Solar radiation forecasting with wrf model in the iberian peninsula
- 1. Solar radiation forecasting with WRF model in the Iberian Peninsula L. Mart├Łn, J. Polo, L.F.Zarzalejo, A. Navarro Energy department CIEMAT R. Marchante Investigaciones y Recursos Solares Avanzados IRSOLAV (www.irsolav.com) E. Lorenz, A. Sood, K. Suselj Oldenburg University, Germany Energy and Semiconductor Research Laboratory Energy Meteorology Group 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007
- 2. Outlook 1. Motivation and objectives 2. ECMWF ERA-40 validation 3. WRF validation 4. Synoptic situation: comparison of ECMWF and WRF models 5. Conclusions 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36Lisbon, October 2008 EUROSUN 2008, Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 2
- 3. Motivation and objectives The need to characterize and predict solar radiation as a solar resource is legislated in Spain by different Royal decrees (RD 436/2004 661/2007). Solar thermal and photovoltaic plants operator will compete in energy stock market. There are two basic rules in the market. Objectives ’üĘ Validate ECMWF ERA-40 ’āĀ Global Model. ’üĘ Validate Anailsys Mesoescale WRF Model predictions with hourly resolution. 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 4. ECMWF ERA-40 VALIDATION ŌĆóData Period: 1994-2004 ten years. ŌĆóDaily Goblal Solar Radiation ŌĆóResolution 1┬║ Ōēł 100Km ŌĆóGround measurements from National Radiometric Network from AEMet. ŌĆóCM11 pyranometer ŌĆóData filtered BSRN recomendations 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 4 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 5. ECMWF ERA-40 Daily Validation W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
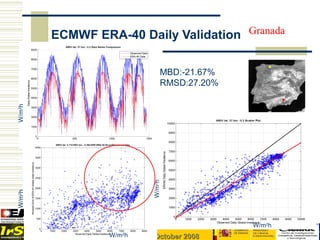
- 6. ECMWF ERA-40 Daily Validation Granada MBD:-21.67% RMSD:27.20% W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 W/m2h EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 7. Oviedo ECMWF ERA-40 Daily Validation MBD:-7.52% RMSD:39.55% W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h W/m2h 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 2Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 W/m h
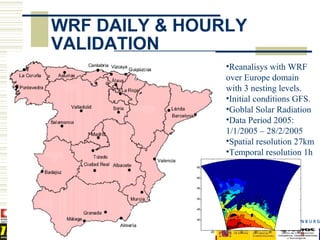
- 8. WRF DAILY & HOURLY VALIDATION ŌĆóReanalisys with WRF over Europe domain with 3 nesting levels. ŌĆóInitial conditions GFS. ŌĆóGoblal Solar Radiation ŌĆóData Period 2005: 1/1/2005 ŌĆō 28/2/2005 ŌĆóSpatial resolution 27km ŌĆóTemporal resolution 1h 65 60 55 50 45 40 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 8
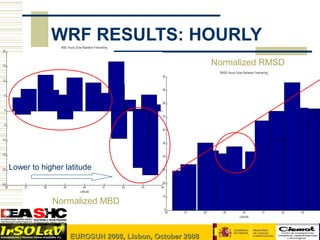
- 9. WRF RESULTS: HOURLY M B E Hourly S olar R adiation F orec as ting 20 15 Normalized RMSD R M S E H ourly S olar Radiation F orec as ting 100 10 90 5 80 0 70 -5 60 -10 % RM S E 50 -15 40 -20 Lower to higher latitude 30 -25 20 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Latitude 10 Normalized MBD 0 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 Latitude 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 9 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
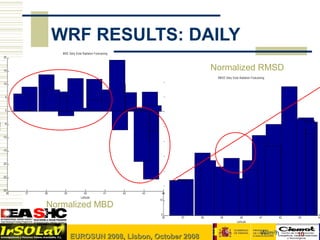
- 10. WRF RESULTS: DAILY M B E Daily S olar R adiation F orec as ting 20 15 Normalized RMSD RM S E D aily S olar R adiation F orec as ting 90 10 5 80 0 70 % MBE -5 60 -10 50 % RM S E -15 40 -20 30 -25 20 -30 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Latitude 10 Normalized MBD 0 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Latitude 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 W/m2h 10 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 11. SINOPTIC SITUATION 22/2/2005 CI from Meteosat 12:00 Albedo Granada W/m2 ECMWF Operational Model 12:00 ECMWF Mask L/O Oviedo W/m2 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 11 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 12. Conclusions ’üĘ ECMWF ERA-40 understimates daily solar irradiance. Errors are quite high. ’üĘ Analisys errors of WRF model goes from 30-98% RMSD hourly and from 23-89% daily. ’üĘ WRF fed with NCEP data doesnŌĆÖt reproduce synoptic situations. Further improvement using data from ECMWF. ’üĘ Cloud movement is a dynamic chaotic system. A paradigm based on deterministic (NWP) and probabilistic (Statistic). ’üĘ RD 661/2007 needs hourly predictions with errors lower than 20%. 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
- 13. Thank you for your attention 4th Meeting IEA SHC Task 36 Hamburg 23-25 Oct 2007 EUROSUN 2008, Lisbon, October 2008
Editor's Notes
- #2: Good afternoon I am going to present you ongoing works made in collaboration between CIEMAT, Irsolav and Oldenburg University in solar radiation forecasting in the Iberian Peninsula. This research is based on validation of WRF model executed in analisys mode which is based on the integration of observations to obtain the state of the atmosphere in grid points of WRF model. So, this predictions that are obtained are spatial predictions which gives an idea of the lowest uncertainty we will obtain in temporal predictions.
- #3: I have organized this presentation explaining first motivation and objectivos of this research. Later I will show you solar irradiance validation results of reanalsys model of ECMWF (the European Prediction Center) which are used to feed Mesoscale models like MM5 and WRF. Afterwards, WRF validations for solar irradiance hourly and daily time steps is presented. Both models will be compared for a specific synoptic situation ending this presentation with conclusions and future main research lines.
- #4: The need to predict solar to be used in solar thermal power and fotovoltaic plants is stablished in Spain by sucessive royal decrees. The predictions will allow the operators of the facilities to enter in the energy stock market and compete freely with other sources of energy. The stock market has two basic rules: it is necessary to predict the amount of energy which will be produced up to 72 hours before and deviations of energy produced compared to programmed are strongly penalized. So the aim of this research is to validate the quality of predictions offered by numerical weather predictions models. First we will evaluated reanalisys predictions ERA-40 which will show us the quality of the predictions offered by global models used as initial conditions for Mesoescale Models. Later we will also evaluate the quality of the dynamic downscaling made by WRF with higher temporal and spatial resolution.
- #5: Data used from ECMWF model covers a period of ten year of daily global solar radiation data and the model output resolution is 100km. The validation of reanalys is done with ground measurements from stations which belong to National Radiometric Network from Spanish Weather Service. The pyranometer used in the network is CM11 from Kipp and Zonen and data is properly filtered.
- #6: Absolute errors against observed daily global solar irradiance show us that deviations are quite high specially for days with low and high solar irradiance accumulated. In the scatter plot what we can see is that there is clearly an understimation of solar irradiance.
- #7: I have selected the southern station of Granada and we can see clearly how ERA-40 model (in red color) is understimating solar irradiance (blue color). This station presents a predominance of clear sky days in its distribution probabily funcion which the model fails predicting. Bias and RMSD are quite high.
- #8: Oviedo which is sited in the north of Spain is characterized by having a rainny weather. So with a predominance of days with low daily solar irradiance erros are mainly done in this kind of days. Bias is lower becouse errors for cloudy and clear sky days are compensating although there is a systematic understatimation of daily solar irradiance. And RMSD is significantly higher than in the case of southern mediterranean station.
- #9: WRF prediction model is run in analysis mode over Europe with 3 nesting levels and using GFS model from NCEP as boundary condition data. The variable validated is global solar radiation which is a direct output from WRF model. The period of data studied is the year 2005 although I will show you just two months: january and february. The spatial resolution of the domain over Spain is 27km and values obtained are hourly.
- #10: The validation of WRF model is done in terms of Normalized bias and RMSD in hourly and daily basis. The sations are represented in X axis ordered from lower latitude to higher latitude. The stations in the southern presetns mainly an overstimation and nothern a understimation as we see in bias graphic. Besides a predominance of clear sky situtations in southern stations results in small RMSD. It is also interesting to see the stations located in the center of iberian peninunla which show a relative low RMSD.
- #11: In the case of daily preditions erros are the same although it maginute is reduced.
- #12: Overall the model is able to reproduce clearsky synoptic conditions. Errors are mainly in situations where huge clouds and fronts movements need to be reproduced. The date shows a particulay curious situation Granada in the south