SocSci 2 Introduction to Civilization
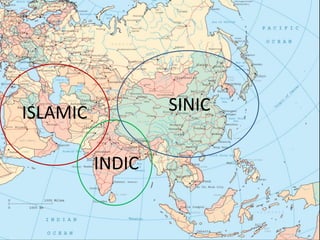
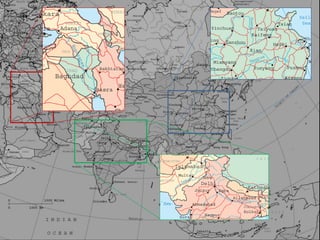
- 2. ISLAMIC SINIC INDIC
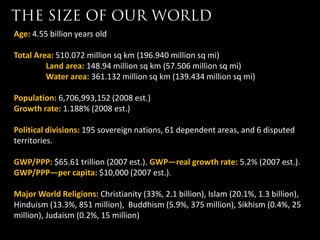
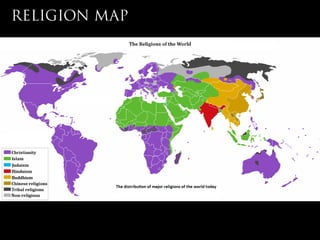
- 3. Age: 4.55 billion years old Total Area: 510.072 million sq km (196.940 million sq mi) Land area: 148.94 million sq km (57.506 million sq mi) Water area: 361.132 million sq km (139.434 million sq mi) Population: 6,706,993,152 (2008 est.) Growth rate: 1.188% (2008 est.) Political divisions: 195 sovereign nations, 61 dependent areas, and 6 disputed territories. GWP/PPP: $65.61 trillion (2007 est.). GWPŌĆöreal growth rate: 5.2% (2007 est.). GWP/PPPŌĆöper capita: $10,000 (2007 est.). Major World Religions: Christianity (33%, 2.1 billion), Islam (20.1%, 1.3 billion), Hinduism (13.3%, 851 million), Buddhism (5.9%, 375 million), Sikhism (0.4%, 25 million), Judaism (0.2%, 15 million)
- 9. ŌĆ£If you want knowledge, you must take part in the practice of changing reality. If you want to know the taste of a pear, you must change the pear by eating it yourself.ŌĆ£ Mao Zedong
- 10. Read the full account of my encounter with Sitio Target over at my blog. The following are the relevant articles. The Myth of Gawad Kalinga (the original article I wrote in 2007) We All Have Our Eden (the reflections after our December immersion) Sitio Target and Gawad Kalinga: The Social Context (an explanation of the impact of the unat)
- 11. Gawad Kalinga did not have bad intentions. Theirs was good. But why did they end up doing harm? Is civilization a relative term? Is one a civilization only from a certain point of view? What do we really mean when we say ŌĆścivilizedŌĆÖ or ŌĆśmodernŌĆÖ? Where did our standards come from?
- 12. The first human who We never really grow up, we hurled an insult instead only learn how to act in public. of a stone was the Bryan White founder of civilization. songwriter Sigmund Freud psychologist Progress is man's ability to complicate simplicity. Civilization begins with soap. Thor Heyerdahl Galveston Times Ethnographer and adventurer defunct 19th century Indiana newspaper I've made an odd discovery. Every time I talk to a savant I feel quite sure that happiness is no longer a possibility. Yet when I talk with my gardener, I'm convinced of the opposite. Bertrand Russell Philosopher
- 13. Civilization is social order promoting cultural creation. Four elements constitute it: 1. A system of economic provision that leads to a food surplus, 2. A system of political organization and social stratification, 3. A system of social norms, standards and moral traditions, 4. The pursuit of knowledge, science, and the arts. Civilization begins where chaos and insecurity end.
- 14. ŌĆó 200: Earliest possible evidence of modern humans in Africa ŌĆó 175 THOUSANDS OF YEARS BEFORE THE PRESENT ŌĆó 150 ŌĆó 125 ŌĆó 100: Last ice age begins 90: Modern humans found in Southwest Asia ŌĆó 75: 60: Modern humans found in Australia/Sahul ŌĆó 50 40: Modern humans found in northern Eurasia ŌĆó 25 10: End of ice age, beginnings of agriculture 5: Earliest cities and states ŌĆó 0: Industrial Revolution
- 15. ŌĆó 12 11.5: End of ice ages ŌĆó 11 Earliest evidence of agriculture in near east ŌĆó 10 THOUSANDS OF YEARS BEFORE THE PRESENT Earliest evidence of agriculture in Southeast Asia ŌĆó9 ŌĆó8 ŌĆó7 Evidence of pastoralism in Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan ŌĆó6 Evidence of agriculture in Americas ŌĆó 5: First cities and city states First empires ŌĆó4 ŌĆó3 First superempire (Persia) ŌĆó2 Foundation of world religions ŌĆó1 Foundation of largest pastoral empire (Genghis Khan, 1220CE) ŌĆó0 Industrial Revolution
- 17. ŌĆ£Civilization is the stage in human organization when governmental, social, and economic institutions have developed to sufficiently manage (however imperfectly) the problems of order, security, and efficiency in a complex society.ŌĆØ - Philip Lee Ralph, World Civilizations ŌĆ£Civilization is the limitless multiplication of unnecessary necessities.ŌĆØ - Mark Twain They civilize what's pretty / By puttin' up a city Where nothin' that's / Pretty can grow... They civilize left/ They civilize right Till nothing is left / Till nothing is right - Alan Jay Lerner, The First Thing You Know
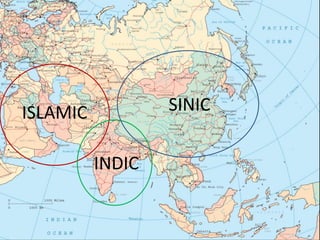
- 21. ISLAMIC SINIC INDIC
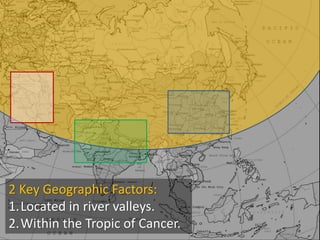
- 23. 2 Key Geographic Factors: 1.Located in river valleys. 2.Within the Tropic of Cancer.
- 26. 1. DECLINE IN AVAILABILITY OF WILD FOODS. 2. INCREASE IN AVAILABILITY OF DOMESTICABLE PLANTS. 3. DEVELOPMENT OF TECHNOLOGIES HELPFUL TO FOOD PRODUCTION. 4. TWO WAY LINK IN RISE OF POPULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FOOD PRODUCTION. (AUTOCATALYTIC) 5. DENSER FOOD PRODUCING SOCIETIES OUTPACED THEIR SURROUNDING HUNTER GATHERERS.
- 27. 1. FIXED SETTLEMENTS AND VILLAGES EMERGED. 2. MORE FOOD MEANS MORE CONSUMABLE CALORIES. 3. WITH DOMESTICATED ANIMALS CAME LIVESTOCK. 4. FOOD PRODUCTION LED TO A MORE SEDENTARY LIFESTYLE. 5. DOMESTICATED ANIMALS MADE TRADE AND WARFARE POSSIBLE.
- 31. Having written The Muqaddimah, Ibn Khaldun is now considered the father of the social sciences.
- 32. Premises in his theory of civilization: 1. Man is political. He cannot do without social organization. 2. The power of the individual is insufficient for him to obtain the food he needs. 3. ManŌĆÖs ability to think allows him to prepare the crafts needed to create instruments such as tools and weapons. 4. Cooperation is necessary to bring all these crafts together. 5. Royal authority is needed to be a restraining influence and keep men apart. 6. Restraining influence is derived from ŌĆ£prophecyŌĆØ or religious law.
- 33. Lecture notes are available for the following three slides. Download them at http://sirmartin.wordpress.com While viewing this file online or in you computer, you can click here for a direct link to the lecture notes.
- 34. BAND TRIBE CHIEFDOM STATE MEMBERSHIP Number of dozens Hundreds thousands over 50,000 people Settlement nomadic fixed: 1 village fixed: 1 or more fixed: many Pattern villages villages and cities Basis of kin kin-based clans class and class and relationships residence residence Ethnicities and 1 1 1 1 or more Languages This table is adapted from Guns, Germs and Steel by Jared Diamond.
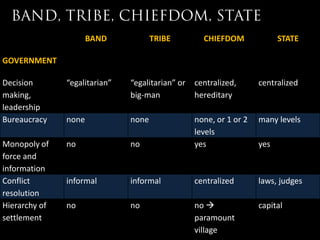
- 35. BAND TRIBE CHIEFDOM STATE GOVERNMENT Decision ŌĆ£egalitarianŌĆØ ŌĆ£egalitarianŌĆØ or centralized, centralized making, big-man hereditary leadership Bureaucracy none none none, or 1 or 2 many levels levels Monopoly of no no yes yes force and information Conflict informal informal centralized laws, judges resolution Hierarchy of no no no ’āĀ capital settlement paramount village
- 36. BAND TRIBE CHIEFDOM STATE ECONOMY Food no no ’āĀ yes yes ’āĀ intensive intensive production Division of labor no no no ’āĀ yes yes Exchanges reciprocal reciprocal redistributive redistributive (ŌĆ£tributeŌĆØ) (ŌĆ£taxesŌĆØ) Control of land band clan chief various SOCIETY Stratified no no yes, by kin yes, not by kin Slavery no no small-scale large-scale Luxury goods no no yes Yes for elite Public no no no ’āĀ yes yes architecture Indigenous no no no often
- 37. Hammurabi, the prince, called of Bel am I, making riches and increase, enriching Nippur and Dur-ilu beyond compare, sublime patron of E-kur; who reestablished Eridu and purified the worship of E-apsu; who conquered the four quarters of the world, made great the name of Babylon, rejoiced the heart of Marduk, his lord who daily pays his devotions in Saggil; the royal scion whom Sin made; who enriched Ur; the humble, the reverent, who brings wealth to Gish-shir-gal; the white king, heard of Shamash, the mighty, who again laid the foundations of Sippara; who clothed the gravestones of Malkat with green; who made E- babbar great, which is like the heavens, the warrior who guarded Larsa and renewed E-babbar, with Shamash as his helper; the lord who granted new life to Uruk, who brought plenteous water to its inhabitants, raised the head of E-anna, and perfected the beauty of Anu and Nana; shield of the land, who reunited the scattered inhabitants of Isin; who richly endowed E-gal-mach; the protecting king of the city, brother of the god Zamama; who firmly founded the farms of Kish, crowned E-me-te-ursag with glory, redoubled the great holy treasures of Nana, managed the temple of Harsag-kalama; the grave of the enemy, whose help brought about the victory; who increased the power of Cuthah; made all glorious in E- shidlam, the black steer, who gored the enemy; beloved of the god Nebo, who rejoiced the inhabitants of Borsippa, the Sublime; who is indefatigable for E-zida; the divine king of the city; the White, Wise; who broadened the fields of Dilbat, who heaped up the harvests for Urash; the Mighty, the lord to whom come scepter and crown, with which he clothes himself; the Elect of Ma-ma; who fixed the temple bounds of Kesh, who made rich the holy feasts of Nin-tu; the provident, solicitous, who provided food and drink for Lagash and Girsu, who provided large sacrificial offerings for the temple of Ningirsu; who captured the enemy, the Elect of the oracle who fulfilled the prediction of Hallab, who rejoiced the heart of Anunit; the pure prince, whose prayer is accepted by Adad; who satisfied the heart of Adad, the warrior, in Karkar, who restored the vessels for worship in E-ud-gal-gal; the king who granted life to the city of Adab; the guide of E-mach; the princely king of the city, the irresistible warrior, who granted life to the inhabitants of Mashkanshabri, and brought abundance to the temple of Shidlam; the White, Potent, who penetrated the secret cave of the bandits, saved the inhabitants of Malka from misfortune, and fixed their home fast in wealth; who established pure sacrificial gifts for Ea and Dam-gal-nun-na, who made his kingdom everlastingly great; the princely king of the city, who subjected the districts on the Ud-kib-nun-na Canal to the sway of Dagon, his Creator; who spared the inhabitants of Mera and Tutul; the sublime prince, who makes the face of Ninni shine; who presents holy meals to the divinity of Nin-a-zu, who cared for its inhabitants in their need, provided a portion for them in Babylon in peace; the shepherd of the oppressed and of the slaves; whose deeds find favor before Anunit, who provided for Anunit in the temple of Dumash in the suburb of Agade; who recognizes the right, who rules by law; who gave back to the city of Ashur its protecting god; who let the name of Ishtar of Nineveh remain in E-mish-mish; the Sublime, who humbles himself before the great gods; successor of Sumula-il; the mighty son of Sin-muballit; the royal scion of Eternity; the mighty monarch, the sun of Babylon, whose rays shed light over the land of Sumer and Akkad; the king, obeyed by the four quarters of the world; Beloved of Ninni, am I.
- 38. Hammurabi, the prince, called of Bel am I, making riches and increase, enriching Nippur and Dur-ilu beyond compare, sublime patron of E-kur; who reestablished Eridu and purified the worship of E-apsu; who conquered the four quarters of the world, made great the name of Babylon, rejoiced the heart of Marduk, his lord who daily pays his devotions in Saggil; the royal scion whom Sin made; who enriched Ur; the humble, the reverent, who brings wealth to Gish-shir-gal; the white king, heard of Shamash, the mighty, who again laid the foundations of Sippara; who clothed the gravestones of Malkat with green; who made E- babbar great, which is like the heavens, the warrior who guarded Larsa and renewed E-babbar, with Shamash as his helper; the lord who granted new life to Uruk, who brought plenteous water to its inhabitants, raised the head of E-anna, and perfected the beauty of Anu and Nana; shield of the land, who reunited the scattered inhabitants of Isin; who richly endowed E-gal-mach; the protecting king of the city, brother of the god Zamama; who firmly founded the farms of Kish, crowned E-me-te-ursag with glory, redoubled the great holy treasures of Nana, managed the temple of Harsag-kalama; the grave of the enemy, whose help brought about the victory; who increased the power of Cuthah; made all glorious in E- shidlam, the black steer, who gored the enemy; beloved of the god Nebo, who rejoiced the inhabitants of Borsippa, the Sublime; who is indefatigable for E-zida; the divine king of the city; the White, Wise; who broadened the fields of Dilbat, who heaped up the harvests for Urash; the Mighty, the lord to whom come Considered to be scepter and crown, with which he clothes himself; the Elect of Ma-ma; who fixed the temple bounds of Kesh, who made rich the holy feasts of Nin-tu; the provident, solicitous, who provided food and drink for the first ever code Lagash and Girsu, who provided large sacrificial offerings for the temple of Ningirsu; who captured the of laws in history enemy, the Elect of the oracle who fulfilled the prediction of Hallab, who rejoiced the heart of Anunit; the pure prince, whose prayer is accepted by Adad; who satisfied the heart of Adad, the warrior, in Karkar, who restored the vessels for worship in E-ud-gal-gal; the king who granted life to the city of Adab; the guide of E-mach; the princely king of the city, the irresistible warrior, who granted life to the inhabitants of Mashkanshabri, and brought abundance to the temple of Shidlam; the White, Potent, who penetrated the secret cave of the bandits, saved the inhabitants of Malka from misfortune, and fixed their home fast in wealth; who established pure sacrificial gifts for Ea and Dam-gal-nun-na, who made his kingdom everlastingly great; the princely king of the city, who subjected the districts on the Ud-kib-nun-na Canal to the sway of Dagon, his Creator; who spared the inhabitants of Mera and Tutul; the sublime prince, who makes the face of Ninni shine; who presents holy meals to the divinity of Nin-a-zu, who cared for its inhabitants in their need, provided a portion for them in Babylon in peace; the shepherd of the oppressed and of the slaves; whose deeds find favor before Anunit, who provided for Anunit in the temple of Dumash in the suburb of Agade; who recognizes the right, who rules by law; who gave back to the city of Ashur its protecting god; who let the name of Ishtar of Nineveh remain in E-mish-mish; the Sublime, who humbles himself before the great gods; successor of Sumula-il; the mighty son of Sin-muballit; the royal scion of Eternity; the mighty monarch, the sun of Babylon, whose rays shed light over the land of Sumer and Akkad; the king, obeyed by the four quarters of the world; Beloved of Ninni, am I.
- 39. Hammurabi, the prince, called of Bel am I, making riches and increase, enriching Nippur and Dur-ilu beyond compare, sublime patron of E-kur; who reestablished Eridu and purified the worship of E-apsu; who conquered the four quarters of the world, made great the name of Babylon, rejoiced the heart of Marduk, his lord who daily pays his devotions in Saggil; the royal scion whom Sin made; Considered to be who enriched Ur; the first ever code of laws in history the humble, the reverent, who brings wealth to Gish-shir-gal; the white king, heard of Shamash, the mighty, who again laid the foundations of Sippara; who clothed the gravestones of Malkat with green; who made E-babbar great, which is like the heavens, the warrior who guarded Larsa and renewed E-babbar, with Shamash as his helper; the lord who granted new life to Uruk, who brought plenteous water to its inhabitants, raised the head of E-anna, and perfected the beauty of Anu and Nana;
- 40. Insights from the code: 1. To justify his rule over the Amorites (early Babylonians), Hammurabi presented the following in his introduction: a. Presenting his character b. Presenting his royal lineage Considered to be the first ever code c. Presenting his track record of laws in history d. Alluding to the Gods 2. This is what Ibn Khaldun was referring to when he mentioned the role of prophecy in establishing royal authority: it must be based upon a higher ideal.
- 44. 1. THE NOTION OF THE ABSOLUTE OR TRANSCENDENCE. There is a belief in either a higher being or a higher state of life. 2. MYTHS AND SACRED TRUTHS. Stories, parables, and myths that reveal divine realities and paths to morality. 3. ORGANIZED WORSHIP OR DEVOTION. There are behavioural demands on the believers. 4. SOCIAL NORMS AND STANDARDS. There are values every believer aspires to. 5. A COMMUNITY OF BELIEVERS. Religion is a social activity.
- 45. 1. BY NUMBER OF GODHEADS. monotheist, dualist, polytheist, atheist, non-theist, pantheist, etc. 2. BY COMPLEXITY OF LITERATURE AND WORSHIP. a. animistic, nature worship b. ancestor worship c. anthropomorphic religion d. organized religion 3. BY GEO-CULTURAL REGIONS. a. Abrahamic: Judaism, Christianity, Islam b. Dharmic: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism c. Sinic: Confucianism, Taoism
- 46. 1. ANIMISTIC, NATURE WORSHIP Three elements of Shinto: purification, offering and prayer
- 50. 1. ABRAHAMIC RELIGIONS SIMILARITIES ŌĆó Originated in Southwest Asia ŌĆó Traces their sacred history to Abraham ŌĆó Teachings can be summarized as ŌĆ£Love God above all, and love your neighbor as you love yourselfŌĆØ DIFFERENCES ŌĆó Social history birthed different traditions ŌĆó Primary figures vary: Jews (patriarchs), Christians (Jesus Christ), Muslims (Muhammad)
- 51. 2. DHARMIC RELIGIONS SIMILARITIES ŌĆó Originated in South Asia ŌĆó Highly spiritual and devotional ŌĆó Shares common teachings such as dharma, karma and ahimsa DIFFERENCES ŌĆó Buddhism and Jainism were reactions to Hinduism ŌĆó Hinduism subscribes to the caste system
- 52. 3. SINIC RELIGION SIMILARITIES ŌĆó Originated in East Asia ŌĆó Non-theistic ŌĆó Began not as religions but as philosophical schools ŌĆó Philosophy answered important questions on statecraft DIFFERENCES ŌĆó Confucianism and Taoism vary in their approaches to government, the value of knowledge, the emphasis on ritual, and the meaning of happiness
- 53. ŌĆ£Civilization is the stage in human organization when governmental, social, and economic institutions have developed to sufficiently manage (however imperfectly) the problems of order, security, and efficiency in a complex society.ŌĆØ - Philip Lee Ralph, World Civilizations
- 54. How are the stages in the development of economic provision, social organization, and organized religion related to each other? ŌĆó Why do hunting societies tend to be animist? ŌĆó Why is organized religion a feature of states? ŌĆó Why is fertility worshipped in farming societies? ŌĆó And so on and so forth. What are mankindŌĆÖs various achievements in the different stages of civilization?
- 55. 1. ENVIROMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY. Climate change, the rising price of food and oil, dwindling biodiversity, and a coming water war are just among our environmental challenges. 2. POPULATION CHALLENGE. Our worldŌĆÖs population threatens to hit 12 billion by 2050 if nothing is changed. 3. GLOBAL INEQUALITY. In 2005, the poorest 40% of the world population accounted for 5% of global income. The richest 20% accounted for 75% of world income, and the richest 10% accounted for 54%. 4. DEMOCRATIC RECESSION. More and more governments are retreating into autocratic rule. What does that mean for democracy? 5. GLOBAL INSECURITY. 9/11 has exposed the geo-political tensions in the world. What have we done since?