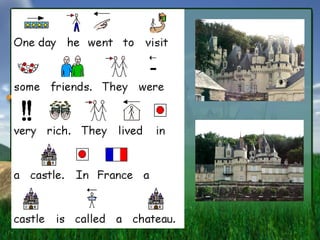
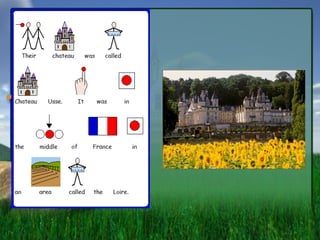
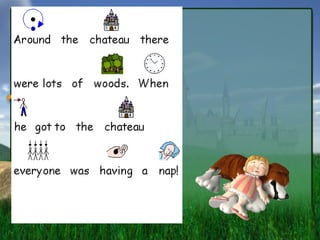
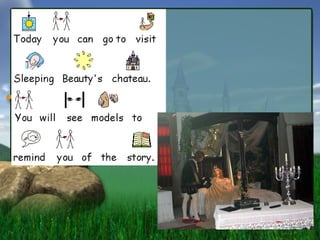
- 1. Sleeping Beauty By Patricia L├│pez Alvarez