Solar energy and PV cells
- 1. Solar energy and PV Cells Supervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi Agarwal
- 2. Contents Basic Concept of Solar energy Physics of Photovoltaic cells PV modules Emerging Technologies Environmental Aspects Indian Scenario Application of solar panel Disadvantages of solar cells
- 3. What is solar energy? radiant energy emitted by the sun. The Sun daily provides about 10,000 times more energy to the Earth than we consume. The earth receives 174 petawatts [1015 watts] of solar radiations from the sun. The total energy absorbed by earthâs atmosphere, oceans, land mass is 3,850,000 exajoules [1018 joules] per year. The energy reaching earthâs atmosphere consists of about 8% UV radiation, 46% visible light, 46% infrared radiations.
- 5. Why Solar Energy ? Solar energy is the most readily available source of energy. It is free. It is also the most important of the non-conventional sources of energy because it is non-polluting. It is a renewable source of energy. (Renewable Energy) (Nonrenewable Energy)
- 6. What is a Photovoltaic Cell? also called solar cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect. Solar Cell (PV) Light Electricity
- 7. Photovoltaic effect Sunlight is composed of photons, or particles of solar energy that contain various amounts of energy corresponding to the different wavelengths of the solar spectrum. The electrons present in the valence band absorb energy and, being excited, jump to the conduction band and become free. These highly excited electrons are accelerated into a different material by a built-in potential. This generates an electromotive force, and thus some of the light energy is converted into electric energy.
- 8. History of Solar Cells Discovery of Photovoltaic effect by French physicist , Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel. A description of the first solar cells made from selenium wafer were made by Charles Fritts and operated at 1% effeciency . Charles Fritts constructed what was probably the first true solar cell. He coated a semiconductor material (selenium) with an extremely thin layer of gold. A cadmium sulphide p-n junction was produced with an efficiency of 6% Audobert and Stora discover the photovoltaic effect in cadmium sulfide (CdS). The The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy achieve a 44.7% efficiency in solar cell technology. The University of South Wales breaks the 20% efficiency barrier for silicon solar cells under one sun conditions.
- 9. Basic structure of a SOLAR CELL
- 10. When sun light falls on silicon metal cell, the photon energy allows the electrons from the P- layer to move to the N-layer, creating an electric potential difference on the semiconductor borders. If these borders are connected to a load by conductive wires, there will be a flow of electric current, getting back the electrons to the P-layer and starting the process again. A photovoltaic cell generally has low current and voltage levels, of about 3 A and 0.7 V, respectively. Operation of a solar cells
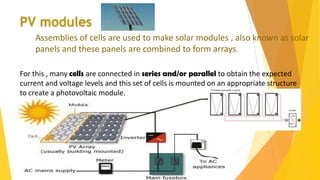
- 11. For this , many cells are connected in series and/or parallel to obtain the expected current and voltage levels and this set of cells is mounted on an appropriate structure to create a photovoltaic module. Assemblies of cells are used to make solar modules , also known as solar panels and these panels are combined to form arrays. PV modules
- 13. âNellis solar power plantâ contains 70,000 solar panels that generate 25 gigawatt-hours âsolar oneâ, California 1,800 sun-tracking mirrors reflect heat to a central collector a solar farm in the PhilippinesâĶ Major Solar Plants
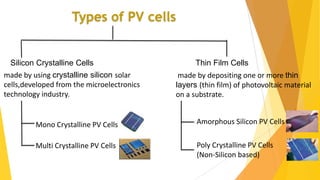
- 14. Types of PV cells Silicon Crystalline Cells Thin Film Cells made by using crystalline silicon solar cells,developed from the microelectronics technology industry. made by depositing one or more thin layers (thin film) of photovoltaic material on a substrate. Mono Crystalline PV Cells Multi Crystalline PV Cells Amorphous Silicon PV Cells Poly Crystalline PV Cells (Non-Silicon based)
- 15. Silicon Crystalline Technology Currently makes up 86% of PV market Very stable with module efficiencies 10-16% Mono crystalline PV Cells Made using saw-cut from single cylindrical crystal of Si Operating efficiency up to 15% Multi Crystalline PV Cells Caste from ingot of melted and recrystallised silicon Cell efficiency ~12% Accounts for 90% of crystalline Si market
- 16. Thin Film Technology Silicon deposited in a continuous on a base material such as glass, metal or polymers. Thin-film crystalline solar cell consists of layers about 10Ξm thick compared with 200- 300Ξm layers for crystalline silicon cells. PROS âĒ Low cost substrate and fabrication process. CONS âĒ Not very stable .
- 17. Amorphous Silicon PV Cells ï§ The most advanced of thin film technologies . ï§ Operating efficiency ~6% . ï§ Makes up about 13% of PV market . PROS âĒ Mature manufacturing technologies available . CONS âĒ Initial 20-40% loss in efficiency .
- 18. Poly Crystalline PV Cells ( Non â Silicon Based Technology ) PROS ïĩ 16% laboratory efficiency ïĩ 6-9% module efficiency CONS ïĩ Immature manufacturing process Unlike most other II/IV material CdTe exhibits direct band gap of 1.4eV and high absorption coefficient
- 20. Emerging Technologies Electrochemical solar cells have their active component in liquid phase. Dye sensitizers are used to absorb light and create electron-hole pairs in nanocrystalline titanium dioxide semiconductor layer. Cell efficiency ~ 7% â Discovering new realms of Photovoltaic Technologies â Electrochemical solar cells
- 21. Ultra Thin Wafer Solar Cells Thickness ~ 45Ξm Cell Efficiency as high as 20.3% Anti- Reflection Coating Low cost deposition techniques use a metalorganic titanium or tantanum mixed with suitable organic additives Emerging Technologies â Discovering new realms of Photovoltaic Technologies â
- 22. Environmental Aspects ï§ Exhaustion of raw materials ï§ CO2 emission during fabrication process ï§ Disposal problems of hazardous semiconductor material In spite of all these environmental concerns, Solar Photovoltaic is one of the cleanest form of energy
- 23. In terms of overall installed PV capacity, India comes fourth after Japan, Germany and U.S. (With Installed capacity of 110 MW). India today is the second largest manufacturer in the world of PV panels. The Delhi Government has decided to make use of solar power compulsory for lighting up hoardings and for street lighting . Solar power generation is merely concentrated in three states. Gujarat Rajasthan Maharashtra Where India now and its total installed capacity?
- 24. ï Solar panels are expensive. ï Solar power is inefficient in cloudy areas. ï A solar energy installation requires a large area for the system to be efficient in providing a source of electricity. ï Solar power maintenance is a problem especially to those who doesnât know the proper techniques. ï Disposal is difficult for the batteries and solar panels when they have broken down because they contain toxic chemicals like lead, sulfuric acid & cadmium telluride. Disadvantages of solar cells Solarbuzz European and US All Solar Module Retail Price Index
- 25. Conclusions âĒ Solar energy is the energy emitted by the sun. âĒ It is the most abundant and renewable form of energy. âĒ Photovoltaic cells convert light energy into electrical energy. âĒ Assembly of PV cells make solar panels. âĒ Solar panels finds its applications in many fields such as domestic lighting, solar vehicles etc. âĒ Cost and area are big disadvantage of solar cells.
- 26. [1] V. Smil, âEnergy at the crossroadsâ, OECD Global Science Forum, 2006. [2] V. Smil, âGeneral Energetics Energy in the Biosphere and Civilizationâ , xiii + 369 pp (1991). [3] "Climate and Earthâs Energy Budget". NASA Earth Observatory, (2009). [4] Donald A. Neaman, âSemiconductor Physics and devicesâ, fourth edition, Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd., pg:- 177-197. [5] B.H.Khan, âNon âconventional energy resourcesâ, second edition , Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd., pg:-88-192 [6] Mohit Kr. Srivastava, Sharad Kr. Gupta, Ashish Gupta, âEnvironmental Aspects of Solar Cell Modulesâ. References:
- 27. ThankYou!!!



![What is solar energy?
radiant energy emitted by the sun.
The Sun daily provides about 10,000 times more energy to the Earth than we
consume.
The earth receives 174 petawatts [1015 watts] of solar radiations from the sun.
The total energy absorbed by earthâs atmosphere, oceans, land mass is 3,850,000
exajoules [1018 joules] per year.
The energy reaching earthâs atmosphere consists of about 8% UV radiation, 46% visible
light, 46% infrared radiations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140410222550-phpapp01/85/Solar-energy-and-PV-cells-3-320.jpg)




















![[1] V. Smil, âEnergy at the crossroadsâ, OECD Global Science Forum, 2006.
[2] V. Smil, âGeneral Energetics Energy in the Biosphere and Civilizationâ , xiii + 369 pp (1991).
[3] "Climate and Earthâs Energy Budget". NASA Earth Observatory, (2009).
[4] Donald A. Neaman, âSemiconductor Physics and devicesâ, fourth edition, Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd., pg:-
177-197.
[5] B.H.Khan, âNon âconventional energy resourcesâ, second edition , Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd., pg:-88-192
[6] Mohit Kr. Srivastava, Sharad Kr. Gupta, Ashish Gupta, âEnvironmental Aspects of Solar Cell Modulesâ.
References:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140410222550-phpapp01/85/Solar-energy-and-PV-cells-26-320.jpg)
