Slovenia - Dying
- 2. Dye Substance used to import colour to various materials Organic compounds (carbon) Pigment Finely ground solids dispersed in a liquid or blended with other materials Inorganic or organic compounds Give brighter colours ï Synthetic dyes can be harmful: mercury, lead, chromium, copper, sodium, chloride, toulene, benzene ï Differnet things used to dye fabric: boiled shellfish, plants, mudâĶï Natural dyes: Plant-based, insects Fade faster
- 3. DIRECT COLORING ï― Direct dye = substantive dye ï― water soluble compounds ï― benzidine derivatives ï― cheap, easily applied, bright colours ï― positively and negatively charged groups ï― Methyl orange ï― Congo red: ï― belongs to a group of azo dyes derived from benzidine ï― synthetic dye ï― mordant â a substance used to fix the colour to cotton fibers ï― histology, acid-based indicator
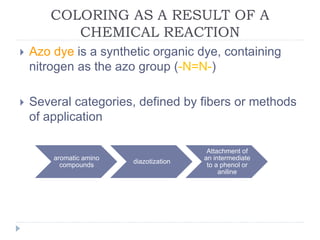
- 4. COLORING AS A RESULT OF A CHEMICAL REACTION ï― Azo dye is a synthetic organic dye, containing nitrogen as the azo group (-N=N-) ï― Several categories, defined by fibers or methods of application aromatic amino compounds diazotization Attachment of an intermediate to a phenol or aniline
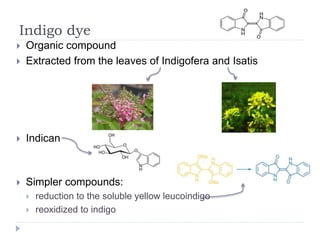
- 5. Indigo dye ï― Organic compound ï― Extracted from the leaves of Indigofera and Isatis ï― Indican ï― Simpler compounds: ï― reduction to the soluble yellow leucoindigo ï― reoxidized to indigo
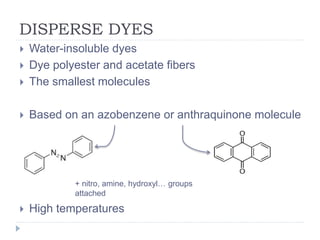
- 6. DISPERSE DYES ï― Water-insoluble dyes ï― Dye polyester and acetate fibers ï― The smallest molecules ï― Based on an azobenzene or anthraquinone molecule ï― High temperatures + nitro, amine, hydroxylâĶ groups attached